Wolfram Neural Net Repository
Immediate Computable Access to Neural Net Models
Transcribe an English audio recording
Get the pre-trained net:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[2]= |  |
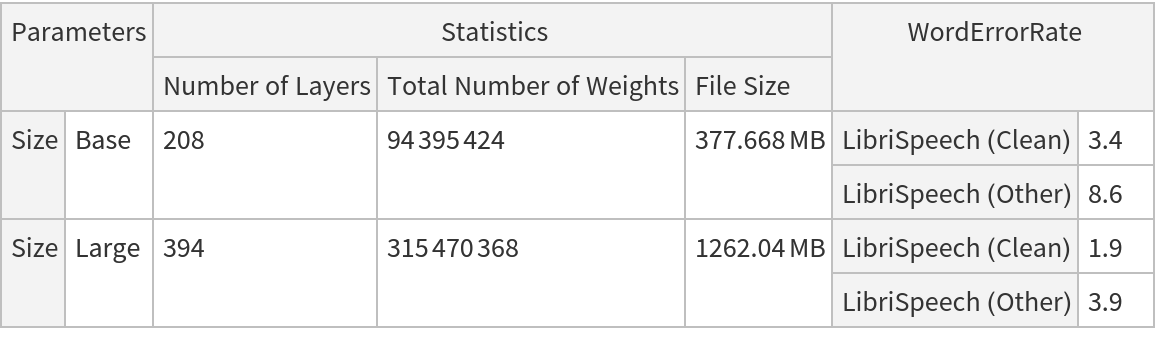
This model consists of a family of individual nets, each identified by a specific parameter. Inspect the available parameters:
| In[3]:= |
| Out[4]= | 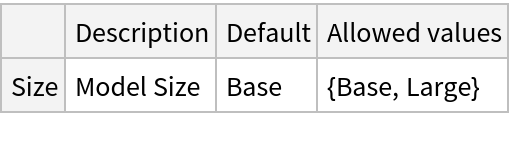 |
Pick a non-default net by specifying the parameters:
| In[5]:= |
| Out[6]= |  |
Pick a non-default uninitialized net:
| In[7]:= |
| Out[8]= | 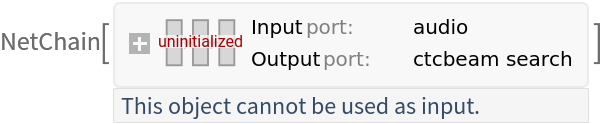 |
Define an evaluation function that runs the net and produces the final transcribed text:
| In[9]:= | ![Copy to Clipboard netevaluate[audio_] := Module[{chars},
chars = NetModel["Wav2Vec2 Trained on LibriSpeech Data"][audio];
StringReplace[StringJoin@chars, "|" -> " "]
]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/dee/dee14dce-11ca-4913-a1a7-0773b924a858/1c79bb51483a12ff.png) |
Record an audio sample and transcribe it:
| In[10]:= |
| Out[11]= |
| In[12]:= |
| Out[12]= |
Try it over different audio samples. Notice that the output can contain spelling mistakes, especially with noisy audio. Hence a spellchecker is usually needed as a post-processing step:
| In[13]:= |
