Guttenberg plagiarism scandal

Guttenberg plagiarism scandal refers to the German political scandal that led to the resignation of Karl-Theodor zu Guttenberg as Minister of Defence of Germany over the plagiarism of his doctoral dissertation. The first accusations of plagiarism in Guttenberg's dissertation were made public in February 2011. Guttenberg's doctoral dissertation, "Verfassung und Verfassungsvertrag" ("Constitution and Constitutional Treaty"), had been the basis of his 2007 doctorate from the University of Bayreuth.[1][2] Guttenberg at first denied intentional plagiarism, calling the accusations "absurd," but acknowledged that he may have made errors in his footnotes.[3][4][5] In addition, it emerged that Guttenberg had requested a report from the Bundestag's research department, which he had then inserted into his thesis without attribution.[6] On 23 February 2011, Guttenberg apologized in parliament for flaws in his thesis, but denied intentional deception and denied the use of a ghostwriter.[7]
On 23 February 2011, the University of Bayreuth withdrew Guttenberg's doctorate.[8][9] In part due to the expressions of confidence by Angela Merkel, the scandal continued to evoke heavy criticism from prominent academics, legal scholars (who accused Guttenberg of intentional plagiarism), and politicians both in the opposition and in the governing coalition.[10][11][12] On 1 March 2011, Guttenberg announced his resignation as Minister of Defense, from his seat in the Bundestag, and from all other political offices.[13]
In May 2011, a University of Bayreuth commission tasked with investigating Guttenberg's dissertation came to the conclusion that Guttenberg had engaged in intentional deception in the writing of his dissertation, and had violated standards of good academic practice.[14][15] The commission found that he had included borrowed passages throughout his thesis, without citation, and had modified those passages in order to conceal their origin.[16][17]
In November 2011, the prosecution in Hof discontinued the criminal proceedings for copyright violations against Guttenberg on condition of Guttenberg paying €20,000 to a charity. The prosecutor found 23 prosecutable copyright violations in Guttenberg's dissertation, but estimated that the material damage suffered by the authors of those texts was marginal.[18][19]
Background[edit]
Guttenberg studied law at the University of Bayreuth,[20] where he passed the first legal state examination in 1999. In 2007, he was awarded a doctorate in law, under supervision of Peter Häberle, with a dissertation on the development of constitutional law in the United States and the European Union. The doctoral thesis was titled "Verfassung und Verfassungsvertrag. Konstitutionelle Entwicklungsstufen in den USA und der EU" (translation: "Constitution and Constitutional Treaties – Constitutional Steps of Development in the USA and the EU"). The university awarded the dissertation with the highest honor “summa cum laude”.
Loss of doctorate and resignation[edit]
Fischer-Lescano plagiarism review[edit]
On 12 February 2011 Andreas Fischer-Lescano, professor of law at the University of Bremen, prepared a review of Guttenberg's thesis[21] for the left-leaning[22] German legal quarterly Kritische Justiz.[23] Fischer-Lescano was co-editor of this publication. During a reference check he discovered an article of the Neue Zürcher Zeitung (NZZ), published in 2003,[24] of which passages had been included in Guttenberg's thesis without citation.[23][25] After this discovery Fischer-Lescano performed further searches and discovered seven more passages lacking proper citation.[26] He discussed the findings with the other editors of Kritische Justiz and they decided that their publication, with only 1,800 subscribers, was not the appropriate forum to make the findings public.[23] So Fisher-Lescano contacted the German newspaper Süddeutsche Zeitung in Munich.[27]
On February 15, 2011, the newspaper contacted law professor Diethelm Klippel, the Bayreuth University ombudsman, and informed him of the plagiarism charges.[28] Klippel had also been on the review committee for Guttenberg's doctoral thesis. On the same day the newspaper informed Guttenberg and gave him a few hours to respond to the allegations.[29] Guttenberg was on an official visit in Poland that day.[30][31] Fischer-Lescano informed Guttenberg's thesis supervisors Peter Häberle and Rudolf Streinz about the charges.[23]
Guttenberg offers resignation[edit]
On 16 February 2011 the Süddeutsche Zeitung published an article reporting the allegations against Guttenberg.[32] On the same day the German newspaper Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung (FAZ) reported that the introduction of his thesis was borrowed from an FAZ-article from 1997, written by the political scientist Barbara Zehnpfennig.[33]
In a first statement Guttenberg, who was still in Poland, called the charge of his thesis being a plagiarism “abstruse”.[34][35] He insisted that the thesis was his own achievement and that none of his employees helped him to draft it.[36] The University of Bayreuth delegated the allegations against Guttenberg to its Commission on Professional Self Regulation in Science.[37] On 16 February 2011, after his return from Poland, Guttenberg left for a surprise visit to German soldiers in Afghanistan.[35][38] He spent the night in the military camp “OP North” in the war zone Baghlan province.[39][40] Although the visit had been planned weeks in advance, allegations were raised that this trip was some kind of “getaway” for Guttenberg.[39]
Guttenberg returned the next day, 17 February 2011, and had a meeting with German chancellor Angela Merkel.[39] His offer to resign was refused by Merkel.[29] The same day the University of Bayreuth sent a letter to Guttenberg conceding him two weeks to respond to the plagiarism allegations.[41][42] The crowd-source Guttenplag Wiki was launched by anonymous user PlagDoc as a platform for internet user to submit claims of unattributed work in Guttenberg's thesis.[43][44][45] A scheduled speech at an election campaign in Saxony-Anhalt was cancelled by Guttenberg[46] because of his meeting with Angela Merkel.[39]
The district attorney's office in Hof, Bavaria, announced it would wait on the results of the Bayreuth University's examination of Guttenberg's thesis[47] and confirmed that two criminal complaints had been filed against Guttenberg, one regarding possible copyright violations and another on a possible false statutory declaration. The second was immediately declined by the attorney due to apparent insubstantiality.[48] The same day the newspaper Süddeutsche Zeitung reported its findings that Guttenberg had used texts of 19 authors without correct attribution.[49]
Chancellor Angela Merkel declared: “He has my full confidence for his work, and this work is important. He has my support […] and we must wait until the university has completed its examination of the allegations”.[50][51] In an interview the chancellor attested Guttenberg had a “head-on approach” on the allegations.[52]
Use of Parliamentary Research Service[edit]
On February 19, 2011, the German news magazine Der Spiegel reported that Guttenberg had used works of the German Parliamentary Research Service (PRS) without proper attribution.[45][53] Any publication of PRS papers requires prior approval by the German Bundestag's departmental management.[54] During the weekend of February 20, 2011, Guttenberg re-read his thesis to examine Guttenplag's and other's findings.[29]
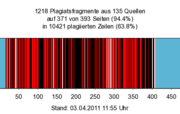
