ബോറിക് ആസിഡ്
രാസസംയുക്തം
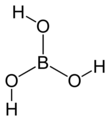
ബോറോണിന്റെ ഒരു ലൂയിസ് അമ്ലം ആണ് ബോറിക് ആസിഡ്. hydrogen borate, boracic acid, orthoboric acid എന്നീ പേരുകളിലും ഇത് അറിയപ്പെടുന്നു. രാസ സൂത്രം: H3BO3 (B(OH)3) ജലത്തിൽ ലയിക്കുന്ന ഇത് നിറമില്ലാത്ത പരലുകളായോ വെളുത്ത പൊടിയായോ കാണപ്പെടുന്നു. ധാതുരൂപത്തിൽ ഇത് Sassolite എന്ന് വിളിക്കപ്പെടുന്നു.
| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC names
Boric acid
Trihydrooxidoboron | |||
| Other names
Orthoboric acid,
Boracic acid, Sassolite, Optibor, Borofax, Trihydroxyborane, Boron(III) hydroxide, Boron Trihydroxide | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.114 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| E number | E284 (preservatives) | ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| InChI | |||
| SMILES | |||
| Properties | |||
| തന്മാത്രാ വാക്യം | |||
| Molar mass | 0 g mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | White crystalline solid | ||
| സാന്ദ്രത | 1.435 g/cm3 | ||
| ദ്രവണാങ്കം | |||
| ക്വഥനാങ്കം | |||
| 2.52 g/100 mL (0 °C) 4.72 g/100 mL (20 °C) 5.7 g/100 mL (25 °C) 19.10 g/100 mL (80 °C) 27.53 g/100 mL (100 °C) | |||
| Solubility in other solvents | Soluble in lower alcohols moderately soluble in pyridine very slightly soluble in acetone | ||
| അമ്ലത്വം (pKa) | 9.24, 12.4, 13.3 | ||
| -34.1·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
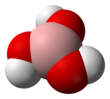
| Structure | |||
| Trigonal planar | |||
| Zero | |||
| Hazards | |||
| EU classification | {{{value}}} | ||
| R-phrases | R60 R61 | ||
| S-phrases | S53 S45 | ||
| Flash point | {{{value}}} | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
2660 mg/kg, oral (rat) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
പ്രകൃതിയിലെ സാന്നിദ്ധ്യം
തിരുത്തുകഅഗ്നിപർവ്വത പ്രദേശങ്ങളിൽ ബോറിക് ആസിഡ് രൂപത്തിലോ sassolite രൂപത്തിലോ കാണപ്പെടുന്നു. കടൽജലത്തിലും സസ്യ ശരീരത്തിലും ഇതിന്റെ സാന്നിദ്ധ്യമുണ്ട്[1].
നിർമ്മാണം
തിരുത്തുകകൃത്രിമമായി ആദ്യമായി നിർമ്മിച്ചത് വില്യം ഹോം ബെർഗ് ( 1652-1715) ആണ്. ബോറാക്സ് മിനറൽ ആസിഡുകളുമായി പ്രവർത്തിപ്പിച്ചായിരുന്നു നിർമ്മാണം.
സവിശേഷതകൾ
തിരുത്തുകതിളച്ച ജലത്തിൽ ലയിക്കുന്നു. 170 °C നു മുകളിൽ ചൂടാക്കിയാൽ, ഇത് വിഘടിച്ച് മെറ്റാബോറിക് ആസിഡ് ഉണ്ടാവുന്നു.
- H3BO3 → HBO2 + H2O
ഘടന
തിരുത്തുകഅവലംബം
തിരുത്തുക- ↑ Allen, A. H.; Tankard, A. R. (1904). "The Determination of Boric Acid in Cider, Fruits, etc". Analyst. 29 (October): 301–304. Bibcode:1904Ana....29..301A. doi:10.1039/an9042900301.