Announcements
Advertisement
-
-
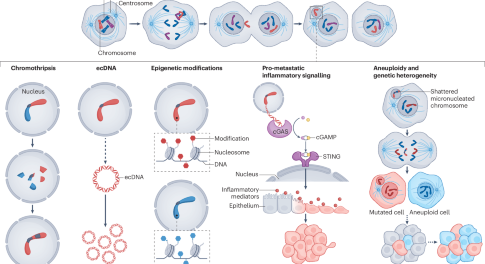
Targeting chromosomal instability in patients with cancer
Chromosomal instability (CIN) is a dynamic phenotype characterized by changes in chromosome number and structure and is a hallmark of clinically aggressive malignancies. Nonetheless, the ability of cancer cells to tolerate CIN creates several potential therapeutic vulnerabilities. In this Review, the authors describe the development of CIN and how this phenotype promotes carcinogenesis and tumour progression as well as describing the various attempts to develop targeted therapies based on the specific vulnerabilities of these tumours.
-
-