The next day in a letter Guttenberg asked the University of Bayreuth to revoke his title[55][56] and declared that he had “lost track of the use of sources over the course of the seven years in which [he] worked on the thesis”, but “at no point made mistakes by intention”.[57][58]
Also on 21 February 2011, chancellor Merkel reiterated her support for Guttenberg and told journalists “I appointed Guttenberg as Minister of Defence. I did not appoint him as an academic assistant or doctor. What is important to me is his work as Minister of Defence and he carries out these duties perfectly.”[59][60] This statement caused anger in the German academic community.[61]
Annette Schavan, German minister of Education and Research, who two years later had to resign herself because of plagiarism-accusations related to her own thesis,[62] declared that she didn't “consider the incident to be a trifle”, because “intellectual theft is not a small thing. The protection of intellectual property is a higher good.”[63] The same day it became known that Guttenberg had used another PRS paper without proper citation.[56][64] That evening Guttenberg attended a campaign event in Kelkheim[65] and stated that he would give up his doctorate title permanently.[66] “Over the weekend I had another look at my doctorate thesis”, Guttenberg declared and continued "I lost sight of the sources in one or two places. I wrote this piece of work myself and I stand by it, but I also stand by the rubbish I wrote".[65][67] Guttenberg admitted “serious mistakes”, which had not been made intentionally[68] but “do not meet the ethical code of science”,[69] and apologized to people who had been hurt by his work.[56] Guttenberg called his decision to give up the title “painful”.[65] He rejected all speculation about his resignation and declared: “I will perform my duties with all my powers”.[68] The University of Bayreuth confirmed the same day that Guttenberg had asked them to revoke his title.[69] Chancellor Merkel approved his decision to give up his title, a spokesman declared.[70]
Distinct criticism on Guttenberg's crisis management was passed by Norbert Lammert, President of the German Bundestag. In an interview on 22 February 2013, Lammert also expressed his doubts about the reliability of the university's awarding process.[71]
Loss of doctorate[edit]
Parliamentary questioning[edit]
On 23 February 2011, Lammert presided over a parliamentary questioning in the Bundestag on Guttenberg's use of PRS papers in his thesis.[63][72] During the questioning, politicians from the opposition called for Guttenberg's resignation[60] and accused him of cheating, lying, and intentions to deceive.[57] In his reply Guttenberg again apologized and admitted: “I wrote a dissertation that was obviously flawed”.[60] He described himself as “a man of mistakes and weaknesses”[73] and stated “I did not deliberately cheat, but made serious errors”.[74] Guttenberg declared: “I was certainly so arrogant as to believe that I could square the circle by trying to coordinate political passion and work, as well as academic and intellectual challenges, with being a young father” and apologized “for me this was overload, and today I regret to say that I couldn’t manage it.”[73] Asked whether his call for the allegations as “abstruse” hadn't been premature, Guttenberg confirmed this part of his previous statement as it was related to the accusation of his thesis as being a plagiarism.[75][76] According to accusations of misusing the German Parliamentary Research Service (PRS), Guttenberg pointed out that all studies had been related to his political work.[77] He noted that all papers had been cited, but without the authors’ names, as they had been employees of the PRS. Guttenberg stated that he couldn't answer whether he had sought prior approval to use these reports for his thesis, but that he had already apologized to Bundestag President Lammert in case of a potential oversight.[54]
University revoked title[edit]
On the same day the doctoral commission of Bayreuth University revoked Guttenberg's PhD.[78][79] The University's president Rüdiger Bormann declared that Guttenberg had “objectively not conformed” to academic standards.[80] According to Bormann, this fast revocation was possible because of Guttenberg's statement.[74][81] The doctoral commission made no judgment as to whether Guttenberg had acted intentionally,[80] something that led to criticism.[81][82] Such an investigation would “surely have been an extended process”, Bormann declared, which was unnecessary after Guttenberg's request for a withdrawal of his title.[80] Further inquiries would be done by the Commission of Professional Self Conduct in Science, Bormann announced.[81][83] Chancellor Merkel commented on the revocation of Guttenberg's title as being “in line of what he had requested”.[73]
Further investigations[edit]
On 24 February 2011, President of the Bundestag Norbert Lammert declared that Guttenberg had used six reports by the parliament's research service for his doctoral thesis without prior approval.[84][85] However, Lammert acknowledged the fact that it was widespread practice among Bundestag Members to use documents prepared by the parliamentary research service without first obtaining the necessary approval.[84] The same day, an open letter to chancellor Merkel was published to be signed by doctoral students and researchers.[86] The successor of Guttenberg's thesis supervisor Peter Häberle at the University of Bayreuth, Oliver Lepsius, alleged that the minister made the mistakes deliberately, and accused him of fraud.[87]
Media reported that between 1999 and 2006, a new chair of the University of Bayreuth had been sponsored with €747.000 by Rhön-Klinikum.[88] Until 2002, Guttenberg's family held a major stake in the hospital, and he had been a member of its supervisory board. In a statement, the university denied any sponsoring by Guttenberg, as the funding had been part of a cooperation between the university, a health insurance, the state of Bavaria, and Rhön-Klinikum.[89]
Two days later, minister Schavan in an interview[90] criticized Guttenberg for his thesis: “As someone who earned my doctorate 31 years ago and has worked with many doctoral candidates during my career, I’m embarrassed, and not just privately.”[91][92] Bundestag's president Lammert called the affair a “nail in the coffin for trust in our democracy”.[63]
Chancellor Merkel announced through her spokesman Steffen Seibert on 28 February 2011 that Guttenberg still had her full confidence.[93] Asked for Merkel's opinion on the fraud accusation by Oliver Lepsius, Seibert declared that “fraud requires intention. Any intention was denied by Guttenberg. The Chancellor believes him.”[94][95] Guttenberg himself gained strong support at a CSU meeting in Munich, while several CSU politicians sharply criticized Lammert and Schavan for their comments.[96][97]
Resignation as Defense Minister[edit]
On 1 March 2011, Guttenberg declared his resignation from all political offices at national level.[98][99][100] He called this decision the “most painful step of my life” and declared "I was always ready to fight, but I have reached the limits of my strength".[101] "I must agree with my enemies who say that I was not appointed minister for self-defence, but defence minister" Guttenberg said in view of his ministerial office. As for the inquiry regarding his thesis, he announced his full cooperation with the district attorney's investigations.[102] Guttenberg thanked Angela Merkel for her support, trust, and understanding.[100]
Chancellor Merkel reacted to Guttenberg's decision by saying that “I deeply regret his resignation”.[101] For Merkel he had “a unique and extraordinary ability” relating to people. For the future, the Chancellor declared that "I am convinced that we will have the opportunity to work together again in the future, in whatever form that may take".[100]
