Lipoic acid (LA), also known as
| |
| |

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(R)-5-(1,2-Dithiolan-3-yl)pentanoic acid
| |
| Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 81851 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.793 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Lipoic+acid |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H14O2S2 | |
| Molar mass | 206.32 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Yellow needle-like crystals |
| Melting point | 60–62 °C (140–144 °F; 333–335 K) |
| Very Slightly Soluble(0.24 g/L)[1] | |
| Solubility in ethanol 50 mg/mL | Soluble |
| Pharmacology | |
| A16AX01 (WHO) | |
| Pharmacokinetics: | |
| 30% (oral)[2] | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Lipoamide Asparagusic acid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Physical and chemical properties
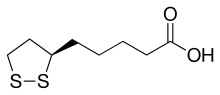
Lipoic acid (LA), also known as
The carbon atom at C6 is chiral and the molecule exists as two enantiomers (R)-(+)-lipoic acid (RLA) and (S)-(-)-lipoic acid (SLA) and as a racemic mixture (R/S)-lipoic acid (R/S-LA).
LA appears physically as a yellow solid and structurally contains a terminal carboxylic acid and a terminal dithiolane ring.
For use in dietary supplement materials and compounding pharmacies, the USP established an official monograph for R/S-LA.[6][7]
Biological function
Lipoic acid is a cofactor for five enzymes or classes of enzymes: pyruvate dehydrogenase, a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, the glycine cleavage system, branched chain keto acid dehydrogenase, and the alpha-oxo(keto)adipate dehydrogenase. The first two are critical to the citric acid cycle. The GCS regulates glycine concentrations.[8]
HDAC1, HDAC2, HDAC3, HDAC6, HDAC8, and HDAC10 are targets of the reduced form (open disulfide) of (R)-lipoic acid. [9]
Biosynthesis and attachment
Most endogenously produced RLA are not "free" because octanoic acid, the precursor to RLA, is bound to the enzyme complexes prior to enzymatic insertion of the sulfur atoms. As a cofactor, RLA is covalently attached by an amide bond to a terminal lysine residue of the enzyme's lipoyl domains. The precursor to lipoic acid, octanoic acid, is made via fatty acid biosynthesis in the form of octanoyl-acyl carrier protein.[3] In eukaryotes, a second fatty acid biosynthetic pathway in mitochondria is used for this purpose.[3] The octanoate is transferred as a thioester of acyl carrier protein from fatty acid biosynthesis to an amide of the lipoyl domain protein by an enzyme called an octanoyltransferase.[3] Two hydrogens of octanoate are replaced with sulfur groups via a radical SAM mechanism, by lipoyl synthase.[3] As a result, lipoic acid is synthesized attached to proteins and no free lipoic acid is produced. Lipoic acid can be removed whenever proteins are degraded and by action of the enzyme lipoamidase.[10] Free lipoate can be used by some organisms as an enzyme called lipoate protein ligase that attaches it covalently to the correct protein. The ligase activity of this enzyme requires ATP.[11]
Cellular transport
Along with sodium and the vitamins biotin (B7) and pantothenic acid (B5), lipoic acid enters cells through the SMVT (sodium-dependent multivitamin transporter). Each of the compounds transported by the SMVT is competitive with the others. For example research has shown that increasing intake of lipoic acid[12] or pantothenic acid[13] reduces the uptake of biotin and/or the activities of biotin-dependent enzymes.
Enzymatic activity
Lipoic acid is a cofactor for at least five enzyme systems.[3] Two of these are in the citric acid cycle through which many organisms turn nutrients into energy. Lipoylated enzymes have lipoic acid attached to them covalently. The lipoyl group transfers acyl groups in 2-oxoacid dehydrogenase complexes, and methylamine group in the glycine cleavage complex or glycine dehydrogenase.[3]
2-Oxoacid dehydrogenase transfer reactions occur by a similar mechanism in:
- the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
- the
α -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase or 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex - the branched-chain oxoacid dehydrogenase (BCDH) complex
- the acetoin dehydrogenase complex.
