Slovak Republic (1939–1945): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Meleager91 (talk | contribs) ce |
||
| Line 91: | Line 91: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
The ('''First''') '''Slovak Republic''' ({{lang-sk|(Prvá) Slovenská republika}}), otherwise known as the '''Slovak State''' ({{Lang|sk|Slovenský štát}}), was a partially-recognized [[client state]] of [[Nazi Germany]] which existed between 14 March 1939 and 4 April 1945 in [[Central Europe]]. The Slovak part of [[Second Czechoslovak Republic|Czechoslovakia]] declared independence with German support one day before the [[German occupation of Czechoslovakia|German occupation]] of [[Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia|Bohemia and Moravia]]. It controlled most of the territory of present |
The ('''First''') '''Slovak Republic''' ({{lang-sk|(Prvá) Slovenská republika}}), otherwise known as the '''Slovak State''' ({{Lang|sk|Slovenský štát}}), was a partially-recognized [[client state]] of [[Nazi Germany]] which existed between 14 March 1939 and 4 April 1945 in [[Central Europe]]. The Slovak part of [[Second Czechoslovak Republic|Czechoslovakia]] declared independence with German support one day before the [[German occupation of Czechoslovakia|German occupation]] of [[Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia|Bohemia and Moravia]]. It controlled most of the territory of present-day [[Slovakia]], without its current southern parts, which were [[First Vienna Award|ceded]] by [[Czechoslovakia]] to [[Kingdom of Hungary (1920–46)|Hungary]] in 1938. Slovakia had been a formally independent state for the first time in history. [[Bratislava]] was declared the capital city. |
||
A [[one-party state]] governed by the far-right [[Slovak People's Party|Hlinka's Slovak People's Party]], the Slovak Republic is primarily known for its [[collaborationism|collaboration]] with Nazi Germany, which included sending troops to the [[Slovak invasion of Poland|invasion of Poland]] in [[September Campaign|September 1939]] and the [[Operation Barbarossa|Soviet Union]] in 1941. In 1940, the country joined the [[Axis powers|Axis]] when its leaders signed the [[Tripartite Pact]]. |
A [[one-party state]] governed by the far-right [[Slovak People's Party|Hlinka's Slovak People's Party]], the Slovak Republic is primarily known for its [[collaborationism|collaboration]] with Nazi Germany, which included sending troops to the [[Slovak invasion of Poland|invasion of Poland]] in [[September Campaign|September 1939]] and the [[Operation Barbarossa|Soviet Union]] in 1941. In 1940, the country joined the [[Axis powers|Axis]] when its leaders signed the [[Tripartite Pact]]. |
||
In 1942, the country [[deportation of Jews from Slovakia|deported 58,000 Jews]] (two-thirds of the Slovak Jewish population) to German-occupied Poland, paying Germany 500 Reichsmarks each. After an increase in the activity of anti-Nazi [[Slovak partisans]], Germany invaded Slovakia, triggering a |
In 1942, the country [[deportation of Jews from Slovakia|deported 58,000 Jews]] (two-thirds of the Slovak Jewish population) to German-occupied Poland, paying Germany 500 Reichsmarks each. After an increase in the activity of anti-Nazi [[Slovak partisans]], Germany invaded Slovakia, triggering a significant [[Slovak National Uprising|uprising]]. The Slovak Republic was abolished after the Soviet occupation in 1945, and its territory was reintegrated into the recreated [[Third Czechoslovak Republic]]. |
||
The current [[Slovak Republic]] does not consider itself a [[successor state]] of the wartime Slovak Republic, instead a successor to the [[Czechoslovak Federal Republic]]. However, some nationalists |
The current [[Slovak Republic]] does not consider itself a [[successor state]] of the wartime Slovak Republic, instead a successor to the [[Czechoslovak Federal Republic]]. However, some nationalists celebrate 14 March as a day of independence. |
||
==Name== |
==Name== |
||
The official name of the country was the Slovak State ({{lang-sk|Slovenský štát|link=no}}) from 14 March to 21 July 1939 (until the adoption of the [[Constitution of Slovakia (1939)|Constitution]]), and the Slovak Republic ({{lang-sk|Slovenská Republika|link=no}}) from 21 July 1939 to its end in April 1945. |