Rüdiger Bormann, president of University of Bayreuth, declared that the inquiries of its Commission on Professional Self Regulation in Science would continue.[103]
Apology[edit]
On 2 March 2011 the district attorney's office in Hof announced the launch of an investigation into potential copyright violations contained in Guttenberg's thesis as soon as his immunity would be withdrawn.[104] With his official resignation as Member of Parliament the following day,[105] Guttenberg abandoned his parliamentary immunity, thus allowing the district attorney's investigations to proceed. Media reported on more than 80 charges, which had been filed.[106] On 3 March 2011 Guttenberg received his dismissal certificate in a ceremony hosted by German President Christian Wulff.[107]
The same day, media reported about an anonymous member of the Commission of Professional Self Regulation in Science allegedly accusing Guttenberg of deception.[108] In contrast, Volker Rieble, law professor at Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, himself a strong critic of Guttenberg's thesis,[109] published an op-ed disputing the legal basis for further investigations in view of the fact that the university had already revoked Guttenberg's title and that he was no longer affiliated with the university.[110]
On March 5, 2011, the thesis supervisors Peter Häberle and Rudolf Streinz issued a statement declaring that in 2006, when the thesis was finished, the plagiarism wasn't detectable for lack of technical opportunities.[111] Without knowledge of the copied passages, Guttenberg's thesis demonstrated “a high degree of analytical depths and penetrated the dissertation topic in all its facets”, Häberle emphasized.[112] “It is important to note that the candidate [Guttenberg] was able to respond successfully to even intense questioning regarding the methodology and content of the thesis and was completely able to hold his own during the discussion as part of the oral PhD exam”,[113] the supervisors declared on Guttenberg's doctoral examination procedure and its grading (summa cum laude).[114]
On 7 March 2011 the district attorney's office in Hof announced the launch of a preliminary investigation into potential copyright violations by Guttenberg.[113][115][116] The University of Bayreuth, on 8 March 2011, announced the expansion of the commission investigating Guttenberg's dissertation to also include Wolfgang Löwer, professor of law at University of Bonn, and Jürgen Mittelstraß, professor of philosophy at University of Konstanz.[117]
A few days later, as a means of taking responsibility for his error, Guttenberg sent personal apology letters to all those authors who were not properly quoted in his thesis.[118][119] Guttenberg resigned from his last political office, the Kulmbach county council, on 15 March 2011.[120] At the same day the open letter, signed by 63,713 people, was delivered to the Chancellery in Berlin.[121] On 20 March 2011 the Zurich weekly Neue Zürcher Zeitung published extracts of an apology Guttenberg had sent to Klara Obermüller for not quoting her in his dissertation.[122][123]
Commission report and response[edit]
On 7 April 2011, the Commission of Professional Self Regulation in Science sent its report of preliminary findings to Guttenberg asking for his response by 26 April 2011.[124][125]
On 9 April 2011, there was a first leak of the commission's initial findings to the press, in which Guttenberg was accused of deliberate deception[126] Guttenberg's lawyer sharply criticized the commission's leaks as an unfair "prejudgment"[127][128][129] of his client given that the press reports were published both before the end of the investigation and before the 26 April deadline Guttenberg had been given by the university to respond to the commission's report before its public release.[130] His lawyer also pointed out that the leaks were a violation of Guttenberg's personal rights.[125] Critics accused Guttenberg of trying to prevent the public release of the commission's final report,[131][132][133] an allegation that he rejected.[134][135] Several representatives from universities and science demanded the release of the commission's report due to public interest.[136] A spokesman of the university rejected the lawyer's charges and stated that there had been no official report accusing Guttenberg of deliberate deception.[128] The spokesman of chancellor Merkel declared on 11 April 2011 that she was expecting full clarification of the matter.[137][138] Guttenberg's lawyers declared on 13 April 2011 that he was still standing by his commitment of full cooperation but that he was opposed to leaks to the press, which violated proper proceedings and caused prejudgment. Guttenberg had no objection against publishing the commission's report after end of proceedings, the lawyers said.[133][134][135] The same day it was reported that the Bundestag would not press charges against Guttenberg.[131]
A few days later media published extracts from Guttenberg's initial response to the commission. Guttenberg denied any deliberate plagiarism. He described the working-method during the several years of his dissertation as often working in short periods and using various different data carriers. This led to his losing track of the PhD dissertation, Guttenberg stated.[139][140] Guttenberg sent his response to the commission's draft report on 26 April 2011.[141][142] In the following days media again published extracts of his response.[143][144] On 10 May 2011 media reported that one author, whose work was copied, filed a complaint against Guttenberg with the district attorney's office in Hof.[145]
Report of Commission of Professional Self Regulation in Science[edit]

After an announcement on 6 May 2011,[146] already citing the conclusions,[147][148] the university released the report to the public on 11 May 2011.[147][149] According to that document, he had "grossly violated standard research practices and in so doing deliberately deceived"[150] and it further stated that it was "obvious that plagiarism was involved".[151]
Preliminaries[edit]
The report started with the elaboration of the commission's historical background,[152] its internal duties within the Bayreuth University, also in relation to other committees like the university's promotion commission.[153] These included institutional enhancements, the evaluation of academic misconduct corresponding to standards of scientific community.[154] The report then defined the criteria of academic misconduct: deliberately or grossly negligent use of “Falschangaben” (misrepresentations), the violation of other's intellectual property, and the obstruction of research. “Falschangaben” were defined as the fabrication or distortion of data and the “obstruction of research” was defined as unauthorized use of material with arrogation of its authorship.[155] The commission comprised as regular members Wiebke Putz-Osterloh, Nuri Aksel, Paul Rösch, Stephan Rixen as chairman, and Diethelm Klippel as a consulting member – all from the University of Bayreuth.[156] On 8 March 2011 Wolfgang Löwer, professor of law at University of Bonn, and Jürgen Mittelstraß, professor of philosophy at University of Konstanz joined the commission as consulting members.[157] The report listed four commission's meeting on Guttenberg's thesis: 16 February 2011, 8 and 23 March 2011, and the final meeting on 7 April 2011. The hearings of the thesis’ supervisors were on 23 March 2011.[156] Then the report specified the used material including its communications with Guttenberg himself.[114]
Commission’s findings[edit]