The most-studied of these is the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.[3] These complexes have three central subunits: E1-3, which are the decarboxylase, lipoyl transferase, and dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase, respectively. These complexes have a central E2 core and the other subunits surround this core to form the complex. In the gap between these two subunits, the lipoyl domain ferries intermediates between the active sites.[3] The lipoyl domain itself is attached by a flexible linker to the E2 core and the number of lipoyl domains varies from one to three for a given organism. The number of domains has been experimentally varied and seems to have little effect on growth until over nine are added, although more than three decreased activity of the complex.[14]
Lipoic acid serves as co-factor to the acetoin dehydrogenase complex catalyzing the conversion of acetoin (3-hydroxy-2-butanone) to acetaldehyde and acetyl coenzyme A.[3]
The glycine cleavage system differs from the other complexes, and has a different nomenclature.[3] In this system, the H protein is a free lipoyl domain with additional helices, the L protein is a dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase, the P protein is the decarboxylase, and the T protein transfers the methylamine from lipoate to tetrahydrofolate (THF) yielding methylene-THF and ammonia. Methylene-THF is then used by serine hydroxymethyltransferase to synthesize serine from glycine. This system is part of plant photorespiration.[15]
Biological sources and degradation
Lipoic acid is present in many foods in which it is bound to lysine in proteins,[3] but slightly more so in kidney, heart, liver, spinach, broccoli, and yeast extract.[16] Naturally occurring lipoic acid is always covalently bound and not readily available from dietary sources.[3] In addition, the amount of lipoic acid present in dietary sources is low. For instance, the purification of lipoic acid to determine its structure used an estimated 10 tons of liver residue, which yielded 30 mg of lipoic acid.[17] As a result, all lipoic acid available as a supplement is chemically synthesized.
Baseline levels (prior to supplementation) of RLA and R-DHLA have not been detected in human plasma.[18] RLA has been detected at 12.3−43.1 ng/mL following acid hydrolysis, which releases protein-bound lipoic acid. Enzymatic hydrolysis of protein bound lipoic acid released 1.4−11.6 ng/mL and <1-38.2 ng/mL using subtilisin and alcalase, respectively.[19][20][21]
Digestive proteolytic enzymes cleave the R-lipoyllysine residue from the mitochondrial enzyme complexes derived from food but are unable to cleave the lipoic acid-L-lysine amide bond.[22] Both synthetic lipoamide and (R)-lipoyl-L-lysine are rapidly cleaved by serum lipoamidases, which release free (R)-lipoic acid and either L-lysine or ammonia.[3] Little is known about the degradation and utilization of aliphatic sulfides such as lipoic acid, except for cysteine.[3]
Lipoic acid is metabolized in a variety of ways when given as a dietary supplement in mammals.[3][23] Degradation to tetranorlipoic acid, oxidation of one or both of the sulfur atoms to the sulfoxide, and S-methylation of the sulfide were observed. Conjugation of unmodified lipoic acid to glycine was detected especially in mice.[23] Degradation of lipoic acid is similar in humans, although it is not clear if the sulfur atoms become significantly oxidized.[3][24] Apparently mammals are not capable of utilizing lipoic acid as a sulfur source.
