ভাগবতবাদ
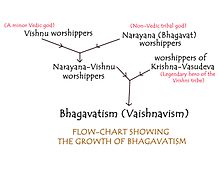
ভাগবতবাদ ("ভগবান" শব্দের বর্ধিত রূপ; শব্দার্থ "ভগবান-সম্পর্কিত") বা ভাগবত সম্প্রদায় হলো হিন্দুধর্মের একটি দার্শনিক ধারণা। এই ধারণায় ভক্তি হল পূজার প্রাথমিক উপাদান। "ভগবৎ" শব্দের অর্থ "পূজনীয়" "সম্মানীয়", শ্রদ্ধেয় এবং "ভাগবত" শব্দের অর্থ হল "যিনি পূজনীয়ের পূজা করেন।"[১] "ভাগবত" বলতে একটি কৃষ্ণ-উপাসনা প্রথাকে বোঝায়। ভগবান শব্দটির অর্থ যাকে শ্রদ্ধা করা যায় বা যার পূজা করা যায়। পরবর্তীকালে এটি নারায়ণ[২] বা আদি মূর্তি স্বয়ং ভগবানের উপাসনার সঙ্গে যুক্ত হয়। কোনো কোনো গবেষকের মতে, খ্রিস্টপূর্ব প্রথম শতাব্দীতে কৃষ্ণপূজার উদ্ভব হয়। যদিও বৈষ্ণব গবেষকদের মতে, কৃষ্ণপূজার উদ্ভব হয়েছিল খ্রিস্টপূর্ব চতুর্থ অব্দে।[৩] বেদ ভাগবত ধর্ম সম্পর্কে নীরব থাকলেও, ভগবদ্গীতায় একেশ্বরবাদী ভাগবত ধর্মের নানা বৈশিষ্ট্য উল্লেখ করা হয়েছে। কোনো কোনো মতে, ভগবদ্গীতায় বাসুদেব-কৃষ্ণকে বৈদিক বিষ্ণুর অবতার হিসেবে না দেখিয়ে সর্বোচ্চ উপাস্য হিসেবে দেখানো হয়েছে।[৪]
ভাগবত ধর্মের সংজ্ঞা
[সম্পাদনা]খ্রিস্টীয় নবম শতাব্দীতে ভাগবত ধর্ম মোটামুটি সহস্রাব্দ প্রাচীন একটি ধর্মমত ছিল। এই সময় ভাগবত পুরাণ-অনুসারী অনেকগুলি সম্প্রদায়ের গোড়াপত্তন সম্পূর্ণ হয়েছিল। এই গোপাল-পূজক সম্প্রদায়গুলি বিভিন্ন পরম্পরার অন্তর্গত ছিল। বর্তমানে তাদের সম্প্রদায়ের সঙ্গে এই সব পরম্পরার নাম যুক্ত হয়ে আছে। এই সব ধারাগুলিকে একসঙ্গে ভাগবত ধর্ম শব্দটির অধীনে আনা হয়। বর্তমানে এই ধর্মমত ভারতের বাইরেও ছড়িয়ে পড়েছে।[৫] বৃন্দাবনের অনেক স্থান বহু শতাব্দী ধরে কৃষ্ণের জীবনকাহিনির সঙ্গে যুক্ত। এখানে কৃষ্ণভক্তেরা তীর্থ করতে যান এবং কৃষ্ণের জীবনকাহিনির সঙ্গে জড়িত বিভিন্ন ঘটনার স্মরণে উৎসব পালিত হয়। কোনো কোনো গবেষকের মতে, এই ধর্মমতের মানবিক দিকটি এটিকে শক্তিশালী ও জনপ্রিয় করে তুলেছিল। যার ফলে প্রথম যুগ থেকেই এই মত অত্যন্ত সমৃদ্ধ হয়েছিল।[৬]
ভাগবত ধর্মের আদি ইতিহাস
[সম্পাদনা]গবেষকদের মতে, ভাগবতেরা সাংখ্য দর্শনের পুরুষ ধারণা থেকে তাঁদের একেশ্বরবাদী ধর্মের তত্ত্বটি গ্রহণ করেছেন। খ্রিস্টপূর্ব চতুর্থ শতাব্দীর শেষভাগে এই দর্শনটি গড়ে উঠেছিল। পরবর্তীকালে প্রধান দেবতা কৃষ্ণ-বাসুদেবের সঙ্গে নারায়ণ ইত্যাদি নাম যুক্ত হয়।[৭]
পরবর্তী দ্বিতীয় পর্যায়