The commission reported missing citations and violations of the academic rules of citations.[158] It reported numerous verbatim forms of plagiarism and plagiarism with regard to content[159][160] where the use of other authors’ material was not clearly expressed.[161] The commission exemplified this in detail on the basis of six Parliamentary Research Service (PRS) papers and listed the passages Guttenberg had used in his thesis, including all text modifications and extensions. Two of the PRS papers lacked any citation and four PRS papers were cited insufficiently,[162] leading to misconceptions about the initial authorship of the passages.[163] The commission judged this as deception and described a pattern of creation (werkprägendes Bearbeitungsmuster).[164] As for Guttenberg, the commission concluded on intentional actions and deliberate deception due to the numbers of violations of academic rules of citations.[163] Both the use of verbatim text elements and the use with marginal text changes lacking proper citation or listing cited sources only in bibliography were evaluated as attempts to cover up.[165] The commission saw no indications that the thesis had been written by a ghost-writer.[164][166]
Contrary to previous expectations,[148] the commission denied any responsibility of the thesis supervisors[160][166] due to a lack of semantic or other indicators for plagiarism[167] and Guttenberg's “exceedingly convincing” oral PhD exam ("rigorosum").[168] Only the supervisors’ omission to ask for the PRS papers cited in the bibliography and the grading with “summa cum laude” was criticized by the commission.[169]
Guttenberg’s statement[edit]
In his final response, Guttenberg once again denied that he had deliberately deceived the university and instead blamed severe “errors in workmanship” for the grave deficiencies in his doctoral thesis.[143][170][171] He described a high burden of professional commitments as a result of new political responsibilities[160] during the years of his dissertation, which led to an ad-hoc and sometimes chaotic working-method[171][172] with long intervals between working periods.[173] Guttenberg reported on diverse collections of material such as books, loose sheets of papers, more than 80 data carriers, and several laptops spread across several domiciles,[172][174] used for his thesis. This led to an overburdening by the thesis, which further increased during the years, Guttenberg described.[160] Family expectations, namely that a started task had to be finished,[170][173] his intention to not disappoint his supervisor,[173][175] and his unwillingness to admit weakness,[160][173] hindered him to quit the dissertation, Guttenberg explained. The commission however, based on the view, that Guttenberg had continued his dissertation despite the feeling of being overburdened, denied negligence and concluded on intention.[176][177]
Reactions[edit]
Criticism by Walter Schmitt-Glaeser[edit]
The University of Bayreuth's handling of the matter was sharply criticized by its former vice-president and law professor Walter Schmitt-Glaeser, who, while agreeing that revoking the doctoral degree was justified, described the additional measures taken by the institution as an attempt at character assassination ("Treibjagd").[178] As any affiliation of Guttenberg to the university was severed by the withdrawal of his title, the university therefore lacked legal standing for any further investigation,[179][180] Schmitt-Glaeser argued. The leaking of information from the commission's confidential meetings to the press – according to Schmitt-Glaeser most-likely done by its members – he called “outrageous” and “more than embarrassing”.
For Schmitt-Glaeser especially the part of the report looking into a possible deception by Guttenberg should not have been published. Also, according to Schmitt-Glaeser, the fact that Guttenberg had to agree to the report's publication due to massive public pressure, including from University of Bayreuth, cast a shadow of suspicion on the entire proceedings.[178] The professor, former president (CSU) of the Bavarian senate, also criticized the lack of conclusive evidence to prove the university's assertion that there was "deliberate deception" on the part of Guttenberg,[181] Schmitt-Glaeser referred to the multiple instances of minor text changes – which the commission viewed as indicators of cheating – as a typical procedure with a text considered by an author as his own work.[178] With the proceedings the university denied any solicitousness for its former student Guttenberg[182] and damaged his social existence,[180] the professor criticized. From the judicial proceeding on this case he expected a result solely based on facts without regard to the person concerned.[178] In an interview, Schmitt-Glaeser described the university's intention as an attempt to “drag Guttenberg in front of a tribunal and find him guilty”.[181] In the professor's conviction, knowing Guttenberg personally, he had not committed intentional cheating.[179]
Disputed neutrality[edit]
Others[who?] criticized the commission's final report for not decrying the university's own lack of due diligence[160] in the matter and noted that the university had first awarded Guttenberg's degree with the highest possible distinction ("summa cum laude").[183][184] Furthermore, the commission's neutrality was disputed as the University of Bayreuth was party to the proceedings. Among these critics was Thomas Goppel (CSU), former Bavarian Minister of Education, who viewed the report as an attempt by the university to downplay its own responsibility and acquit itself.[185] Others complained about the university's lack of control provisions.[164]
Volker Rieble[edit]
Professor Volker Rieble approved the report of the university but saw the case as an expression of the public desire for “ritual punishment”. Rieble decried the widespread practice of academic publications being written by assistants but published by professors as much worse for academia than any plagiarism.[184]
Günther Beckstein[edit]
Günther Beckstein, former Minister-President of Bavaria, referred to Guttenberg by saying that everyone deserves a second chance, after some period of time.[164]
August 2011[edit]
In August 2011, the authors of Guttenplag Wiki, which triggered similar initiatives on VroniPlag Wiki, were accused of running a partisan campaign after it emerged that the founder of VroniPlag was a member of the opposition SPD party.[44][186][187]
Cessation of proceedings[edit]
In November 2011 the attorney's office in Hof dropped the charges against Guttenberg after having found 23 relevant copyright violations with only minor economic damage.[188][189][190] This decision was criticized for being biased toward economic criteria.[191][192] The court approved this arrangement after Guttenberg had agreed to make a donation of 20,000 Euro to a German charitable foundation.[188][191]
The attorney's office saw no indications that Guttenberg had intentionally used other authors’ texts within his thesis without proper attribution and judged his explanation of losing track of sources as “comprehensible and irrefutable”.[193][194] Contrary to University of Bayreuth, which had accused Guttenberg of deliberate deception, the prosecution concluded that Guttenberg had made the thesis’ errors only with contingent intent (dolus eventualis).[195] The attorney's office also stated that there was no criminal abuse of his PhD title nor fraud or breach of trust related to PRS papers either.[196]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ Roland Preuß (2011-02-16). "Summa cum laude? – "Mehr als schmeichelhaft"". sueddeutsche.de. Retrieved 2011-02-22.
