Introduction to Evaluation Function of Minimax Algorithm in Game Theory
Prerequisite: Minimax Algorithm in Game Theory
As seen in the above article, each leaf node had a value associated with it. We had stored this value in an array. But in the real world when we are creating a program to play Tic-Tac-Toe, Chess, Backgammon, etc. we need to implement a function that calculates the value of the board depending on the placement of pieces on the board. This function is often known as Evaluation Function. It is sometimes also called a Heuristic Function.
The evaluation function is unique for every type of game. In this post, the evaluation function for the game Tic-Tac-Toe is discussed. The basic idea behind the evaluation function is to give a high value for a board if the maximizer turn or a low value for the board if the minimizer turn.
For this scenario let us consider X as the maximizer and O as the minimizer.
Let us build our evaluation function :
- If X wins on the board we give it a positive value of +10.
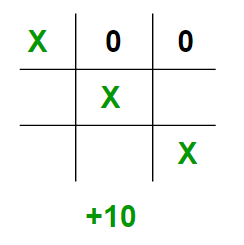
- If O wins on the board we give it a negative value of -10.

- If no one has won or the game results in a draw then we give a value of +0.
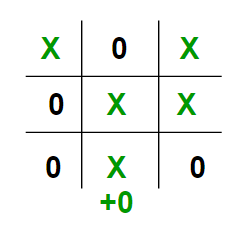
We could have chosen any positive/negative. For the sake of simplicity, we chose 10 and shall use lowercase ‘x’ and lowercase ‘o’ to represent the players and an underscore ‘_’ to represent a blank space on the board.
If we represent our board as a 3x3 2D character matrix, like char board[3][3]; then we have to check each row, each column, and the diagonals to check if either of the players has gotten 3 in a row.
// C++ program to compute evaluation function for
// Tic Tac Toe Game.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
// Returns a value based on who is winning
// b[3][3] is the Tic-Tac-Toe board
int evaluate(char b[3][3])
{
// Checking for Rows for X or O victory.
for (int row = 0; row<3; row++)
{
if (b[row][0]==b[row][1] && b[row][1]==b[row][2])
{
if (b[row][0]=='x')
return +10;
else if (b[row][0]=='o')
return -10;
}
}
// Checking for Columns for X or O victory.
for (int col = 0; col<3; col++)
{
if (b[0][col]==b[1][col] && b[1][col]==b[2][col])
{
if (b[0][col]=='x')
return +10;
else if (b[0][col]=='o')
return -10;
}
}
// Checking for Diagonals for X or O victory.
if (b[0][0]==b[1][1] && b[1][1]==b[2][2])
{
if (b[0][0]=='x')
return +10;
else if (b[0][0]=='o')
return -10;
}
if (b[0][2]==b[1][1] && b[1][1]==b[2][0])
{
if (b[0][2]=='x')
return +10;
else if (b[0][2]=='o')
return -10;
}
// Else if none of them have won then return 0
return 0;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
char board[3][3] =
{
{ 'x', '_', 'o'},
{ '_', 'x', 'o'},
{ '_', '_', 'x'}
};
int value = evaluate(board);
printf("The value of this board is %d\n", value);
return 0;
}
// Java program to compute evaluation function for
// Tic Tac Toe Game.
class GFG
{
// Returns a value based on who is winning
// b[3][3] is the Tic-Tac-Toe board
static int evaluate(char b[][])
{
// Checking for Rows for X or O victory.
for (int row = 0; row < 3; row++)
{
if (b[row][0] == b[row][1] && b[row][1] == b[row][2])
{
if (b[row][0] == 'x')
return +10;
else if (b[row][0] == 'o')
return -10;
}
}
// Checking for Columns for X or O victory.
for (int col = 0; col < 3; col++)
{
if (b[0][col] == b[1][col] && b[1][col] == b[2][col])
{
if (b[0][col] == 'x')
return +10;
else if (b[0][col] == 'o')
return -10;
}
}
// Checking for Diagonals for X or O victory.