Chemical synthesis
SLA did not exist prior to chemical synthesis in 1952.[25][26] SLA is produced in equal amounts with RLA during achiral manufacturing processes. The racemic form was more widely used clinically in Europe and Japan in the 1950s to 1960s despite the early recognition that the various forms of LA are not bioequivalent.[27] The first synthetic procedures appeared for RLA and SLA in the mid-1950s.[28][29][30][31] Advances in chiral chemistry led to more efficient technologies for manufacturing the single enantiomers by both classical resolution and asymmetric synthesis and the demand for RLA also grew at this time. In the 21st century, R/S-LA, RLA and SLA with high chemical and/or optical purities are available in industrial quantities. At the current time, most of the world supply of R/S-LA and RLA is manufactured in China and smaller amounts in Italy, Germany, and Japan. RLA is produced by modifications of a process first described by Georg Lang in a Ph.D. thesis and later patented by DeGussa.[32][33] Although RLA is favored nutritionally due to its “vitamin-like” role in metabolism, both RLA and R/S-LA are widely available as dietary supplements. Both stereospecific and non-stereospecific reactions are known to occur in vivo and contribute to the mechanisms of action, but evidence to date indicates RLA may be the eutomer (the nutritionally and therapeutically preferred form).[34][35]
Pharmacology
Pharmacokinetics
A 2007 human pharmacokinetic study of sodium RLA demonstrated the maximum concentration in plasma and bioavailability are significantly greater than the free acid form, and rivals plasma levels achieved by intravenous administration of the free acid form.[36] Additionally, high plasma levels comparable to those in animal models where Nrf2 was activated were achieved.[36]
The various forms of LA are not bioequivalent.[27][non-primary source needed] Very few studies compare individual enantiomers with racemic lipoic acid. It is unclear if twice as much racemic lipoic acid can replace RLA.[36]
The toxic dose of LA in cats is much lower than that in humans or dogs and produces hepatocellular toxicity.[37]
Pharmacodynamics
The mechanism and action of lipoic acid when supplied externally to an organism is controversial. Lipoic acid in a cell seems primarily to induce the oxidative stress response rather than directly scavenge free radicals. This effect is specific for RLA.[4] Despite the strongly reducing milieu, LA has been detected intracellularly in both oxidized and reduced forms.[38] LA is able to scavenge reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen species in a biochemical assay due to long incubation times, but there is little evidence this occurs within a cell or that radical scavenging contributes to the primary mechanisms of action of LA.[4][39] The relatively good scavenging activity of LA toward hypochlorous acid (a bactericidal produced by neutrophils that may produce inflammation and tissue damage) is due to the strained conformation of the 5-membered dithiolane ring, which is lost upon reduction to DHLA. In cells, LA is reduced to dihydrolipoic acid, which is generally regarded as the more bioactive form of LA and the form responsible for most of the antioxidant effects and for lowering the redox activities of unbound iron and copper.[40] This theory has been challenged due to the high level of reactivity of the two free sulfhydryls, low intracellular concentrations of DHLA as well as the rapid methylation of one or both sulfhydryls, rapid side-chain oxidation to shorter metabolites and rapid efflux from the cell. Although both DHLA and LA have been found inside cells after administration, most intracellular DHLA probably exists as mixed disulfides with various cysteine residues from cytosolic and mitochondrial proteins.[34] Recent findings suggest therapeutic and anti-aging effects are due to modulation of signal transduction and gene transcription, which improve the antioxidant status of the cell. However, this likely occurs via pro-oxidant mechanisms, not by radical scavenging or reducing effects.[4][39][41]
All the disulfide forms of LA (R/S-LA, RLA and SLA) can be reduced to DHLA although both tissue specific and stereoselective (preference for one enantiomer over the other) reductions have been reported in model systems. At least two cytosolic enzymes, glutathione reductase (GR) and thioredoxin reductase (Trx1), and two mitochondrial enzymes, lipoamide dehydrogenase and thioredoxin reductase (Trx2), reduce LA. SLA is stereoselectively reduced by cytosolic GR whereas Trx1, Trx2 and lipoamide dehydrogenase stereoselectively reduce RLA. (R)-(+)-lipoic acid is enzymatically or chemically reduced to (R)-(-)-dihydrolipoic acid whereas (S)-(-)-lipoic acid is reduced to (S)-(+)-dihydrolipoic acid.[42][43][44][45][46][47][48] Dihydrolipoic acid (DHLA) can also form intracellularly and extracellularly via non-enzymatic, thiol-disulfide exchange reactions.[49]