- ^ Roland Preuß and Tanjev Schultz (2011-02-16). "Plagiatsvorwurf gegen Verteidigungsminister: zu Guttenberg soll bei Doktorarbeit abgeschrieben haben". sueddeutsche.de. Retrieved 2011-02-21.
- ^ "Fußnoten-Streit: Dr. Guttenberg nennt Plagiatsvorwürfe abstrus". Spiegel Online. 2011-02-16. Retrieved 2011-02-21.
- ^ "German minister denies plagiarism on PhD thesis". BBC News. 2011-02-17. Retrieved 2016-11-21.
- ^ Helen Pidd (2011-03-01). "German defence minister resigns in PhD plagiarism row". The Guardian. Retrieved 2016-11-21.
- ^ "Plagiarism Accusations Widen: Guttenberg Copied Work of German Parliament's Research Department". Spiegel Online. 2011-02-19. Retrieved 2016-11-21.
- ^ Erik Kirschbaum (2011-02-23). "German minister admits mistakes in plagiarism row". Reuters. Retrieved 2016-11-21.
- ^ "Uni Bayreuth entzieht Guttenberg den Doktortitel". Spiegel Online. 2011-02-23. Retrieved 2012-02-01.
- ^ "German defense minister loses doctorate amid plagiarism scandal". Deutsche Welle. 2011-02-23. Retrieved 2016-11-21.
- ^ Rudolf Neumaier (2011-02-26). "Plagiatsaffäre um Guttenberg 'Einem Betrüger aufgesessen'". sueddeutsche.de. Retrieved 2011-03-01.
- ^ "Plagiatsaffäre: Juristen unterstellen Guttenberg Vorsatz". Handelsblatt. 2011-02-26. Retrieved 2016-11-21.
- ^ "Plagiarism Affair: Defense Minister Guttenberg Resigns". Spiegel Online. 2011-03-01. Retrieved 2016-11-21.
- ^ Erik Kirschbaum (2011-03-01). "German defense minister quits in plagiarism row". Reuters. Retrieved 2016-11-21.
- ^ "Abschlussbericht in Bayreuth: Guttenberg gibt Familie Mitschuld an Doktorschmu". Spiegel Online. 2011-05-11. Retrieved 2016-11-21.
- ^ "University says ex-defense minister 'deliberately cheated' on thesis". Deutsche Welle. 2011-05-06. Retrieved 2016-11-21.
- ^ "Uni Bayreuth weist Guttenbergs Beteuerungen zurück". Die Welt. 2011-05-11. Retrieved 2016-11-21.
- ^ "Uni Bayreuth: Guttenberg hat vorsätzlich getäuscht". Badische Zeitung. 2011-05-12. Retrieved 2016-11-21.
- ^ "Guttenberg kommt glimpflich davon". Süddeutsche Zeitung. 2011-11-23. Retrieved 2016-11-24.
- ^ Geir Moulson (2011-11-23). "Prosecutors drop case against German ex-minister". Yahoo! News. Associated Press. Retrieved 2016-11-24.
- ^ "Der Herr ist so frei" (in German). Focus Online. 2009-02-16. Retrieved 2011-09-03.
- ^ "Verhasster Enthüller" (in German). Süddeutsche.de. 3 March 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ "German minister faces investigation for "Copygate"". REUTERS. 18 February 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ a b c d "Ich wollte es nicht glauben" (in German). ZEIT ONLINE. 24 February 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ "Gott hat keinen Platz in der europäischen Verfassung" (in German). Neue Zürcher Zeitung. 22 June 2003. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ "German Defense Minister Accused of Plagiarism" (in German). SPIEGEL ONLINE International. 16 February 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ "Summa cum laude? - "Mehr als schmeichelhaft"" (in German). Süddeutsche.de. 16 February 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ "Guttenberg accused of plagiarizing PhD thesis". The Local. 16 February 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ "Dokumentation Fall Guttenberg Ablauf" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 15 March 2011. p. 1. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ a b c "Es war kein Betrug". ZEIT ONLINE. 26 November 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ "Zu Guttenberg zu Gesprächen in Polen" (in German). Bundesministerium der Verteidigung. 16 February 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ "Guttenberg-Besuch in Polen von Plagiats-Diskussion überschattet" (in German). Polen.pl. 21 February 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ Preuß, Roland; Schultz, Tanjev (16 February 2011). "Guttenberg soll bei Doktorarbeit abgeschrieben haben". Süddeutsche Zeitung.
- ^ Georgi, Oliver (16 February 2011). "Anfang bei F.A.Z. abgeschrieben". Faz.net (in German). Frankfurter Allgemeine. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ "Guttenberg weist Plagiatsvorwurf als "abstrus" zurück" (in German). ZEIT ONLINE. 16 February 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ a b "Plagiarism Row Plagues German Official". THE WALL STREET JOURNAL. 18 February 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ "German Minister Rejects Plagiarism Allegations". CBS News. 16 February 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ "Dokumentation Fall Guttenberg Ablauf" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 15 March 2011. pp. 1–2. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ "Guttenberg in Afghanistan" (in German). Neue Zürcher Zeitung. 17 February 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ a b c d "An zwei Fronten". Faz.net (in German). Frankfurter Allgemeine. 20 February 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ "German defense minister on a surprise visit to Afghanistan". Deutsche Welle. 17 February 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ "German minister given deadline in plagiarism row". The Telegraph. 17 February 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ "Uni Bayreuth setzt Guttenberg Frist" (in German). ZEIT ONLINE. 17 February 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ "GuttenPlag - collaborative documentation of plagiarism". Wikia. Retrieved 2011-08-18.