[সম্পাদনা]ভাগবত ধর্মের বিকাশলাভের দ্বিতীয় পর্যায়ে ব্রাহ্মণ্যধর্মের বিশেষ প্রভাব পড়েছিল এই ধর্মমতের উপর। গবেষকদের মতে, এই পর্বেই কৃষ্ণ-বাসুদেব ও ব্রাহ্মণ্য দেবমণ্ডলীর বিষ্ণু একই দেবতা হিসেবে গণ্য হতে শুরু করেন।[৭] দ্বিতীয় চন্দ্রগুপ্ত ও তাঁর পরবর্তী সম্রাটেরা "পরম ভাগবত" বা ভাগবত বৈষ্ণব নামে পরিচিত হতেন। ভাগবত পুরাণে ভাগবত ধর্মের দর্শনটি সম্পূর্ণ রূপ পায়। এই পুরাণেই কৃষ্ণ বাসুদেব, বৈদিক বিষ্ণু ও হরি এক দেবতায় পরিণত হন এবং ভক্তির চরম লক্ষ্যে রূপান্তরিত হন।[৮]
শাস্ত্রীয় উল্লেখ
[সম্পাদনা]"বাসুদেব" শব্দটির উল্লেখ প্রাচীন সংস্কৃত সাহিত্যে পাওয়া যায়। তৈত্তিরীয় আরণ্যকে (দশ। এক। ৬) বাসুদেবকে "নারায়ণ" ও "বিষ্ণু" বলা হয়েছে। পাণিনি তাঁর অষ্টাধ্যায়ী (খ্রিস্টপূর্ব চতুর্থ শতাব্দী) গ্রন্থে "বাসুদেবক" শব্দের অর্থ করেছেন "বাসুদেবের ভক্ত"। বৈদিক যুগে বাসুদেব ও কৃষ্ণ এক দেবতায় পরিণত হয়েছিলেন অথবা বাসুদেব-কৃষ্ণ, কৃষ্ণ-গোপাল ও নারায়ণ - এই তিন আলাদা দেবতাকে বিষ্ণুর সঙ্গে একীভূত হন।[৯] মহাভারত রচনার যুগে এই একত্বীকরণ সম্পূর্ণ হয়েছিল।
গুপ্তযুগে বাসুদেব ছিলেন "ভাগবত" নামে এক সম্প্রদায়ের একক উপাস্য দেবতা।[১০]
কোনো কোনো গবেষকের মতে, পতঞ্জলির আগেই কৃষ্ণ ও বাসুদেব একক দেবতায় পরিণত হয়েছিলেন। কারণ,মহাভাষ্যে "জঘন কংসং কিলা বাসুদেবঃ" বাক্যটি দেখা যায়।[১১] "পাণিনির সময়কাল খ্রিস্টপূর্ব ষষ্ঠ থেকে পঞ্চম শতাব্দী। এই সময় তিনি তাঁর অষ্টাধ্যায়ী গ্রন্থে "বাসুদেবক" শব্দটিকে বাসুদেব ভক্ত হিসেবে উল্লেখ করেছেন। অর্থাৎ বলা চলে বাসুদেব-কৃষ্ণের পূজাকেন্দ্রিক ভাগবত ধর্মই ভারতীয় ইতিহাসে বৈষ্ণবধর্মের আদিরূপ, যা উক্ত সময়কালের মধ্যে প্রতিষ্ঠালাভ করেছিল।"[১২][১৩]
অন্যান্য অর্থ
[সম্পাদনা]সাম্প্রতিক কালে, ভাগবত বলতে পশ্চিম ভারতে একটি বৈষ্ণব সম্প্রদায়ের নাম।[১৪][১৫]
রামানুজ সম্প্রদায় ও অন্যান্য যোগ শাখার একটি সাধারণ সম্বোধন।
ভাগবতদের সঙ্গলাভ, ঈশ্বরের নাম গ্রহণ, প্রার্থনা, ধর্মগ্রন্থ পাঠ, হরিকীর্তন ভাগবত ধর্মের বৈশিষ্ট্য। বৌদ্ধধর্মেও একটি ভাগবত ধারণা প্রচলিত আছে।[১৬][১৭]
আরও দেখুন
[সম্পাদনা]পাদটীকা
[সম্পাদনা]- ↑ Hastings 2003, পৃ. 540
- ↑ Beck, G. (২০০৫)। "Krishna as Loving Husband of God"। Alternative Krishnas: Regional and Vernacular Variations on a Hindu Deity। আইএসবিএন 978-0-7914-6415-1। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২৮ এপ্রিল ২০০৮। Vishnu was by then assimilated with Narayana
- ↑ Hastings 2003, পৃ. 540–42
- ↑ Srinivasan, Doris (১৯৯৭)। Many heads, arms, and eyes: origin, meaning, and form of multiplicity in Indian art। Leiden: Brill। পৃষ্ঠা 134। আইএসবিএন 90-04-10758-4।
