Laudanosine or N-methyltetrahydropapaverine is a toxic metabolite of atracurium and cisatracurium[1] that decreases the seizure threshold, thus it can cause seizures at sufficient concentrations. It also occurs naturally in minute amounts (0.1%) in opium, from which it was first isolated in 1871.[2] Partial dehydration of laudanosine will lead to papaverine.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
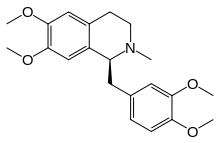
| IUPAC name
(1S)-1-[(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)methyl]-6,7-dimethoxy- 2-methyl-3,4-dihydro-1H-isoquinoline
| |
| Other names
N-Methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropapaverine
| |
| Identifiers | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.018.412 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| C21H27NO4 | |
| Molar mass | 357.450 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 89 °C |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Laudanosine is a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid. It has been shown to interact with GABA receptors, opioid receptors, and nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.[1]
References
- ^ a b Fodale V, Santamaria LB (2002). "Laudanosine, an atracurium and cisatracurium metabolite". Eur J Anaesthesiol. 19 (7): 466–73. PMID 12113608.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Burger A (2005) [1954]. "The Benzylisoquinoline Alkaloids". In Manske RHF, Holmes HL (eds.) (ed.). The Alkaloids: Chemistry and Physiology. Vol. 4. New York: Academic Press. pp. p. 48. ISBN 0124695043.
{{cite book}}:|editor=has generic name (help);|pages=has extra text (help); External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) Retrieved September 18, 2008 through Google Book Search.