- ^ a b "Im Schwarm" (in German). Spiegel Online. 2011-07-18. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ a b "German minister rejects quitting in plagiarism row". REUTERS. 19 February 2011. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ Kelsey, Eric (17 February 2011). "German minister cancels speech amid plagiarism scandal". Reuters. Archived from the original on 20 February 2011. Retrieved 1 March 2011.
- ^ "Strafanzeige gegen Bundesminister Freiherr zu Guttenberg" (in German). Staatsanwaltschaft Hof. 18 February 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ "Regierung: "Das geht noch weiter"". Faz.net (in German). Frankfurter Allgemeine. 18 February 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ "19 Ghostwriter wider Willen" (in German). Süddeutsche.de. 18 February 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ "Merkel pledges support to embattled 'plagiarism' minister". Deutsche Welle. 19 February 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ "Merkel sichert Guttenberg "volles Vertrauen" zu". DIE WELT (in German). 18 February 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ "Merkel bescheinigt Guttenberg offensives Vorgehen". DIE WELT (in German). 18 February 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ "Guttenberg kopierte auch von Bundestagsdienst" (in German). SPIEGEL ONLINE. 19 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ a b "Guttenberg räumt vor Bundestag Fehler ein" (in German). N24. 23 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Dokumentation Fall Guttenberg Ablauf" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 15 March 2011. pp. 2–3. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ a b c "Plagiatsaffäre: Guttenberg verzichtet dauerhaft auf Doktortitel" (in German). FOCUS Online. 21 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ a b "German defense minister loses doctorate amid plagiarism scandal". Deutsche Welle. 23 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Guttenberg-Brief an Uni Bayreuth: "Überblick über Quellen teilweise verloren"" (in German). SPIEGEL ONLINE. 22 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Merkel: Als Minister ist Guttenberg hervorragend". Faz.net (in German). Frankfurter Allgemeine. 21 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ a b c "German minister in plagiarism row stripped of PhD". REUTERS. 23 February 2011. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Wissenschaftler werfen Merkel "Verhöhnung" vor". DIE WELT (in German). 27 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "German education minister quits over PhD plagiarism". The Guardian. 9 February 2013. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ a b c "Political Allies Blast Guttenberg: Support Wanes Fast for German Defense Minister". SPIEGEL ONLINE International. 28 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Guttenberg: Weiteres Bundestags-Gutachten verwendet" (in German). FOCUS Online. 21 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ a b c "German Defense Minister Defies Calls to Quit Over Plagiarism". The New York Times. 22 February 2011. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ Framke, Andreas (21 February 2011). "German minister gives up PhD title amid scandal". Reuters. Archived from the original on 25 February 2011. Retrieved 1 March 2011.
- ^ "Merkel Backs Guttenberg After He Drops Doctor Title Amid Plagiarism Spat". Bloomberg. 22 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ a b "Guttenberg Drops 'Doctor' to Save 'Minister'". SPIEGEL ONLINE International. 22 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ a b "German minister gives up doctorate after plagiarism row". BBC News. 22 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "German minister renounces PhD after accusations of plagiarism". The Independent. 23 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Bundestagspräsident Lammert kritisiert Krisenmanagement zu Guttenbergs" (in German). WDR. 22 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Plenarprotokoll 17/32" (PDF) (in German). Deutscher Bundestag. 23 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ a b c "Merkel's Defense Minister Stripped of University Doctor Title". Bloomberg. 23 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ a b "German defence minister stripped of doctorate for plagiarism". The Guardian. 24 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Guttenbergs Quadratur des Kreises" (in German). Süddeutsche.de. 24 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Guttenberg im Bundestag: "Ich war offensichtlich überfordert"" (in German). SPIEGEL ONLINE. 23 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Guttenberg verwahrt sich gegen Täuschungsvorwurf" (in German). ZEIT ONLINE. 23 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Universität Bayreuth erkennt zu Guttenberg den Doktorgrad ab" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 2011-02-23. Retrieved 2011-08-18.
- ^ "Uni Bayreuth erkennt den Doktortitel ab" (in German). Frankfurter Allgemeine. 24 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ a b c "Defensive Minister: University Withdraws Guttenberg's Doctor Title". SPIEGEL ONLINE International. 24 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ a b c "Die Universität Bayreuth kneift" (in German). Süddeutsche.de. 24 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ ""Die Uni Bayreuth kneift" – kritisiert die SPD" (in German). DIE WELT. 24 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Uni Bayreuth überprüft möglichen Täuschungsvorsatz" (in German). DIE WELT. 24 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ a b "Guttenberg bediente sich bei sechs Bundestags-Expertisen" (in German). Süddeutsche Zeitung. 2011-02-24. Retrieved 2011-08-18.
- ^ "Guttenberg verwendete Bundestags-Expertisen ohne Erlaubnis" (in German). Spiegel Online. 2011-02-24. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ "Offener Brief: "Verhöhnung aller wissenschaftlichen Hilfskräfte"" (in German). SPIEGEL ONLINE. 25 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2015.
- ^ Löwenstein, Stephan; Müller, Reinhard (25 February 2011). "Wir sind einem Betrüger aufgesessen". Faz.net (in German). Frankfurter Allgemeine. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "750.000 Euro für die Uni Bayreuth" (in German). DER TAGESSPIEGEL. 25 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Kooperation mit Rhön-Klinikum AG im Bereich Gesundheitsökonomie" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 2011-02-25. Retrieved 2011-08-18.
- ^ "Ich schäme mich nicht nur heimlich" (in German). Süddeutsche.de. 1 March 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Schavan 'embarrassed' by Guttenberg". The Local. 28 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Schavan: Plagiatsaffäre ist keine Lappalie" (in German). Süddeutsche.de. 27 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Merkel bekräftigt ihr Vertrauen zu Guttenberg" (in German). stern.de. 28 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Doktoranden gegen Dr. Merkel" (in German). taz. 1 March 2013. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Merkel hält weiter zu Guttenberg - Aber Kritik aus Koalition" (in German). Aargauer Zeitung. 28 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "CSU stützt Guttenberg – Seehofer kritisiert Lammert" (in German). DIE WELT. 28 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Seehofer watscht Guttenberg-Kritiker ab" (in German). stern.de. 3 March 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Guttenbergs Erklärung: "Ich habe die Grenzen meiner Kräfte erreicht"" (in German). SPIEGEL ONLINE. 2011-03-02. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "German minister resigns amid plagiarism scandal". The Telegraph. 1 March 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ a b c "German Defence Minister Guttenberg resigns over thesis". BBC News. 1 March 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ a b "German defence minister resigns in plagiarism scandal". Los Angeles Times. 2011-03-02. Retrieved 2011-08-18.