RLA may function in vivo like a B-vitamin and at higher doses like plant-derived nutrients, such as curcumin, sulforaphane, resveratrol, and other nutritional substances that induce phase II detoxification enzymes, thus acting as cytoprotective agents.[41][50] This stress response indirectly improves the antioxidant capacity of the cell.[4]
The (S)-enantiomer of LA was shown to be toxic when administered to thiamine-deficient rats.[51][52]
Several studies have demonstrated that SLA either has lower activity than RLA or interferes with the specific effects of RLA by competitive inhibition.[53][54][55][56][57]
Uses
R/S-LA and RLA are widely available as over-the-counter nutritional supplements in the United States in the form of capsules, tablets, and aqueous liquids, and have been marketed as antioxidants.[3]
Although the body can synthesize LA, it can also be absorbed from the diet. Dietary supplementation in doses from 200–600 mg is likely to provide up to 1000 times the amount available from a regular diet. Gastrointestinal absorption is variable and decreases with the use of food. It is therefore recommended that dietary LA be taken 30–60 minutes before or at least 120 minutes after a meal. Maximum blood levels of LA are achieved 30–60 minutes after dietary supplementation, and it is thought to be largely metabolized in the liver.[58]
In Germany, LA is approved as a drug for the treatment of diabetic neuropathy since 1966 and is available as a non-prescription pharmaceutical.[59]
Clinical research
According to the American Cancer Society as of 2013, "there is no reliable scientific evidence at this time that lipoic acid prevents the development or spread of cancer".[60] As of 2015, intravenously administered ALA is unapproved anywhere in the world except Germany for diabetic neuropathy, but has been proven reasonably safe and effective in four clinical trials; however another large trial over four years found no difference from placebo.[61] As of 2012, there was no good evidence alpha lipoic acid helps people with mitochondrial disorders.[62] A 2018 review recommended ALA as an anti-obesity supplement with low dosage (< 600 mg/day) for a short period of time (<10 weeks); however, it is too expensive to be practical as a complementary therapy for obesity.[63]
Other lipoic acids
β -lipoic acid is a thiosulfinate ofα -lipoic acid
See also
References
- ^ "Lipoic Acid". Pubmed. NCBI. Retrieved October 18, 2018.
- ^ Teichert, J; Hermann, R; Ruus, P; Preiss, R (November 2003). "Plasma kinetics, metabolism, and urinary excretion of alpha-lipoic acid following oral administration in healthy volunteers". The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 43 (11): 1257–67. doi:10.1177/0091270003258654. PMID 14551180. S2CID 30589232.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w "Lipoic acid". Micronutrient Information Center, Linus Pauling Institute, Oregon State University, Corvallis. 1 January 2019. Retrieved 5 November 2019.
- ^ a b c d e Shay, KP; Moreau, RF; Smith, EJ; Hagen, TM (June 2008). "Is alpha-lipoic acid a scavenger of reactive oxygen species in vivo? Evidence for its initiation of stress signaling pathways that promote endogenous antioxidant capacity". IUBMB Life. 60 (6): 362–7. doi:10.1002/iub.40. PMID 18409172. S2CID 33008376.
- ^ Reljanovic, M; Reichel, G; Rett, K; Lobisch, M; et al. (September 1999). "Treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy with the antioxidant thioctic acid (alpha-lipoic acid): A two year multicenter randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial (ALADIN II). Alpha Lipoic Acid in Diabetic Neuropathy". Free Radical Research. 31 (3): 171–9. doi:10.1080/10715769900300721. PMID 10499773.
- ^ USP32-NF27. p. 1042.
- ^ "Unavailable First-Time Official USP Reference Standards" (PDF). Pharmacopeial Forum. 35. USP: 26. February 2009. Archived (PDF) from the original on 5 March 2022. Retrieved 13 January 2023.
- ^ Cronan, John E. (2020). "Progress in the Enzymology of the Mitochondrial Diseases of Lipoic Acid Requiring Enzymes". Frontiers in Genetics. 11: 510. doi:10.3389/fgene.2020.00510. PMC 7253636. PMID 32508887.