if (b[0][0] == b[1][1] && b[1][1] == b[2][2])
{
if (b[0][0] == 'x')
return +10;
else if (b[0][0] == 'o')
return -10;
}
if (b[0][2] == b[1][1] && b[1][1] == b[2][0])
{
if (b[0][2] == 'x')
return +10;
else if (b[0][2] == 'o')
return -10;
}
// Else if none of them have won then return 0
return 0;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
char board[][] =
{
{ 'x', '_', 'o'},
{ '_', 'x', 'o'},
{ '_', '_', 'x'}
};
int value = evaluate(board);
System.out.printf("The value of this board is %d\n", value);
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992
# Python3 program to compute evaluation
# function for Tic Tac Toe Game.
# Returns a value based on who is winning
# b[3][3] is the Tic-Tac-Toe board
def evaluate(b):
# Checking for Rows for X or O victory.
for row in range(0, 3):
if b[row][0] == b[row][1] and b[row][1] == b[row][2]:
if b[row][0] == 'x':
return 10
else if b[row][0] == 'o':
return -10
# Checking for Columns for X or O victory.
for col in range(0, 3):
if b[0][col] == b[1][col] and b[1][col] == b[2][col]:
if b[0][col]=='x':
return 10
else if b[0][col] == 'o':
return -10
# Checking for Diagonals for X or O victory.
if b[0][0] == b[1][1] and b[1][1] == b[2][2]:
if b[0][0] == 'x':
return 10
else if b[0][0] == 'o':
return -10
if b[0][2] == b[1][1] and b[1][1] == b[2][0]:
if b[0][2] == 'x':
return 10
else if b[0][2] == 'o':
return -10
# Else if none of them have won then return 0
return 0
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
board = [['x', '_', 'o'],
['_', 'x', 'o'],
['_', '_', 'x']]
value = evaluate(board)
print("The value of this board is", value)
# This code is contributed by Rituraj Jain
// C# program to compute evaluation function for
// Tic Tac Toe Game.
using System;
class GFG
{
// Returns a value based on who is winning
// b[3,3] is the Tic-Tac-Toe board
static int evaluate(char [,]b)
{
// Checking for Rows for X or O victory.
for (int row = 0; row < 3; row++)
{
if (b[row, 0] == b[row, 1] && b[row, 1] == b[row, 2])
{
if (b[row, 0] == 'x')
return +10;
else if (b[row, 0] == 'o')
return -10;
}
}
// Checking for Columns for X or O victory.
for (int col = 0; col < 3; col++)
{
if (b[0, col] == b[1, col] && b[1, col] == b[2, col])
{
if (b[0, col] == 'x')
return +10;
else if (b[0, col] == 'o')
return -10;
}
}
// Checking for Diagonals for X or O victory.
if (b[0, 0] == b[1, 1] && b[1, 1] == b[2, 2])
{
if (b[0, 0] == 'x')
return +10;
else if (b[0, 0] == 'o')
return -10;
}
if (b[0, 2] == b[1, 1] && b[1, 1] == b[2, 0])
{
if (b[0, 2] == 'x')
return +10;
else if (b[0, 2] == 'o')
return -10;
}
// Else if none of them have won then return 0
return 0;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
char [,]board =
{
{ 'x', '_', 'o'},
{ '_', 'x', 'o'},
{ '_', '_', 'x'}
};
int value = evaluate(board);
Console.Write("The value of this board is {0}\n", value);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
<script>
// Javascript program to compute evaluation function for
// Tic Tac Toe Game.
// Returns a value based on who is winning
// b[3][3] is the Tic-Tac-Toe board
function evaluate(b)
{
// Checking for Rows for X or O victory.
for (let row = 0; row < 3; row++)
{
if (b[row][0] == b[row][1] && b[row][1] == b[row][2])
{
if (b[row][0] == 'x')
return +10;
else if (b[row][0] == 'o')
return -10;
}
}
// Checking for Columns for X or O victory.
for (let col = 0; col < 3; col++)
{
if (b[0][col] == b[1][col] && b[1][col] == b[2][col])
{
if (b[0][col] == 'x')
return +10;
else if (b[0][col] == 'o')
return -10;
}
}
// Checking for Diagonals for X or O victory.
if (b[0][0] == b[1][1] && b[1][1] == b[2][2])
{
if (b[0][0] == 'x')
return +10;
else if (b[0][0] == 'o')
return -10;
}
if (b[0][2] == b[1][1] && b[1][1] == b[2][0])
{
if (b[0][2] == 'x')
return +10;
else if (b[0][2] == 'o')
return -10;
}
// Else if none of them have won then return 0
return 0;
}
// Driver code
let board=[[ 'x', '_', 'o'],
[ '_', 'x', 'o'],
[ '_', '_', 'x']];
let value = evaluate(board);
document.write("The value of this board is "+ value+"<br>");
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
</script>
Output
The value of this board is 10
Time Complexity: O(max(row,col))
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
The idea of this article is to understand how to write a simple evaluation function for the game Tic-Tac-Toe. In the next article we shall see how to combine this evaluation function with the minimax function. Stay Tuned.
This article is written by Akshay L. Aradhya.