JDBC Tutorial
JDBC stands for Java Database Connectivity. JDBC is a Java API or tool used in Java applications to interact with the database. It is a specification from Sun Microsystems that provides APIs for Java applications to communicate with different databases. Interfaces and Classes for JDBC API comes under java.sql package. In this Java JDBC tutorial, we will be learning about what is Java Database Connectivity with suitable example.
In the present world, where we mostly deal with websites and databases it is as if they matter the most but if we closely look over it is data that matters the most. If we look closer that all developers are revolving and working over the web and mobile technologies but what remains the same is the data.

Hence, there is an urgency to figure out how data is being handled for which this concept comes into play.

Let us do have an overview of why do we need this term which can be better interpreted with the image provided below.
Why do we need to learn advanced java?
As we are well versed with all the concepts of Core Java now comes the time to build projects that will results out in building an application as a final product. So if we do are only aware of core java we can only build applications that can be run on the machine where the components of it are stored(in simpler words one can say where all the codes are written). These types of applications are known as standalone applications.

Note: Standalone applications being one of two types of applications in the programming world only holds for 5% of the applications in the real world.
Hence, the scope is very constricted if we only do build standalone applications resulting out in the very little scope of development and scalability which gives birth to advance java which in turn gives birth to 3 components primarily namely JSP, Servlets, and JDBC in order to make the applications run on multiple machines. With the evolution of these 3 components, it removes the constraint of running only a single machine as it was impractical to users in the real-world application is made but forcing users to install then use them. Now, these types of applications are known as web applications that are the applications providing the services to the end-users without installing them. These applications are known as web applications which are not standalone applications.
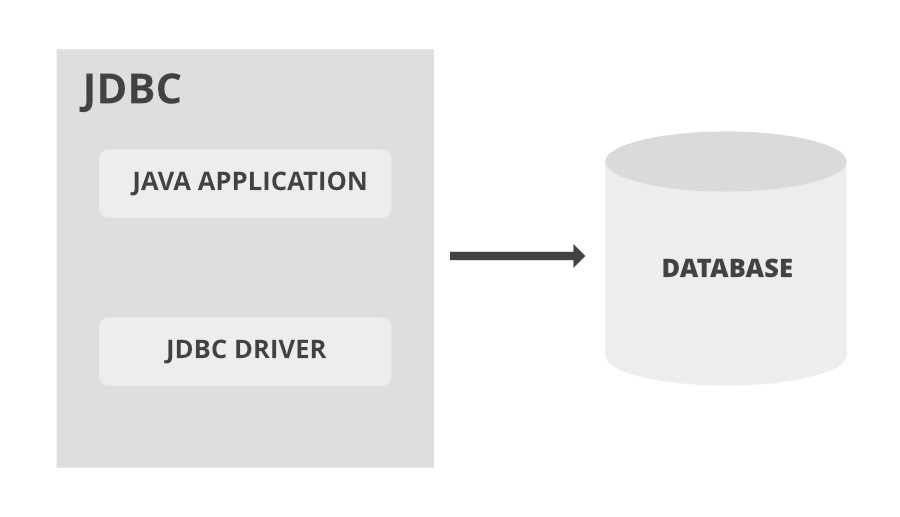
Now you must be wondering what is JSP and Servlet and how JDBC is interrelated with them. For the time being, just focus only on JDBC in order to get started with what exactly it is and how to use it by referring to the image depicted below as follows:

Note: Conclusion drawn from Image is as follows:
- JSP stands for Java Server Pages where these pages are considered as View Components as Presentation logic.
- Servlet is meant for internal processing going on such as reading, fetching values from the database, comparison, etc in the backend as Processing Logic in our process servlet. Servlets do also contain java classes for this background processing for processing logic.
- JDBC is meant for Connectivity of Java Application in servlets as discussed to our Database.
What is JDBC?
Let us try to discuss this from scratch till now in the java domain we were simply writing codes(programming) and interacting with the database. Have you ever wonder imagining how internally our program can be linked to a database giving it enormous power to make projects and applications out of our program. Yes, it is possible with the help of this mechanism. Let us discuss in a real-world scenario which later on we will be mapping with technical terms to get an absolute technical understanding of the same with a pictorial representation.
Real-world example:
Consider two places A and B. Now people residing on A do not know the language of people residing on place B and vice-versa which we will be going to map with technical terms to discuss out major components inside the JDBC.