- ^ Lechner, Severin; Steimbach, Raphael R.; Wang, Longlong; Deline, Marshall L.; Chang, Yun-Chien; Fromme, Tobias; Klingenspor, Martin; Matthias, Patrick; Miller, Aubry K.; Médard, Guillaume; Kuster, Bernhard (2023). "Chemoproteomic target deconvolution reveals Histone Deacetylases as targets of (R)-lipoic acid". Nature Communications. 14 (1): 3548. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-39151-8. PMC 10272112. PMID 37322067.
- ^ Jiang, Y; Cronan, JE (2005). "Expression cloning and demonstration of Enterococcus faecalis lipoamidase (pyruvate dehydrogenase inactivase) as a Ser-Ser-Lys triad amidohydrolase". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 280 (3): 2244–56. doi:10.1074/jbc.M408612200. PMID 15528186.
- ^ Cronan, JE; Zhao, X; Jiang, Y (2005). Poole, RK (ed.). Function, attachment and synthesis of lipoic acid in Escherichia coli. Advances in Microbial Physiology. Vol. 50. pp. 103–46. doi:10.1016/S0065-2911(05)50003-1. ISBN 9780120277506. PMID 16221579.
- ^ Zempleni, J.; Trusty, T. A.; Mock, D. M. (1997). "Lipoic acid reduces the activities of biotin-dependent carboxylases in rat liver". The Journal of Nutrition. 127 (9): 1776–81. doi:10.1093/jn/127.9.1776. PMID 9278559.
- ^ Chirapu, S. R.; Rotter, C. J.; Miller, E. L.; Varma, M. V.; Dow, R. L.; Finn, M. G. (2013). "High specificity in response of the sodium-dependent multivitamin transporter to derivatives of pantothenic acid". Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry. 13 (7): 837–42. doi:10.2174/1568026611313070006. PMID 23578027.
- ^ Machado, RS; Clark, DP; Guest, JR (1992). "Construction and properties of pyruvate dehydrogenase complexes with up to nine lipoyl domains per lipoate acetyltransferase chain". FEMS Microbiology Letters. 79 (1–3): 243–8. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb14047.x. PMID 1478460.
- ^ Douce, R; Bourguignon, J; Neuburger, M; Rebeille, F (2001). "The glycine decarboxylase system: A fascinating complex". Trends in Plant Science. 6 (4): 167–76. doi:10.1016/S1360-1385(01)01892-1. PMID 11286922.
- ^ Durrani, AI; Schwartz, H; Nagl, M; Sontag, G (October 2010). "Determination of free [alpha]-lipoic acid in foodstuffs by HPLC coupled with CEAD and ESI-MS". Food Chemistry. 120 (4): 38329–36. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.11.045.
- ^ Reed, LJ (October 2001). "A trail of research from lipoic acid to alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (42): 38329–36. doi:10.1074/jbc.R100026200. PMID 11477096.
- ^ Hermann, R; Niebch, G; Borbe, HO; Fieger, H; et al. (1996). "Enantioselective pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of different racemic formulations in healthy volunteers". European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 4 (3): 167–74. doi:10.1016/0928-0987(95)00045-3.
- ^ Teichert, J; Preiss, R (1997). High-performance Liquid Chromatography Methods for Determination of Lipoic and Dihydrolipoic Acid in Human Plasma. Methods in Enzymology. Vol. 279. pp. 159–66. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(97)79019-0. ISBN 9780121821807. PMID 9211267.
- ^ Teichert, J; Preiss, R (October 1995). "Determination of lipoic acid in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection". Journal of Chromatography B. 672 (2): 277–81. doi:10.1016/0378-4347(95)00225-8. PMID 8581134.
- ^ Teichert, J; Preiss, R (November 1992). "HPLC-methods for determination of lipoic acid and its reduced form in human plasma". International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, Therapy, and Toxicology. 30 (11): 511–2. PMID 1490813.
- ^ Biewenga, GP; Haenen, GR; Bast, A (September 1997). "The pharmacology of the antioxidant lipoic acid". General Pharmacology. 29 (3): 315–31. doi:10.1016/S0306-3623(96)00474-0. PMID 9378235.