The official name of the country was the Slovak State ({{lang-sk|Slovenský štát|link=no}}) from 14 March to 21 July 1939 (until the adoption of the [[Constitution of Slovakia (1939)|Constitution]]), and the Slovak Republic ({{lang-sk|Slovenská Republika|link=no}}) from 21 July 1939 to its end in April 1945. |
||
The country is often referred to historically as the ''First Slovak Republic'' ({{lang-sk|prvá Slovenská Republika|link=no}}) to distinguish it from the contemporary (Second) [[Slovak Republic]], Slovakia, which is not considered its legal [[Succession of states|successor state]]. |
The country is often referred to historically as the ''First Slovak Republic'' ({{lang-sk|prvá Slovenská Republika|link=no}}) to distinguish it from the contemporary (Second) [[Slovak Republic]], Slovakia, which is not considered its legal [[Succession of states|successor state]]. "Slovak State" was used colloquially, but "First Slovak Republic" was used even in encyclopedias written during the post-war Communist period.<ref>Vladár, J. (Ed.), ''Encyklopédia Slovenska V. zväzok R – Š.'' Bratislava, Veda, 1981, pp. 330–331</ref><ref>Plevza, V. (Ed.) ''Dejiny Slovenského národného povstania 1944 5. zväzok.'' Bratislava, Nakladateľstvo Pravda, 1985, pp. 484–487</ref> |
||
==Creation== |
==Creation== |
||
[[File:Adolf Hitler in Bratislava, 1938.webp|thumb|left|[[Adolf Hitler]] on his visit to [[Bratislava]] after the [[Munich Agreement]], October 1938]] |
[[File:Adolf Hitler in Bratislava, 1938.webp|thumb|left|[[Adolf Hitler]] on his visit to [[Bratislava]] after the [[Munich Agreement]], October 1938]] |
||
After the [[Munich Agreement|Munich Betrayal]], Slovakia gained [[autonomy]] inside Czecho-Slovakia (as former Czechoslovakia had been renamed) and lost its southern territories to Hungary under the [[First Vienna Award]]. As [[Adolf Hitler|Hitler]] was preparing a |
After the [[Munich Agreement|Munich Betrayal]], Slovakia gained [[autonomy]] inside Czecho-Slovakia (as former Czechoslovakia had been renamed) and lost its southern territories to Hungary under the [[First Vienna Award]]. As [[Adolf Hitler|Hitler]] was preparing a mobilization into Czech territory and the creation of the [[Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia]], he had various plans for Slovakia. The Hungarians initially misinformed German officials that the Slovaks wanted to join Hungary. Germany decided to make Slovakia a separate puppet state under German influence and a potential strategic base for German attacks on [[Second Polish Republic|Poland]] and other regions. |
||
On 13 March 1939, Hitler invited [[Monsignor]] [[Jozef Tiso]] (the Slovak ex-[[prime minister]] who had been deposed by Czechoslovak troops several days earlier) to [[Berlin]] and urged him to proclaim Slovakia's independence. Hitler added that |
On 13 March 1939, Hitler invited [[Monsignor]] [[Jozef Tiso]] (the Slovak ex-[[prime minister]] who had been deposed by Czechoslovak troops several days earlier) to [[Berlin]] and urged him to proclaim Slovakia's independence. Hitler added that if Tiso had not consented, he would have allowed events in Slovakia to take place effectively, leaving it to the mercies of Hungary and Poland. During the meeting, [[Joachim von Ribbentrop]] passed on a report claiming that Hungarian troops were approaching the Slovak borders. Tiso refused to make such a decision himself, after which he was allowed by Hitler to organize a meeting of the Slovak parliament ("Diet of the Slovak Land"), which would approve Slovakia's independence. |
||
[[File:Jozef Tiso in Trenčín.png|thumb|left|Jozef Tiso in [[Trenčín]], October 1939]] |
[[File:Jozef Tiso in Trenčín.png|thumb|left|Jozef Tiso in [[Trenčín]], October 1939]] |
||
On 14 March, the Slovak parliament convened and heard Tiso's report on his discussion with Hitler |
