The super keyword in Java is a reference variable that is used to refer to parent class when we’re working with objects. You need to know the basics of Inheritanceand Polymorphism to understand the Java super keyword.
The Keyword “super” came into the picture with the concept of Inheritance. In this article, we gonna covers all about super in Java including definitions, examples, Uses, Syntax, and more.
Characteristics of Super Keyword in Java
In Java, super keyword is used to refer to the parent class of a subclass. Here are some of its key characteristics:
- super is used to call a superclass constructor: When a subclass is created, its constructor must call the constructor of its parent class. This is done using the super() keyword, which calls the constructor of the parent class.
- super is used to call a superclass method: A subclass can call a method defined in its parent class using the super keyword. This is useful when the subclass wants to invoke the parent class’s implementation of the method in addition to its own.
- super is used to access a superclass field: A subclass can access a field defined in its parent class using the super keyword. This is useful when the subclass wants to reference the parent class’s version of a field.
- super must be the first statement in a constructor: When calling a superclass constructor, the super() statement must be the first statement in the constructor of the subclass.
- super cannot be used in a static context: The super keyword cannot be used in a static context, such as in a static method or a static variable initializer.
- super is not required to call a superclass method: While it is possible to use the super keyword to call a method in the parent class, it is not required. If a method is not overridden in the subclass, then calling it without the super keyword will invoke the parent class’s implementation.
Overall, the super keyword is a powerful tool for subclassing in Java, allowing subclasses to inherit and build upon the functionality of their parent classes.
Use of super keyword in Java
It is majorly used in the following contexts as mentioned below:
- Use of super with Variables
- Use of super with Methods
- Use of super with Constructors
1. Use of super with Variables
This scenario occurs when a derived class and base class have the same data members. In that case, there is a possibility of ambiguity r the JVM.
We can understand it more clearly using the following example:
Example
Java
class Vehicle {
int maxSpeed = 120;
}
class Car extends Vehicle {
int maxSpeed = 180;
void display()
{
System.out.println("Maximum Speed: "
+ super.maxSpeed);
}
}
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Car small = new Car();
small.display();
}
}
|
Output
Maximum Speed: 120
In the above example, both the base class and subclass have a member maxSpeed. We could access the maxSpeed of the base class in subclass using super keyword.
2. Use of super with Methods
This is used when we want to call the parent class method. So whenever a parent and child class have the same-named methods then to resolve ambiguity we use the super keyword.
This code snippet helps to understand the said usage of the super keyword.
Example
Java
class Person {
void message()
{
System.out.println("This is person class\n");
}
}
class Student extends Person {
void message()
{
System.out.println("This is student class");
}
void display()
{
message();
super.message();
}
}
class Test {
public static void main(String args[])
{
Student s = new Student();
s.display();
}
}
|
Output
This is student class
This is person class
In the above example, we have seen that if we only call method message() then, the current class message() is invoked but with the use of the super keyword, message() of the superclass could also be invoked.
3. Use of super with constructors
The super keyword can also be used to access the parent class constructor. One more important thing is that ‘super’ can call both parametric as well as non-parametric constructors depending on the situation.
Following is the code snippet to explain the above concept:
Example 1
Java
class Person {
Person()
{
System.out.println("Person class Constructor");
}
}
class Student extends Person {
Student()
{
super();
System.out.println("Student class Constructor");
}
}
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Student s = new Student();
}
}
|
Output
Person class Constructor
Student class Constructor
In the above example, we have called the superclass constructor using the keyword ‘super’ via subclass constructor.
Example 2
Java
class ParentClass {
public boolean isTrue() { return true; }
}
class ChildClass extends ParentClass {
public boolean isTrue()
{
boolean parentResult = super.isTrue();
return !parentResult;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ChildClass child = new ChildClass();
boolean result = child.isTrue();
System.out.println(result);
}
}
|
Advantages of Using Java Super Keyword
The super keyword in Java provides many advantages in object-oriented programming are as follows:
- Enables reuse of code: Using the super keyword allows subclasses to inherit functionality from their parent classes, which promotes the reuse of code and reduces duplication.
- Supports polymorphism: Because subclasses can override methods and access fields from their parent classes using super, polymorphism is possible. This allows for more flexible and extensible code.
- Provides access to parent class behaviour: Subclasses can access and use methods and fields defined in their parent classes through the super keyword, which allows them to take advantage of existing behaviour without having to reimplement it.
- Allows for customization of behaviour: By overriding methods and using super to call the parent implementation, subclasses can customize and extend the behaviour of their parent classes.
- Facilitates abstraction and encapsulation: The use of super promotes encapsulation and abstraction by allowing subclasses to focus on their behaviour while relying on the parent class to handle lower-level details.
Overall, the super keyword is a key feature of inheritance and polymorphism in Java, and it provides several benefits for developers seeking to write reusable, extensible, and well-organized code.
Important Points to Remember While Using “Java Super Keyword”
Here are some Important points that you need to take care of during using super keywords in Java:
- Call to super() must be the first statement in the Derived(Student) Class constructor because if you think about it, it makes sense that the superclass has no knowledge of any subclass, so any initialization it needs to perform is separate from and possibly prerequisite to any initialization performed by the subclass. Therefore, it needs to complete its execution first.
- If a constructor does not explicitly invoke a superclass constructor, the Java compiler automatically inserts a call to the no-argument constructor of the superclass. If the superclass does not have a no-argument constructor, you will get a compile-time error. The object does have such a constructor, so if the Object is the only superclass, there is no problem.
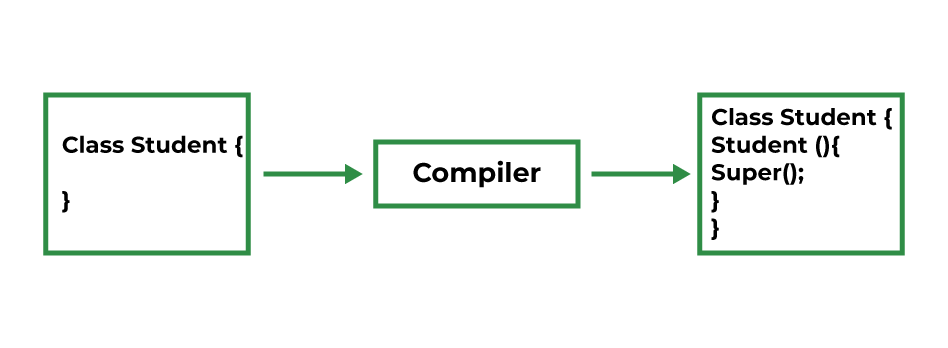
- If a subclass constructor invokes a constructor of its superclass, either explicitly or implicitly, you might think that a whole chain of constructors is called, all the way back to the constructor of Object. This, in fact, is the case. It is called constructor chaining.
FAQs – Java super Keyword
Q1. What is super () and super keyword in Java?
Super() is a Java keyword used to call a superclass constructor. Super accesses superclass members and maintains inheritance hierarchies.
Q2. Which is the super class of Java?
The Object class aka super class is at the top of the class hierarchy in Java’s java.lang package. Every class, whether predefined or user-defined, is a subclass of the Object class.
Q3. Why is Super important in Java?
super is essential in Java as it facilitates the access, initialization, and management of relationships between superclasses and subclasses, thereby promoting code reusability.