Mapping the same with technological terms to illustrate above real illustration. Here place A is referred to as a java application and place B is therefore referred to as a database. Now the translator as discussed above which is responsible for converting java application calls to database calls and database calls to java application calls is nothing but a 'Driver Software'. The road between applications is 'Connection' and lastly the vehicle is our 'statement object'. Now 'requirement' above is our SQL query and the 'small block' generated after processing the SQL statement by the database engine has been passed in nothing but 'ResultSet'. Now, this technology by which java applications is communicating with database is 'Java Database Connectivity. By now we are done with a crystal clear overview of JDBC and geek you will be surprised that we already have covered it, let dig down to get to know the working of components which will be described up to greater depth in the environment setup of JDBC.
Now we will penetrate down into the JDBC component which as discussed above is a technology that is used to connect Java applications with the database. It is an API consisting of lots of classes and interfaces by which with the help of some classes and interfaces we are able to connect the java application to the database as pictorially depicted above. It has mainly two packages namely as follows: java.sql package and javax.sql package.
Note: For reference above SQL is taken as database to illustrate packages names.

Interfaces and Classes of JDBC API
Some popular interfaces of JDBC API are listed below:
- Driver interface
- Connection interface
- Statement interface
- PreparedStatement interface
- CallableStatement interface
- ResultSet interface
- ResultSetMetaData interface
- DatabaseMetaData interface
- RowSet interface
Some important Classes of JDBC API are listed below:
- DriverManager class
- Blob class
- Clob class
- Types class
So here is how we are going to cover JDBC ailments in order to get how technically the whole process revolves.
- What is JDBC
- Need of JDBC
- JDBC Architecture
- JDBC Environment Setup
- Steps to connect JDBC
- JDBC example as implementation
JDBC Architecture

To know in-depth about the above diagram, you can refer this article Architecture of JDBC .
JDBC Environment Setup
Now let us do discuss out various types of drivers in JDBC. So basically there are 4 types of standard drivers listed below:
- Type-1 driver or JDBC-ODBC bridge driver (Bridge Driver)
- Type-2 driver or Native-API driver (Native API)
- Type-3 driver or Network Protocol driver (Network Protocol)
- Type-4 driver or Thin driver (Native protocol)
Now, you must be wondering about they are their point do come out which drivers to be used. The solution to this is as simple as we need to use the driver as per accordance with the database with which we are interacting.
Note: Drivers to be used are directly propionate to which kind of database with which we are dealing.
Drivers are mentioned in the tabular format below corresponding to the database which is as follows:
| Database | Driver name |
|---|---|
| MySQL | com.mysql.jdbc.Driver |
Now you must be wondering out from where these listed drivers are to be imported. So in order to import the drivers, you need to download a JAR file from the web. Considering the most frequently used database namely MySQL you need to download a JAR file named 'mysql.connector' and so on it goes for other databases.
Note: It is not an essential step as different IDE's possesses different traits. In some IDE these connectors are inbuilt such as NetBeans while in Eclipse you need to import this JAR file as discussed above by simply downloading corresponding JAR file from the internet and load in the project.
If you do not know how to import JAR files to libraries in java IDE, first go through this step.