On 14 March, the Slovak parliament convened and heard Tiso's report on his discussion with Hitler and a possible declaration of independence. Some of the deputies were skeptical of making such a move, among other reasons, because some worried that the Slovak state would be too small and with a strong [[Hungarians in Slovakia|Hungarian minority]].<ref name="RadioPrague">{{cite web |author=Dominik Jůn interviewing Professor Jan Rychlík |title=Czechs and Slovaks - more than just neighbours |publisher=Radio Prague |year=2016 |url=http://www.radio.cz/en/section/special/czechs-and-slovaks-more-than-just-neighbours |access-date=28 October 2016}}</ref> The debate was quickly brought to a head when [[Franz Karmasin]], leader of the [[Germans in Slovakia|German minority]] in Slovakia, said that any delay in declaring independence would result in Slovakia being divided between Hungary and Germany. Under these circumstances, Parliament unanimously voted to secede from Czecho-Slovakia, thus creating the first Slovak state in history.<ref name="RadioPrague"/> Jozef Tiso was appointed the first Prime Minister of the new republic. The next day, Tiso sent a telegram (composed the previous day in Berlin) announcing Slovakia's independence, asking the Reich to take over the protection of the newly minted state. The request was readily accepted.<ref name="RiseFall">William Shirer, ''The Rise and Fall of the Third Reich'' (Touchstone Edition) (New York: Simon & Schuster, 1990)</ref> |
||
==Diplomatic recognition== |
==Diplomatic recognition== |
||
| Line 127: | Line 127: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
Germany and Italy immediately recognized the emergent Slovak state a few weeks later. Britain and France refused to do so; in March 1939, both powers sent diplomatic notes to Berlin protesting developments in former Czechoslovakia as a breach of the [[Munich agreement]] and pledged not to acknowledge the territorial changes. Similar notes – though without reference to Munich – were sent by the USSR and the USA. Some non-Axis states, like [[Switzerland]], Poland, and the [[Vatican City|Vatican]], recognized Slovakia in March and April 1939. |
|||
The Great Powers soon changed their position. In May, British diplomacy asked for (and received) a new [[exequatur]] for its former consul in Bratislava, which marked ''de facto'' recognition of Slovakia. France followed suit in July 1939. However, Czechoslovak legations kept operating in London and Paris. Some international organizations like the [[League of Nations]] or the International Labour Union still considered Czechoslovakia their member, but some – like the [[Universal Postal Union]] – admitted Slovakia. |
The Great Powers soon changed their position. In May, British diplomacy asked for (and received) a new [[exequatur]] for its former consul in Bratislava, which marked ''de facto'' recognition of Slovakia. France followed suit in July 1939. However, Czechoslovak legations kept operating in London and Paris. Some international organizations like the [[League of Nations]] or the International Labour Union still considered Czechoslovakia their member, but some – like the [[Universal Postal Union]] – admitted Slovakia. |
||
| Line 133: | Line 133: | ||
[[File:Celebration of the National Day in Bratislava. Members of Hlinka Guard and Slovak Army.jpg|thumb|left|Celebration of the second anniversary of Slovak independence with members of Hlinka Guard and Slovak Army, [[Bratislava]], [[Hviezdoslavovo námestie (Bratislava)|Hviezdoslav Square]], March 14, 1941]] |
[[File:Celebration of the National Day in Bratislava. Members of Hlinka Guard and Slovak Army.jpg|thumb|left|Celebration of the second anniversary of Slovak independence with members of Hlinka Guard and Slovak Army, [[Bratislava]], [[Hviezdoslavovo námestie (Bratislava)|Hviezdoslav Square]], March 14, 1941]] |
||
Following the outbreak of the Second World War, the British and French consulates in Slovakia were closed and the territory was declared |
Following the outbreak of the Second World War, the British and French consulates in Slovakia were closed, and the territory was declared under occupation. However, in September 1939, the USSR recognized Slovakia, admitted a Slovak representative, and closed the hitherto operational Czechoslovak legation in Moscow. Official Soviet-Slovak diplomatic relations were maintained until the outbreak of the German-Soviet war in 1941, when Slovakia joined the invasion on Germany's side, and the USSR recognized the [[Czechoslovak government-in-exile]]; Britain recognized it one year earlier. |
||