- ^ a b Schupke, H; Hempel, R; Peter, G; Hermann, R; et al. (June 2001). "New metabolic pathways of alpha-lipoic acid". Drug Metabolism and Disposition. 29 (6): 855–62. PMID 11353754.
- ^ Teichert, J; Hermann, R; Ruus, P; Preiss, R (November 2003). "Plasma kinetics, metabolism, and urinary excretion of alpha-lipoic acid following oral administration in healthy volunteers". Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 43 (11): 1257–67. doi:10.1177/0091270003258654. PMID 14551180. S2CID 30589232.
- ^ Hornberger, CS; Heitmiller, RF; Gunsalus, IC; Schnakenberg, GHF; et al. (1953). "Synthesis of DL—lipoic acid". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 75 (6): 1273–7. doi:10.1021/ja01102a003.
- ^ Hornberger, CS; Heitmiller, RF; Gunsalus, IC; Schnakenberg, GHF; et al. (1952). "Synthetic preparation of lipoic acid". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 74 (9): 2382. doi:10.1021/ja01129a511.
- ^ a b Kleeman, A; Borbe, HO; Ulrich, H (1991). "Thioctic Acid-Lipoic Acid". In Borbe, HO; Ulrich, H (eds.). Thioctsäure: Neue Biochemische, Pharmakologische und Klinische Erkenntnisse zur Thioctsäure [Thioctic Acid. New Biochemistry, Pharmacology and Findings from Clinical Practice with Thioctic Acid]. Symposium at Wiesbaden, DE, 16–18 February 1989. Frankfurt, DE: Verlag. pp. 11–26. ISBN 9783891191255.
- ^ Fontanella, L (1955). "Preparation of optical antipodes of alpha-lipoic acid". Il Farmaco; Edizione Scientifica. 10 (12): 1043–5. PMID 13294188.
- ^ Walton, E; Wagner, AF; Bachelor, FW; Peterson, LH; et al. (1955). "Synthesis of (+)-lipoic acid and its optical antipode". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 77 (19): 5144–9. doi:10.1021/ja01624a057.
- ^ Acker, DS; Wayne, WJ (1957). "Optically active and radioactive
α -lipoic acids". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 79 (24): 6483–6487. doi:10.1021/ja01581a033. - ^ Deguchi, Y; Miura, K (June 1964). "Studies on the synthesis of thioctic acid and its related compounds. XIV. Synthesis of (+)-thioctamide". Yakugaku Zasshi. 84 (6): 562–3. doi:10.1248/yakushi1947.84.6_562. PMID 14207116.
- ^ Lang, G (1992). In Vitro Metabolism of a-Lipoic Acid Especially Taking Enantioselective Bio-transformation into Account (Ph.D. thesis). Münster, DE: University of Münster.
- ^ US patent 5281722, Blaschke, G; Scheidmantel, U & Bethge, H et al., "Preparation and use of salts of the pure enantiomers of alpha-lipoic acid", issued 1994-01-25, assigned to DeGussa.
- ^ a b Carlson, DA; Young, KL; Fischer, SJ; Ulrich, H (2008). "Ch. 10: An Evaluation of the Stability and Pharmacokinetics of R-lipoic Acid and R-Dihydrolipoic Acid Dosage Forms in Plasma from Healthy Human Subjects". In Mulchand S. Patel; Lester Packer (eds.). Lipoic Acid: Energy Production, Antioxidant Activity and Health Effects. pp. 235–70.
- ^ Packer, L; Kraemer, K; Rimbach, G (October 2001). "Molecular aspects of lipoic acid in the prevention of diabetes complications". Nutrition. 17 (10): 888–95. doi:10.1016/S0899-9007(01)00658-X. PMID 11684397.
- ^ a b c Carlson, DA; Smith, AR; Fischer, SJ; Young, KL; et al. (December 2007). "The plasma pharmacokinetics of R-(+)-lipoic acid administered as sodium R-(+)-lipoate to healthy human subjects" (PDF). Alternative Medicine Review. 12 (4): 343–51. PMID 18069903.