Steps to connect JDBC
There are basically seven steps to get your java application connected to deal with the database. Here database could be structured or non-structured, we have to deal accordingly for the same which will be clear by the end of sequential steps execution. In generic mostly we deal with either MySQL or Oracle database as far it is concerned for our java application. Here we will be dealing out with the MySQL database for our java application wherein processing we just have to execute these listed steps below in sequential order to connect JDBC which is as follows:
- Import the required package for the corresponding database.
- Load and register the JDBC drivers.
- First load then register the same
- Establish the connection
- Create a statement
- Execute the query
- Process the results
- Close the connections
Let us discuss the above steps by picking up cases from the real world to get a clear sake of understanding our concept. Considering an illustration of mobile networking which is as follows:
Real-life implementation of JDBC is most frequently seen in mobile networking which is illustrated as follows:
- Consider you want to talk to somebody far away. For which one needs a device known as cell-phone/telecom which signifies our Step 1.
- Now user needs a network and a SIM card which is equivalent to the loading and registering process signifying Step 2.
- Now with a working SIM card, physical labor is required to dial numbers and pressing the call button signifying step 3 as we are trying to establish the connection to commute.
- Whatever message we need to deliver is equivalent to creating a statement.
- Now once connected we need to speak the message as we have thought off, which is equivalent to the execution of the query.
- Now a response will be received which was our goal signifies step 6 of processing results technically in the case of JDBC.
- Lastly, we need to press the button on the device to close communication, similarly, it is a good practice of closing the connections in the technical aspect which here is JDBC.
Implementation (Working of JDBC)
- Suppose the database with which we want to deal is MySQL. So first we need to import the package, for SQL database it is namely 'java.sql.*'.
- Now as per IDE(we need to load its corresponding JAR file in our project in IDE where JAR is manually supposed to be inserted in the IDE, taking 'eclipse IDE' for reference as an IDE in order to illustrate the same in the below example.
- By far we are done with importing the JAR to our project. Now in order to load the driver, we will be using forName() method by writing “com.mysql.driver_name” which belongs to class 'class'
Syntax:
class com.mysql.jdbc.Driver ;- Now in order to establish the connection, we have to instantiate an interface named 'Connection'
- Now statements are of three types:
- Normal statements:
- Prepared statements:
- Callable statements: Stored procedures
- Once the statement is created, now we will be executing the query in our database as per the perceived response from the database. Suppose if we want to fetch data from the database then the response is table structure here or if we are simply inserting the values then response if the number of rows effectively.
- Lastly, whatever we are getting either a table or simply rows, now we simply need to process the results.
- Also, it is recommended to good practice by closing the connections to release and free up memory resources by closing the object of interface and statement objects.
Illustration: Setting up JDBC
// Java Program to Illustrate Setting Up of JDBC
// Importing SQL database
import java.sql.*;
// Main class to illustrate demo of JDBC
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// Loading and registering drivers
// Optional from JDBC version 4.0
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver");
// Step 2:Establishing a connection
Connection con = DriverManager(
"jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:XE",
"username", "password");
// Step 3: Creating statement
Statement st = con.createStatement();
// Step 4: Executing the query and storing the
// result
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery(
"select * from Students where Marks >= 70");
// Step 5: Processing the results
while (rs.next()) {
System.out.println(rs.getString("students"));
System.out.println(rs.getInt("marks"));
}
// Step 6: Closing the connections
// using close() method to release memory resources
con.close();
// Display message for successful execution of program
System.out.println("Steps in Setting Up of JDBC");
}
}
Output
Steps in Setting Up of JDBC
Now let us move ahead and discuss its interaction with the real database after successfully setting up with the database how internally things are getting managed. Here we will be having to create two classes, one is our connection class and the other one where we will be implementing in application.java class using the connector object. We are done with the connection class in the above illustration, so let us now finally discuss the application class with help of an example. Considering the database 'MySQL here to interpret and code out the same.
Implementation: Query in our MySQL database is as follows:
select * from Student;
insert into Students values(7, geeksforGeeks);
select username from Student where userid = 7;
Example:
// Java Program to Illustrate Working Of JDBC
// with Above Query in Database
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Main class
// JDBC demo class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Declaring and initializing arguments that
// needed to be passed later in getConnection()
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/test";
String uname = "root";
String pass = "";
// Query from the database taken
// Custom query taken to illustrate
String query
= "select username from Student where id=7";
// Loading and registering drivers
Class.forName("com.mysqljdbc.Driver");
// Creating an connection object by
// getConnection() method which is static method and
// returns the instance of Connection class
// This method takes 3 parameters as defined above
Connection con
= DriverManager.getConnection(url, uname, pass);
Statement st = con.createStatement();
// It returns a tabular structure so we need
// ResultSet as it stores chunk of data into
// structures
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery(query);
// Now we are having our data in object of ResultSet
// which is no more tabular
// Note:
// Fetching the above data by storing it as a String
// Here pointer is lagging with data for which we
// use next() method to
// take it to next record
rs.next();
// Here we are fetching username column data
String name = rs.getString("username");
// Lastly print the data
System.out.println(name);
// It is good practice to close the connection
// using close() method
// Closing the statement first
st.close();
// Now close the connection also
con.close();
}
}
Output
GeeksforGeeks