In all, 27 states either ''de iure'' or ''de facto'' recognized Slovakia. They were either Axis countries (like Romania, Finland, Hungary) or Axis-dominated semi-independent states (like [[Vichy France]], [[Manchukuo]])<ref>Pavol Petruf, ''Vichy France and the diplomatic recognition of the Slovak Republic'', [in:] ''Historický Časopis'' 48 (2000), pp. 131-152</ref> or neutral countries like Lithuania, the Netherlands, and Sweden, as well as some beyond Europe (like Ecuador, Costa Rica, Liberia). In some cases, Czechoslovak legations were closed (e.g. in Switzerland), but some countries opted for a somewhat ambiguous stand. The states |
In all, 27 states either ''de iure'' or ''de facto'' recognized Slovakia. They were either Axis countries (like Romania, Finland, Hungary) or Axis-dominated semi-independent states (like [[Vichy France]], [[Manchukuo]])<ref>Pavol Petruf, ''Vichy France and the diplomatic recognition of the Slovak Republic'', [in:] ''Historický Časopis'' 48 (2000), pp. 131-152</ref> or neutral countries like Lithuania, the Netherlands, and Sweden, as well as some beyond Europe (like Ecuador, Costa Rica, Liberia). In some cases, Czechoslovak legations were closed (e.g., in Switzerland), but some countries opted for a somewhat ambiguous stand. The states that maintained their independence ceased recognizing Slovakia in the late stages of World War II. However, some (e.g., [[Francoist Spain|Spain]]) permitted operations of semi-diplomatic representation until the late 1950s.<ref>Michal Považan, ''Slovakia 1939-1945: Statehood and International Recognition'', [in:] ''UNISCI Discussion Papers'' 36 (2014), pp. 75-78</ref> |
||
The |
The [[United States]] never recognized Slovak independence. It remained consistent in their initial approach, as they never recognized the [[Munich Agreement]], the extinction of [[First Czechoslovak Republic|Czechoslovakia]], or any territorial changes made to Czechoslovak territory in the period 1938 – 1939.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://revistas.ucm.es/index.php/UNIS/article/view/48503|title=Slovakia 1939 – 1945: Statehood and International Recognition (de iure or de facto statehood?)|date=May 1, 2024|website=Dialnet}}</ref> |
||
==International relations== |
==International relations== |
||
[[File:Japanese envoy Oshima in Bratislava.png|thumb|[[Hiroshi Ōshima]], Japanese envoy to Slovak Republic and Ambassador to Germany with [[Jozef Tiso]] and [[Vojtech Tuka]], 1941]] |
[[File:Japanese envoy Oshima in Bratislava.png|thumb|[[Hiroshi Ōshima]], Japanese envoy to the Slovak Republic and Ambassador to Germany with [[Jozef Tiso]] and [[Vojtech Tuka]], 1941]] |
||
From the beginning, the Slovak Republic was under the influence of Germany. The so-called "protection treaty" (''Treaty on the protective relationship between Germany and the Slovak State''), signed on 23 March 1939, partially subordinated its foreign, military, and economic policy to that of Germany.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Noack |first1=David X. |title=Slowakei – Der mühsame Weg nach Westen |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=lcJ3DwAAQBAJ |series=Brennpunkt Osteuropa |date=4 October 2012 |location=Vienna |publisher=Promedia |publication-date=2012 |pages=48–50 |isbn= 9783853718025 |access-date=2022-04-19}}</ref> The German [[Wehrmacht]] established the so-called "[[German Zone of Protection in Slovakia|Protective Zone]]" ({{lang-de|Schutzzone}}) in Western Slovakia in August 1939.{{citation needed|date=February 2020}} |
From the beginning, the Slovak Republic was under the influence of Germany. The so-called "protection treaty" (''Treaty on the protective relationship between Germany and the Slovak State''), signed on 23 March 1939, partially subordinated its foreign, military, and economic policy to that of Germany.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Noack |first1=David X. |title=Slowakei – Der mühsame Weg nach Westen |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=lcJ3DwAAQBAJ |series=Brennpunkt Osteuropa |date=4 October 2012 |location=Vienna |publisher=Promedia |publication-date=2012 |pages=48–50 |isbn= 9783853718025 |access-date=2022-04-19}}</ref> The German [[Wehrmacht]] established the so-called "[[German Zone of Protection in Slovakia|Protective Zone]]" ({{lang-de|Schutzzone}}) in Western Slovakia in August 1939.{{citation needed|date=February 2020}} |