- ↑ Schweig, Graham M. (২০০৫)। Dance of Divine Love: The Rڄasa Lڄilڄa of Krishna from the Bhڄagavata Purڄa. na, India's classic sacred love story। Princeton, N.J: Princeton University Press। Front Matter। আইএসবিএন 0-691-11446-3।
- ↑ KLOSTERMAIER, Klaus K. (২০০৭)। A Survey of Hinduism। State University of New York Press; 3 edition। পৃষ্ঠা 204। আইএসবিএন 0-7914-7081-4।
Not only was Krsnaism influenced by the identification of Krsna with Vishnu, but also Vaishnavism as a whole was partly transformed and reinvented in the light of the popular and powerful Krishna religion. Bhagavatism may have brought an element of cosmic religion into Krishna worship; Krishna has certainly brought a strongly human element into Bhagavatism. ... The center of Krishna-worship has been for a long time Brajbhumi, the district of Mathura that embraces also Vrindavana, Govardhana, and Gokula, associated with Krishna from the time immemorial. Many millions of Krishna bhaktas visit these places ever year and participate in the numerous festivals that reenact scenes from Krshnas life on Earth
- ↑ ক খ Hastings 2003, পৃ. 540 উদ্ধৃতি ত্রুটি:
<ref>ট্যাগ বৈধ নয়; আলাদা বিষয়বস্তুর সঙ্গে "Hastings541" নামটি একাধিক বার সংজ্ঞায়িত করা হয়েছে - ↑ Kalyan Kumar Ganguli (১৯৮৮)। Sraddh njali, Studies in Ancient Indian History: D.C. Sircar Commemoration: Puranic tradition of Krishna। Sundeep Prakashan। আইএসবিএন 81-85067-10-4।p.36
- ↑ Flood, Gavin D. (১৯৯৬)। An introduction to Hinduism (Engl. ভাষায়)। Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press। পৃষ্ঠা 341। আইএসবিএন 0-521-43878-0। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২১ এপ্রিল ২০০৮।"Early Vaishnava worship focuses on three deities who become fused together, namely Vasudeva-Krishna, Krishna-Gopala and Narayana, who in turn all become identified with Vishnu. Put simply, Vasudeva-Krishna and Krishna-Gopala were worshiped by groups generally referred to as Bhagavatas, while Narayana was worshipped by the Pancaratra sect."
- ↑ Banerjea, 1966, page 20
- ↑ A Corpus of Indian Studies: Essays in Honour of Professor Gaurinath Sastri, Page 150, 1980 – 416 pages.