- ^ "Minister Guttenberg erklärt seinen Rücktritt" (in German). tagesschau.de. 2011-03-01. Retrieved 2011-08-18.
- ^ "Der Präsident der Universität Bayreuth, Professor Dr. Rüdiger Bormann, zum Rücktritt von Karl-Theodor zu Guttenberg" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 2011-02-25. Retrieved 2011-08-18.
- ^ "Strafanzeigen betreffend Karl-Theodor zu Guttenberg" (in German). Staatsanwaltschaft Hof. 2 March 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Ausgeschiedene Abgeordnete und deren Nachfolger" (in German). Deutscher Bundestag. Archived from the original on 31 December 2013. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Mehr als 80 Anzeigen gegen Guttenberg: Betrug, Untreue, Urheberrechtsverstöße" (in German). SPIEGEL ONLINE. 3 March 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Ermittlungen gegen Guttenberg" (in German). n-tv. 2011-03-03. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ "Staatsanwalt ermittelt gegen Guttenberg" (in German). stern.de. 3 March 2011. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ "Guttenbergs Uni im Visier der Kritik" (in German). stern. 25 February 2011. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ "Bayreuth fehlt Legitimation zur Prüfung" (in German). Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung. 2011-03-03. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ "Plagiat war 2006 noch nicht erkennbar". Faz.net (in German). Frankfurter Allgemeine. 7 March 2011. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ "Plagiat war 2006 noch nicht erkennbar" (in German). Süddeutsche.de. 7 March 2011. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ a b "Staatsanwaltschaft ermittelt gegen Guttenberg" (in German). ZEIT ONLINE. 7 March 2013. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ a b "Dokumentation Fall Guttenberg Ablauf" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 15 March 2011. pp. 9–10. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Plagiatsaffäre: Staatsanwalt leitet Ermittlungen gegen Guttenberg ein" (in German). SPIEGEL ONLINE. 7 March 2011. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ "Staatsanwalt ermittelt gegen Guttenberg" (in German). stern.de. 7 March 2013. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ "Uni entscheidet erst im April" (in German). Spiegel Online. 2011-03-11. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ "Guttenberg bittet persönlich um Entschuldigung" (in German). Focus Online. 2011-03-12. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ "Guttenberg entschuldigt sich bei Wissenschaftlern" (in German). Spiegel Online. 2011-03-12. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ "Guttenberg legt Kreistagsmandat nieder" (in German). Spiegel Online. 2011-04-15. Retrieved 2011-08-18.
- ^ "Causa Guttenberg - Offener Brief von Doktoranden an die Bundeskanzlerin" (in German). Facebook. 17 March 2011. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ "Guttenberg entschuldigt sich bei NZZ-Autorin" (in German). Aargauer Zeitung. 20 March 2011. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ "Karl-Theodor zu Guttenberg apologises to Swiss journalist over plagiarism row". The Telegraph. 20 March 2011. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ "Weitere Schritte der Universität Bayreuth im Fall zu Guttenberg" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 2011-04-12. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ a b "Guttenbergs Anwalt attackiert Uni Bayreuth" (in German). Spiegel Online. 2011-04-11. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ "Gutachten: Guttenberg hat absichtlich abgeschrieben" (in German). Süddeutsche Zeitung. 2011-04-08. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ "Guttenberg-Anwalt keilt gegen Universität Bayreuth" (in German). Focus Online. 2011-04-10. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ a b "Guttenbergs Anwalt spricht von "Vorverurteilung"". Frankfurter Allgemeine. 2011-04-10. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ "Guttenbergs Anwalt greift Uni Bayreuth an" (in German). Zeit Onlie. 2011-04-10. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ "Weitere Schritte der Universität Bayreuth im Fall zu Guttenberg" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 12 April 2011. Retrieved 16 July 2013.
- ^ a b "Bundestag verzichtet auf Strafantrag gegen Guttenberg" (in German). Süddeutsche Zeitung. 2011-04-13. Retrieved 2011-08-18.
- ^ "Gutachten: Guttenberg hat absichtlich abgeschrieben" (in German). Süddeutsche Zeitung. 2011-04-08. Retrieved 2011-08-18.
- ^ a b "Uni Bayreuth darf Guttenberg-Gutachten veröffentlichen" (in German). Spiegel Online. 2011-04-13. Retrieved 2011-08-18.
- ^ a b "Guttenberg stimmt Veröffentlichung des Uni-Berichts zu" (in German). Zeit Online. 2011-04-13. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ a b "Guttenberg lässt Gutachten veröffentlichen" (in German). Focus Online. 2011-04-13. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ "Wissenschaftler: Guttenberg-Bericht veröffentlichen" (in German). T-Online. 12 April 2011. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ "Plagiatsaffäre: Merkel verlangt von Guttenberg Aufklärung" (in German). SPIEGEL ONLINE. 11 April 2011. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ "Guttenbergs Plagiatsaffäre: Merkel fordert Aufklärung" (in German). n-tv. 11 April 2011. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ "Stellungnahme für Uni Bayreuth: Guttenberg bestreitet Plagiatsvorwurf" (in German). SPIEGEL ONLINE. 16 April 2011. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ "Habe die Übersicht verloren". Faz.net (in German). Frankfurter Allgemeine. 17 April 2011. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ "Guttenberg nimmt zu Plagiatsvorwürfen Stellung" (in German). Westdeutsche Zeitung. 2011-04-27. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ "Doktorarbeit: Guttenberg gibt Stellungnahme an Uni Bayreuth ab" (in German). FOCUS Online. 27 April 2011. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ a b "Guttenberg spricht von Missverständnis" (in German). Spiegel Online. 2011-04-30. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ "Guttenberg hält Täuschungsvorwurf für "Missverständnis"" (in German). ZEIT ONLINE. 1 May 2011. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ "Plagiatsopfer stellt Strafantrag gegen Guttenberg" (in German). DIE WELT. 10 May 2011. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ "Fall zu Guttenberg: Kommission legt ihren Abschlussbericht vor" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 6 May 2011. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ a b "Guttenberg hat sich immer wieder die Autorschaft angemaßt" (in German). Spiegel Online. 2011-05-06. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ a b "University says ex-defense minister 'deliberately cheated' on thesis". Deutsche Welle. 6 May 2011. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ "Bericht an die Hochschulleitung der Universität Bayreuth" (PDF) (in German). University of Bayreuth. 2011-05-05. Retrieved 2012-12-18.