||
| Line 148: | Line 148: | ||
Following Slovak participation in the [[invasion of Poland]] in September 1939, [[Polish–Czechoslovak border conflicts|border adjustments]] increased the Slovak Republic's geographical extent in the areas of [[Orava (region)|Orava]] and [[Spiš]], absorbing previously Polish-controlled territory.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Piotrowski |first1=Tadeusz |author-link1=Tadeusz Piotrowski (sociologist) |title=Poland's Holocaust: Ethnic Strife, Collaboration with Occupying Forces and Genocide in the Second Republic, 1918-1947 |year=1998 |url=https://archive.org/details/polandsholocaust00piot |url-access=registration |series=Science Publications |location=Jefferson, NC |publisher=McFarland |publication-date=1998 |page=[https://archive.org/details/polandsholocaust00piot/page/294 294] |isbn=9780786403714 |access-date=2017-02-09 |quote=Between 1920 and 1924, some areas of Orawa and Spisz fell to Poland, others to Slovakia. With Germany's support, on the basis of the November 1 and 30, 1938 agreements between Poland and Czechoslovakia, Poland annexed 226 square kilometers (and 4,280 people) of Orawa and Spisz. The following year, on the basis of an agreement (November 21, 1939) between Germany and Slovakia, these territories, along with some previously Polish sections of Orawa and Spisz (a total of 752 square kilometers of land with 30,000 people) were transferred to Slovakia.}}</ref> |
Following Slovak participation in the [[invasion of Poland]] in September 1939, [[Polish–Czechoslovak border conflicts|border adjustments]] increased the Slovak Republic's geographical extent in the areas of [[Orava (region)|Orava]] and [[Spiš]], absorbing previously Polish-controlled territory.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Piotrowski |first1=Tadeusz |author-link1=Tadeusz Piotrowski (sociologist) |title=Poland's Holocaust: Ethnic Strife, Collaboration with Occupying Forces and Genocide in the Second Republic, 1918-1947 |year=1998 |url=https://archive.org/details/polandsholocaust00piot |url-access=registration |series=Science Publications |location=Jefferson, NC |publisher=McFarland |publication-date=1998 |page=[https://archive.org/details/polandsholocaust00piot/page/294 294] |isbn=9780786403714 |access-date=2017-02-09 |quote=Between 1920 and 1924, some areas of Orawa and Spisz fell to Poland, others to Slovakia. With Germany's support, on the basis of the November 1 and 30, 1938 agreements between Poland and Czechoslovakia, Poland annexed 226 square kilometers (and 4,280 people) of Orawa and Spisz. The following year, on the basis of an agreement (November 21, 1939) between Germany and Slovakia, these territories, along with some previously Polish sections of Orawa and Spisz (a total of 752 square kilometers of land with 30,000 people) were transferred to Slovakia.}}</ref> |
||
In July 1940 at the [[Salzburg Conference]], the Germans forced a reshuffle of the Slovak cabinet by threatening to withdraw their protection guarantees.{{sfn|Ward|2013|pp=211–212}} |
In July 1940, at the [[Salzburg Conference]], the Germans forced a reshuffle of the Slovak cabinet by threatening to withdraw their protection guarantees.{{sfn|Ward|2013|pp=211–212}} |
||
On 24 November 1940, Slovakia joined the [[Axis powers|Axis]] when its leaders signed the [[Tripartite Pact]]. |
On 24 November 1940, Slovakia joined the [[Axis powers|Axis]] when its leaders signed the [[Tripartite Pact]]. |
||
| Line 154: | Line 154: | ||
The Slovak-[[Soviet Union|Soviet]] Treaty of Commerce and Navigation was signed at [[Moscow]] on 6 December 1940.<ref>National Archives, document reference FO 371/24856</ref> |
The Slovak-[[Soviet Union|Soviet]] Treaty of Commerce and Navigation was signed at [[Moscow]] on 6 December 1940.<ref>National Archives, document reference FO 371/24856</ref> |
||
The [[Croatian–Romanian–Slovak friendship proclamation]] was created in May 1942 |
The [[Croatian–Romanian–Slovak friendship proclamation]] was created in May 1942 to stop further Hungarian expansion. It can be compared to the [[Little Entente]].<ref>''Third Axis Fourth Ally: Romanian Armed Forces in the European War, 1941–1945'', by Mark Axworthy, Cornel Scafeş and Cristian Crăciunoiu, page 73</ref> |