- ^ Hill, AS; Werner, JA; Rogers, QR; O'Neill, SL; et al. (April 2004). "Lipoic acid is 10 times more toxic in cats than reported in humans, dogs or rats". Journal of Animal Physiology and Animal Nutrition. 88 (3–4): 150–6. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0396.2003.00472.x. PMID 15059240.
- ^ Packer, L; Witt, EH; Tritschler, HJ (August 1995). "Alpha-lipoic acid as a biological antioxidant". Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 19 (2): 227–50. doi:10.1016/0891-5849(95)00017-R. PMID 7649494.
- ^ a b Shay, KP; Moreau, RF; Smith, EJ; Smith, AR; et al. (October 2009). "Alpha-lipoic acid as a dietary supplement: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subjects. 1790 (10): 1149–60. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2009.07.026. PMC 2756298. PMID 19664690.
- ^ Haenen, GRMM; Bast, A (1991). "Scavenging of hypochlorous acid by lipoic acid". Biochemical Pharmacology. 42 (11): 2244–6. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(91)90363-A. PMID 1659823.
- ^ a b Shay, KP; Shenvi, S; Hagen, TM (2008). "Ch. 14 Lipoic Acid as an Inducer of Phase II Detoxification Enzymes Through Activation of Nr-f2 Dependent Gene Expression". In Mulchand S. Patel; Lester Packer (eds.). Lipoic Acid: Energy Production, Antioxidant Activity and Health Effects. pp. 349–71.
- ^ Arnér, ES; Nordberg, J; Holmgren, A (August 1996). "Efficient reduction of lipoamide and lipoic acid by mammalian thioredoxin reductase". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 225 (1): 268–74. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1996.1165. PMID 8769129.
- ^ Biaglow, JE; Ayene, IS; Koch, CJ; Donahue, J; et al. (April 2003). "Radiation response of cells during altered protein thiol redox". Radiation Research. 159 (4): 484–94. Bibcode:2003RadR..159..484B. doi:10.1667/0033-7587(2003)159[0484:RROCDA]2.0.CO;2. PMID 12643793. S2CID 42110797.
- ^ Haramaki, N; Han, D; Handelman, GJ; Tritschler, HJ; et al. (1997). "Cytosolic and mitochondrial systems for NADH- and NADPH-dependent reduction of alpha-lipoic acid". Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 22 (3): 535–42. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(96)00400-5. PMID 8981046.
- ^ Constantinescu, A; Pick, U; Handelman, GJ; Haramaki, N; et al. (July 1995). "Reduction and transport of lipoic acid by human erythrocytes". Biochemical Pharmacology. 50 (2): 253–61. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(95)00084-D. PMID 7632170.
- ^ May, JM; Qu, ZC; Nelson, DJ (June 2006). "Cellular disulfide-reducing capacity: An integrated measure of cell redox capacity". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 344 (4): 1352–9. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.04.065. PMID 16650819.
- ^ Jones, W; Li, X; Qu, ZC; Perriott, L; et al. (July 2002). "Uptake, recycling, and antioxidant actions of alpha-lipoic acid in endothelial cells". Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 33 (1): 83–93. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(02)00862-6. PMID 12086686.
- ^ Schempp, H; Ulrich, H; Elstner, EF (1994). "Stereospecific reduction of R(+)-thioctic acid by porcine heart lipoamide dehydrogenase/diaphorase". Zeitschrift für Naturforschung C. 49 (9–10): 691–2. doi:10.1515/znc-1994-9-1023. PMID 7945680.
- ^ Biewenga, GP; Haenen, GRMM; Bast, A (1997). "Ch. 1: An Overview of Lipoate Chemistry". In Fuchs, J; Packer, L; Zimmer, G (eds.). Lipoic Acid In Health & Disease. CRC Press. pp. 1–32. ISBN 9780824700935.
- ^ Lii, CK; Liu, KL; Cheng, YP; Lin, AH; et al. (May 2010). "Sulforaphane and alpha-lipoic acid upregulate the expression of the pi class of glutathione S-transferase through c-jun and Nrf2 activation". Journal of Nutrition. 140 (5): 885–92. doi:10.3945/jn.110.121418. PMID 20237067.