- ^ "Germany: Ex-Minister's Plagiarism Was Deliberate, University Says". The New York Times. 6 May 2011. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ "Germany's Guttenberg 'deliberately' plagiarised". BBC News. 2011-05-06. Retrieved 2011-08-18.
- ^ "Dokumentation Fall Guttenberg Ablauf" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 15 March 2011. p. 3. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Dokumentation Fall Guttenberg Ablauf" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 15 March 2011. p. 4. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Dokumentation Fall Guttenberg Ablauf" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 15 March 2011. p. 5. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Dokumentation Fall Guttenberg Ablauf" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 15 March 2011. p. 6. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ a b "Dokumentation Fall Guttenberg Ablauf" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 15 March 2011. p. 7. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Dokumentation Fall Guttenberg Ablauf" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 15 March 2011. p. 9. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Dokumentation Fall Guttenberg Ablauf" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 15 March 2011. p. 13. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Dokumentation Fall Guttenberg Ablauf" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 15 March 2011. p. 14. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f "Uni Bayreuth weist Guttenbergs Beteuerungen zurück" (in German). DIE WELT. 11 May 2011. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ "Dokumentation Fall Guttenberg Ablauf" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 15 March 2011. p. 15. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Dokumentation Fall Guttenberg Ablauf" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 15 March 2011. pp. 15–20. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ a b "Dokumentation Fall Guttenberg Ablauf" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 15 March 2011. p. 20. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ a b c d "Universität Bayreuth gibt Guttenberg alle Schuld" (in German). DIE WELT. 11 May 2011. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ "Dokumentation Fall Guttenberg Ablauf" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 15 March 2011. p. 21. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ a b "Dokumentation Fall Guttenberg Ablauf" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 15 March 2011. p. 26. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Dokumentation Fall Guttenberg Ablauf" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 15 March 2011. p. 28. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Dokumentation Fall Guttenberg Ablauf" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 15 March 2011. p. 30. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Dokumentation Fall Guttenberg Ablauf" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 15 March 2011. p. 29. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ a b "Guttenberg erklärt Plagiat mit Mehrfachbelastung - Uni legt Abschlussbericht vor" (in German). DerWesten.de. 2011-05-11. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ a b "Guttenberg erklärt Plagiat mit Dauerstress" (in German). Handelsblatt. 2011-05-11. Retrieved 2012-02-28.
- ^ a b "Dokumentation Fall Guttenberg Ablauf" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 15 March 2011. p. 23. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ a b c d "Dokumentation Fall Guttenberg Ablauf" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 15 March 2011. p. 24. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ Schmoll, Heike (11 May 2011). "Nicht fahrlässig, sondern vorsätzlich". Faz.net (in German). Frankfurter Allgemeine. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ "Guttenberg ist die Arbeit "über den Kopf gewachsen"" (in German). Süddeutsche.de. 11 May 2011. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ "Dokumentation Fall Guttenberg Ablauf" (PDF) (in German). Universität Bayreuth. 15 March 2011. pp. 24–25. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "Guttenbergs Doktorarbeit: "Eine große Schlamperei in Folge von Dauerstress"" (in German). FOCUS Online. 11 May 2011. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ a b c d "Über die Ohnmacht des Gejagten" (in German). Bild.de. 2011-05-10. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ a b "Bayreuth-Professor rügt "Treibjagd" auf Guttenberg" (in German). Welt Online. 2011-05-10. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ a b "Ex-Uni-Präsident spricht von "Treibjagd" gegen Guttenberg" (in German). Augsburger Allgemeine. 10 May 2011. Retrieved 23 January 2014.
- ^ a b "Was jetzt passiert, ist eine Treibjagd" (in German). Bild.de. 2011-05-10. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ "Walter Schmitt-Glaeser kritisiert Uni Bayreuth" (in German). stern.de. 2011-05-10. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ "War das die Landesblindenanstalt?" (in German). Deutschlandfunk. 2011-05-11. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ a b "Guttenberg rührt seine Richter" (in German). stern.de. 11 May 2011. Retrieved 23 January 2014.
- ^ "Goppel: Guttenbergs Politikkarriere "im Prinzip vorbei"" (in German). Deutschlandfunk. 11 May 2011. Retrieved 23 January 2014.
- ^ "Plagiatsjäger enttarnt – Vorwurf der Parteilichkeit" (in German). Badische Zeitung. 2011-08-05. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ "VroniPlag-Gründer sichert sich Namensrechte" (in German). Welt Online. 2011-08-05. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ a b "Ermittlungsverfahren Karl-Theodor zu Guttenberg" (in German). Staatsanwaltschaft Hof. 2011-11-23. Retrieved 2012-02-28.
- ^ "Guttenberg kommt glimpflich davon" (in German). Süddeutsche.de. 23 November 2011. Retrieved 13 February 2014.
- ^ "Germany Drops Criminal Probe of zu Guttenberg". THE WALL STREET JOURNAL. 24 November 2011. Retrieved 13 February 2014.
- ^ a b "Staatsanwaltschaft stellt Ermittlungen gegen Guttenberg ein" (in German). Spiegel Online. 2011-11-23. Retrieved 2012-12-21.
- ^ "Guttenberg-Opfer: "Er hat getäuscht, ohne zu bereuen"" (in German). Spiegel online. 2011-11-23. Retrieved 2012-12-20.
- ^ "Staatsanwaltschaft geht nicht von Täuschungsabsicht aus" (in German). Spiegel Online. 2011-12-04. Retrieved 2012-02-28.
- ^ "Staatsanwalt entlastet zu Guttenberg" (in German). Kölnische Rundschau. 2011-12-04. Retrieved 2012-02-28.
- ^ "Guttenberg soll nicht absichtlich getäuscht haben" (in German). Die Welt. 2011-12-11. Retrieved 2012-12-18.
- ^ "Prosecutors drop case against German ex-minister". 23 November 2011. Retrieved 13 February 2014.