| Out[13]= | 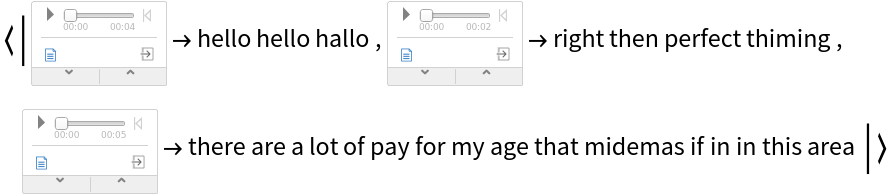 |
Take the feature extractor from the trained net and aggregate the output so that the net produces a vector representation of an audio clip:
| In[14]:= | ![Copy to Clipboard extractor = NetAppend[
NetTake[NetModel["Wav2Vec2 Trained on LibriSpeech Data"], "FeatureExtractor"], "Mean" -> AggregationLayer[Mean, 1]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/dee/dee14dce-11ca-4913-a1a7-0773b924a858/7a7a41050f7c654f.png) |
| Out[15]= |
Get a set of utterances in English and Spanish:
| In[16]:= | ![Copy to Clipboard (* Evaluate this cell to get the example input *) CloudGet["https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/7f452647-8ab1-4beb-a361-2eb460ae4984"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/dee/dee14dce-11ca-4913-a1a7-0773b924a858/7d8276803b228527.png) |
Visualize the utterances in feature space:
| In[17]:= |
| Out[17]= | 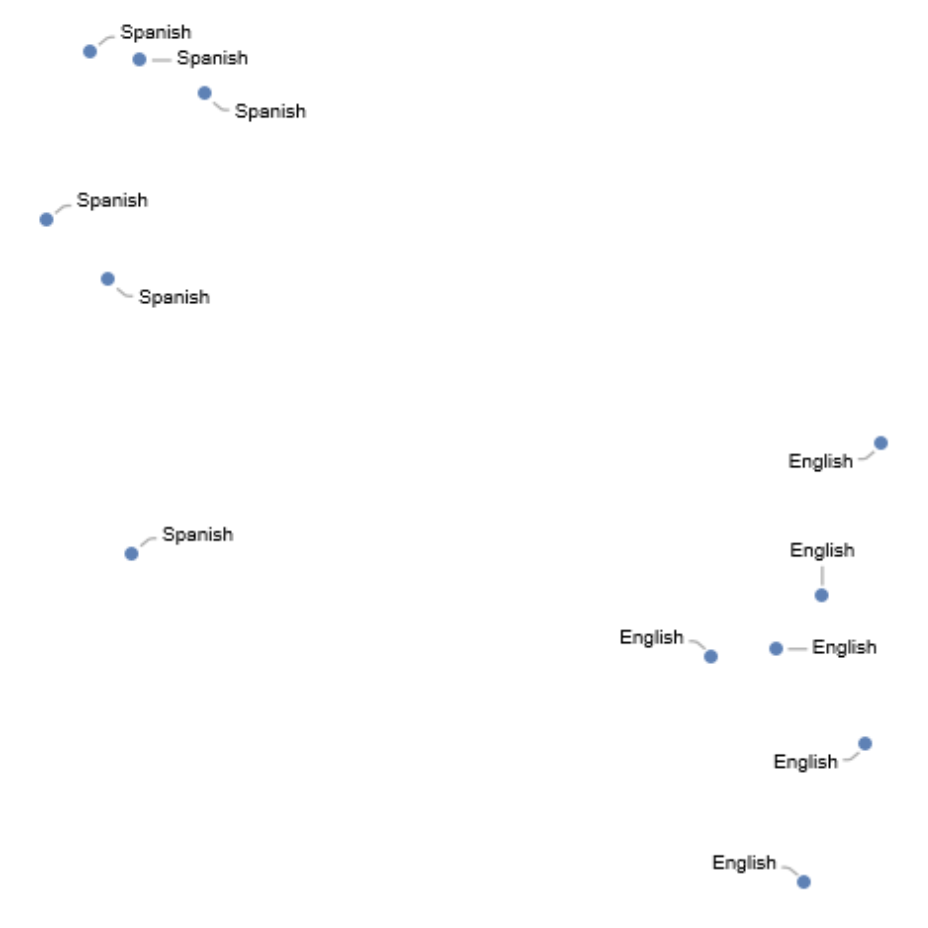 |
Inspect the sizes of all arrays in the net:
| In[18]:= |
| Out[26]= | 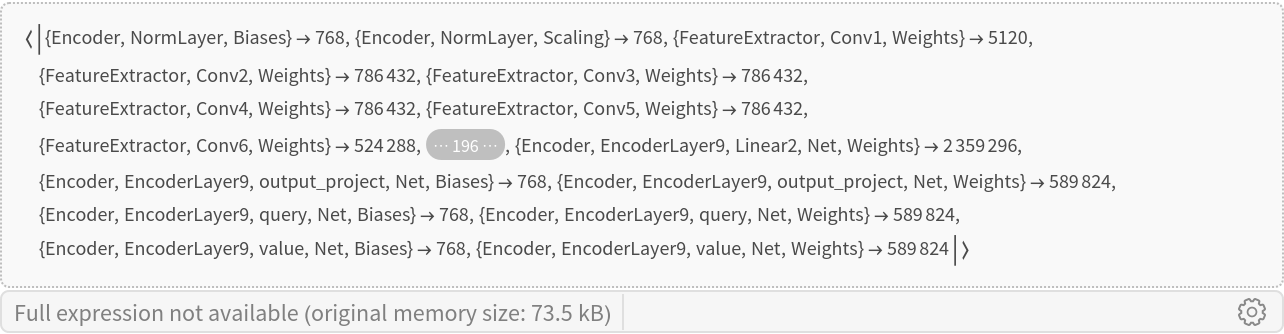 |
Obtain the total number of parameters:
| In[27]:= |
| Out[28]= |
Obtain the layer type counts:
| In[29]:= |
| Out[30]= |
Display the summary graphic:
| In[31]:= |
| Out[32]= |
Wolfram Language 13.2 (December 2022) or above