- ↑ Page 76 of 386 pages: The Bhagavata religion with the worship of Vasudeva Krishna as the ... of Vasudeva Krishna and they are the direct forerunners of Vaisnavism in India.Ehrenfels, U.R. (১৯৫৩)। "The University of Gauhati"। Dr. B. Kakati Commemoration Volume।
- ↑ Page 98: In the Mahabharata, Vasudeva-Krishna is identified with the highest God.Mishra, Y.K. (১৯৭৭)। Socio-economic and Political History of Eastern India। Distributed by DK Publishers' Distributors।
- ↑ General, A. (১৯২০)। "I. The Bhagavata Sampradaya"। An Outline of the Religious Literature of India।
- ↑ Singhal, G.D. (১৯৭৮)। "The Cultural Evolution of Hindu Gaya, the Vishnu Dham"। The Heritage of India: LN Mishra Commemoration Volume।
- ↑ "The Newly Discovered Three Sets of Svetaka Gangacopper Plates" (পিডিএফ)। ৪ মার্চ ২০০৯ তারিখে মূল (পিডিএফ) থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২০ এপ্রিল ২০০৮।
- ↑ Kielhorn, F. (১৯০৮)। "Bhagavats, Tatrabhavat, and Devanampriya"। Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society: 502–505। ২০ মে ২০১১ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২০ এপ্রিল ২০০৮।
আরও পড়ুন
[সম্পাদনা]- Dahmen-Dallapiccola, Anna Libera; Dallapiccola, Anna L. (২০০২)। Dictionary of Hindu lore and legend। London: Thames & Hudson। আইএসবিএন 0-500-51088-1।
- Hastings, James Rodney (2nd edition 1925–1940, reprint 1955, 2003) [1908–26]। Encyclopedia of Religion and Ethics। John A Selbie (Volume 4 of 24 ( Behistun (continued) to Bunyan.) সংস্করণ)। Edinburgh: Kessinger Publishing, LLC। পৃষ্ঠা 476। আইএসবিএন 0-7661-3673-6। সংগ্রহের তারিখ 3 May 2008।
The encyclopaedia will contain articles on all the religions of the world and on all the great systems of ethics. It will aim at containing articles on every religious belief or custom, and on every ethical movement, every philosophical idea, every moral practice.
এখানে তারিখের মান পরীক্ষা করুন:|তারিখ=(সাহায্য) - Thompson, Richard, PhD (ডিসেম্বর ১৯৯৪)। "Reflections on the Relation Between Religion and Modern Rationalism"। ৪ জানুয়ারি ২০১১ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ১২ এপ্রিল ২০০৮।
- Gupta, Ravi M. (২০০৪)। Caitanya Vaisnava Vedanta: Acintyabhedabheda in Jiva Gosvami's Catursutri tika। University of Oxford।
- Gupta, Ravi M. (২০০৭)। Caitanya Vaisnava Vedanta of Jiva Gosvami। Routledge। আইএসবিএন 0-415-40548-3।
- Ganguli, K.M. (১৮৮৩–১৮৯৬)। The Mahabharata of Krishna Dwaipayana Vyasa। Kessinger Publishing।
- Ganguli, K.M. (১৮৯৬)। Bhagavad-gita (Chapter V). The Mahabharata, Book 6। Calcutta: Bharata Press।
- Wilson, H.H. (১৮৪০)। The Vishnu Purana, a System of Hindu Mythology and Tradition: Translated from the Original Sanscrit and Illustrated by Notes Derived Chiefly from Other Puranas। Printed for the Oriental Translation Fund of Great Britain and Ireland।
- Prabhupada, A.C. (১৯৮৮)। Srimad Bhagavatam। Bhaktivedanta Book Trust।
- Kaviraja, K.; Prabhupada, A.C.B.S.; Bhaktivedanta, A.C. (১৯৭৪)। Sri Caitanya-Caritamrta of Krsnadasa Kaviraja। Imprint unknown।
- Goswami, S.D. (১৯৯৮)। The Qualities of Sri Krsna। GNPress। পৃষ্ঠা 152 pages। আইএসবিএন 0-911233-64-4।
- Garuda Pillar of Besnagar, Archaeological Survey of India, Annual Report (1908–1909). Calcutta: Superintendent of Government Printing, 1912, 129.
- Rowland, B., Jr. (১৯৩৫)। "Notes on Ionic Architecture in the East"। American Journal of Archaeology। 39 (4): 489–496। জেস্টোর 498156। ডিওআই:10.2307/498156।
- Delmonico, N. (২০০৪)। "The History of Indic Monotheism And Modern Chaitanya Vaishnavism"। The Hare Krishna Movement: the Postcharismatic Fate of a Religious Transplant। আইএসবিএন 978-0-231-12256-6। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ১২ এপ্রিল ২০০৮।
- Mahony, W.K. (১৯৮৭)। "Perspectives on Krsna's Various Personalities"। History of Religions। 26 (3): 333–335। জেস্টোর 1062381। ডিওআই:10.1086/463085।
- Beck, Guy L., সম্পাদক (২০০৫)। Alternative Krishnas: Regional and Vernacular Variations on a Hindu Deity। SUNY Press। আইএসবিএন 0-7914-6415-6।
- Vyasanakere, Prabhanjanacharya। Download and Listen to Bhagavata in Kannada। Vyasamadhwa Samshodhana Pratishtana। ১৬ এপ্রিল ২০১৪ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২৫ এপ্রিল ২০১৪।
