Idazoxan (INN) is a drug which is used in scientific research. It acts as both a selective
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
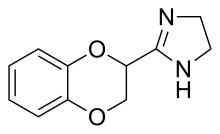
| Formula | C11H12N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 204.229 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| |
| |
| | |
Alzheimer's research
editMice treated with idazoxan, which blocks the
Synthesis
editNote that the literature method claims that the old original patented procedure gives a different reaction product formed through a rearrangement.
The reaction of catechol (1) with 2-Chloroacrylonitrile [920-37-6] (2) gives 2-cyano-1,4-benzodioxan [1008-92-0] (3). Pinner reaction with alcoholic hydrogen chloride leads to the iminoether,[11] (4). Treatment with ethylenediamine [107-15-3] (5) gives the imidazoline ring affording Idazoxin (6).
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Bousquet P, Bruban V, Schann S, Greney H, Ehrhardt JD, Dontenwill M, Feldman J (June 1999). "Participation of imidazoline receptors and alpha(2-)-adrenoceptors in the central hypotensive effects of imidazoline-like drugs". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 881 (1): 272–8. Bibcode:1999NYASA.881..272B. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb09369.x. PMID 10415925. S2CID 38772290.
- ^ Clarke RW, Harris J (2002). "RX 821002 as a tool for physiological investigation of alpha(2)-adrenoceptors". CNS Drug Reviews. 8 (2): 177–92. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2002.tb00222.x. PMC 6741674. PMID 12177687.
- ^ Yakubu MA, Hamilton CA, Howie CA, Reid JL (1988). "Idazoxan and brain alpha2-adrenoceptor in the rabbit". Brain Research. 436: 289–296. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(88)90402-7. PMID 2848612.
- ^ Hamilton CA, Yakubu MA, Jardine E, Reid JL (1991). "Imidazole binding sites in rabbit kidney and forebrain membranes". J Auton Pharmacol. 11 (4): 277–83. doi:10.1111/j.1474-8673.1991.tb00325.x. PMID 1939285.
- ^ Zhang F, Gannon M, Chen Y, Yan S, Zhang S, Feng W, et al. (January 2020). "
β -amyloid redirects norepinephrine signaling to activate the pathogenic GSK3β /tau cascade". Science Translational Medicine. 12 (526). doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aay6931. PMC 7891768. PMID 31941827. - ^ Chapleo CB, Myers PL (January 1981). "2-[2-(1, 4-benzodioxanyl)]-2-imidazoline hydrochloride". Tetrahedron Letters. 22 (48): 4839–4842. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(01)92358-5.
- ^ Chapleo CB, Davis JA, Myers PL, Readhead MJ, Stillings MR, Welbourn AP, Hampson FC, Sugden K (January 1984). "An investigation of some base induced transformations of the 1, 4‐benzodioxan ring system". Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry. 21 (1): 77–80. doi:10.1002/jhet.5570210117.
- ^ Chapleo CB, Myers PL, Butler RC, Doxey JC, Roach AG, Smith CF (June 1983). "alpha-adrenoreceptor reagents. 1. Synthesis of some 1,4-benzodioxans as selective presynaptic alpha 2-adrenoreceptor antagonists and potential antidepressants". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 26 (6): 823–31. doi:10.1021/jm00360a008. PMID 6133953.
- ^ US 2979511, Krapcho J, Lott WA, "Certain 1, 4-benzodioxanyl imidazolines and corresponding pyrimidines and process", issued 11 April 1961, assigned to Olin Corp.
- ^ US 7338970, Bougaret J, Avan JL, Segonds R, "Pharmaceutical composition based on idazoxan, salts, hydrates or polymorphs thereof", issued 3 March 2008, assigned to Pierre Fabre Medicament.
- ^ "2,3-Dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-2-carbimidic acid ethyl ester". PubChem. U.S. National Library of Medicine. CID:10035919.