||
The most difficult foreign policy problem |
The state's most difficult foreign policy problem involved relations with Hungary, which had annexed one-third of Slovakia's territory by the [[First Vienna Award]] of 2 November 1938. Slovakia tried to achieve a revision of the Vienna Award, but Germany did not allow it.{{citation needed|date=July 2011}} There were also constant quarrels concerning Hungary's treatment of Slovaks living in Hungary. |
||
==Characteristics== |
==Characteristics== |
||
[[File:Slovakia borderHungary.png|thumb|Territorial changes of Slovak Republic from 1938 to 1947 (Red indicating areas which became a part of Hungary, due to the [[First Vienna Award]]. Changes on border with Poland are missing)]] |
[[File:Slovakia borderHungary.png|thumb|Territorial changes of Slovak Republic from 1938 to 1947 (Red indicating areas which became a part of Hungary, due to the [[First Vienna Award]]. Changes on the border with Poland are missing)]] |
||
2.6 million people lived within the 1939 borders of the Slovak State, and 85 percent had declared Slovak nationality on the 1938 census. Minorities included Germans (4.8 percent), Czechs (2.9 percent), [[Rusyns]] (2.6 percent), Hungarians (2.1 percent), Jews (1.1 percent), and [[Romani people]] (0.9 percent).{{sfn|Kamenec|2011a|p=175}} Seventy-five percent of Slovaks were Catholics |
2.6 million people lived within the 1939 borders of the Slovak State, and 85 percent had declared Slovak nationality on the 1938 census. Minorities included Germans (4.8 percent), Czechs (2.9 percent), [[Rusyns]] (2.6 percent), Hungarians (2.1 percent), Jews (1.1 percent), and [[Romani people]] (0.9 percent).{{sfn|Kamenec|2011a|p=175}} Seventy-five percent of Slovaks were Catholics. Most of the remainder belonged to the [[Evangelical Church of the Augsburg Confession in Slovakia|Lutheran]] and [[Slovak Greek Catholic Church|Greek Catholic]] churches.{{sfn|Rothkirchen|2001|p=596}} 50% of the population were employed in agriculture. The state was divided in six counties (''[[župa|župy]]''), 58 districts (''[[okres]]y'') and 2659 municipalities. The capital, Bratislava, had over 140,000 inhabitants. |
||
{{Multiple image |
{{Multiple image |
||
| Line 173: | Line 173: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
The state continued the legal system of Czechoslovakia, which was modified only gradually. According to the Constitution of 1939, the "President" (Jozef Tiso) was the head of the state, the "Assembly/Diet of the Slovak Republic" elected for five years was the highest legislative body (no general elections took place, however), and the "State Council" performed the duties of a senate. The government |
The state continued the legal system of Czechoslovakia, which was modified only gradually. According to the Constitution of 1939, the "President" (Jozef Tiso) was the head of the state, the "Assembly/Diet of the Slovak Republic" elected for five years, was the highest legislative body (no general elections took place, however), and the "State Council" performed the duties of a senate. The government, which had eight ministries, was the executive body. |
||
[[File:Slovak women performing the Nazi salute.jpg|thumb|Slovak women performing the Nazi salute]] |
[[File:Slovak women performing the Nazi salute.jpg|thumb|Slovak women performing the Nazi salute]] |
||
The Slovak Republic was an authoritarian regime where German pressure resulted in the adoption of many elements of [[Nazism]]. Some historians characterized Tiso's regime as [[Clerical Fascism|clerical fascism]]. The government issued |
The Slovak Republic was an authoritarian regime where German pressure resulted in the adoption of many elements of [[Nazism]]. Some historians characterized Tiso's regime as [[Clerical Fascism|clerical fascism]]. The government issued many [[antisemitism|antisemitic]] laws prohibiting the [[Jews]] from participation in public life and later supported their deportation to [[concentration camp]]s erected by Germany on [[Occupation of Poland (1939–1945)|occupied Polish territory]]. |
||