- ^ Gal, EM; Razevska, DE (August 1960). "Studies on the in vivo metabolism of lipoic acid. 1. The fate of DL-lipoic acid-S35 in normal and thiamine-deficient rats". Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. 89 (2): 253–61. doi:10.1016/0003-9861(60)90051-5. PMID 13825981.
- ^ Gal, EM (July 1965). "Reversal of selective toxicity of (-)-alpha-lipoic acid by thiamine in thiamine-deficient rats". Nature. 207 (996): 535. Bibcode:1965Natur.207..535G. doi:10.1038/207535a0. PMID 5328673. S2CID 4146866.
- ^ US patent 6271254, Ulrich, H; Weischer, CH & Engel, J et al., "Pharmaceutical compositions containing R-alpha-lipoic acid or S-alpha.-lipoic acid as active ingredient", issued 2001-08-07, assigned to ASTA Pharma.
- ^ Kilic, F; Handelman, GJ; Serbinova, E; Packer, L; et al. (October 1995). "Modelling cortical cataractogenesis 17: In vitro effect of a-lipoic acid on glucose-induced lens membrane damage, a model of diabetic cataractogenesis". Biochemistry and Molecular Biology International. 37 (2): 361–70. PMID 8673020.
- ^ Artwohl, M; Schmetterer, L; Rainer, G; et al. (September 2000). Modulation by antioxidants of endothelial apoptosis, proliferation, & associated gene/protein expression. 36th Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes, 17–21 September 2000, Jerusalem, Israel. Diabetologia. Vol. 43, no. Suppl 1 (published August 2000). Abs 274. PMID 11008622.
- ^ Streeper, RS; Henriksen, EJ; Jacob, S; Hokama, JY; et al. (July 1997). "Differential effects of lipoic acid stereoisomers on glucose metabolism in insulin-resistant skeletal muscle". AJP: Endocrinology and Metabolism. 273 (1 Pt 1): E185–91. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.1997.273.1.E185. PMID 9252495.
- ^ Frölich, L; Götz, ME; Weinmüller, M; Youdim, MB; et al. (March 2004). "(r)-, but not (s)-alpha lipoic acid stimulates deficient brain pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in vascular dementia, but not in Alzheimer dementia". Journal of Neural Transmission. 111 (3): 295–310. doi:10.1007/s00702-003-0043-5. PMID 14991456. S2CID 20214857.
- ^ McIlduff, Courtney E; Rutkove, Seward B (2011-01-01). "Critical appraisal of the use of alpha lipoic acid (thioctic acid) in the treatment of symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy". Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management. 7: 377–385. doi:10.2147/TCRM.S11325. ISSN 1176-6336. PMC 3176171. PMID 21941444.
- ^ Ziegle, D.; Reljanovic, M; Mehnert, H; Gries, F. A. (1999). "
α -Lipoic acid in the treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy in Germany". Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes. 107 (7): 421–30. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1212132. PMID 10595592. - ^ "Lipoic Acid". American Cancer Society. November 2008. Retrieved 5 October 2013.
- ^ Javed, S; Petropoulos, IN; Alam, U; Malik, RA (January 2015). "Treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy". Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease. 6 (1): 15–28. doi:10.1177/2040622314552071. PMC 4269610. PMID 25553239.
- ^ Pfeffer G, Majamaa K, Turnbull DM, Thorburn D, Chinnery PF (April 2012). "Treatment for mitochondrial disorders". Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 (4): CD004426. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004426.pub3. PMC 7201312. PMID 22513923.
- ^ Namazi, Nazli; Larijani, Bagher; Azadbakht, Leila (2018). "Alpha-lipoic acid supplement in obesity treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials". Clinical Nutrition. 37 (2): 419–428. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2017.06.002. ISSN 0261-5614. PMID 28629898.
External links
- Media related to Lipoic acid at Wikimedia Commons