The only political parties permitted were the dominant [[Hlinka's Slovak People's Party]] and two smaller openly fascist parties, these being the [[Hungarian National Party (Czechoslovakia)|Hungarian National Party]] which represented the Hungarian minority and the [[German Party (Slovakia)|German Party]] which represented the [[Carpathian Germans|German minority]]. However, those two parties formed part of a coalition with the Hlinka's Slovak People's Party; for all intents and purposes, Slovakia was a one-party state. |
The only political parties permitted were the dominant [[Hlinka's Slovak People's Party]] and two smaller openly fascist parties, these being the [[Hungarian National Party (Czechoslovakia)|Hungarian National Party]] which represented the Hungarian minority and the [[German Party (Slovakia)|German Party]] which represented the [[Carpathian Germans|German minority]]. However, those two parties formed part of a coalition with the Hlinka's Slovak People's Party; for all intents and purposes, Slovakia was a one-party state. |
||
The state advocated excluding women from public sphere and politics. While promoting "natural" maternal duties of women, the regime aimed to restrict women's space to the privacy of family life.<ref>Nešťáková, Denisa (2023). Be Fruitful and Multiply. Slovakia's Family Planning Under Three Regimes (1918-1965), Marburg. https://bam-mr.buchkatalog.de/be-fruitful-and-multiply-9783879694853</ref> Slovakia's pro-natalist programs limited access to previously available birth-control methods |
The state advocated excluding women from the public sphere and politics. While promoting "natural" maternal duties of women, the regime aimed to restrict women's space to the privacy of family life.<ref>Nešťáková, Denisa (2023). Be Fruitful and Multiply. Slovakia's Family Planning Under Three Regimes (1918-1965), Marburg. https://bam-mr.buchkatalog.de/be-fruitful-and-multiply-9783879694853</ref> Slovakia's pro-natalist programs limited access to previously available birth-control methods and introduced harsher punishments for already criminalized abortions.<ref>Denisa Nešťáková (2023) In the Name of Helping Women: Women Against the Family Policy of the Slovak State, Central Europe, 21:2, 78-96, DOI: 10.1080/14790963.2023.2294409</ref> |
||
==Leaders and politicians== |
==Leaders and politicians== |
||
| Line 224: | Line 224: | ||
[[File:Alexander Mach Wilhelm Frick 1942.jpg|thumb|Commander of Hlinka Guard Interior Minister [[Alexander Mach]] and German Interior Minister [[Wilhelm Frick]] visit in [[Nazi Germany]]]] |
[[File:Alexander Mach Wilhelm Frick 1942.jpg|thumb|Commander of Hlinka Guard Interior Minister [[Alexander Mach]] and German Interior Minister [[Wilhelm Frick]] visit in [[Nazi Germany]]]] |
||
Although the official policy of the Nazi regime was in |
Although the official policy of the Nazi regime was in favor of an independent Slovak state dependent on Germany and opposed to any annexations of Slovak territory, [[Heinrich Himmler]]'s [[SS]] considered ambitious population policy options concerning the [[Carpathian Germans|German minority of Slovakia]], which numbered circa 130,000 people.<ref name="Longerich">Longerich, P. (2008), ''Heinrich Himmler'', p. 458, {{ISBN|0-19-161989-2}}</ref> |
||
In 1940, [[Günther Pancke]], head of the SS [[RuSHA]] ("Race and Settlement Office") undertook a study trip in Slovak lands where ethnic Germans were present |
In 1940, [[Günther Pancke]], head of the SS [[RuSHA]] ("Race and Settlement Office"), undertook a study trip in Slovak lands where ethnic Germans were present and reported to Himmler that the Slovak Germans were in danger of disappearing.<ref name="Longerich"/> Pancke recommended that action should be taken to fuse the racially valuable part of the Slovaks into the German minority and remove the Romani and Jewish populations.<ref name="Longerich"/> He stated that this would be possible by "excluding" the [[Hungarians in Slovakia|Hungarian minority]] of the country and by settling some 100,000 ethnic German families in Slovakia.<ref name="Longerich"/> The racial core of this Germanization policy was to be gained from the [[Hlinka Guard]], which was to be further integrated into the SS shortly.<ref name="Longerich"/> |
||
==Slovak military== |
==Slovak military== |
||
| Line 239: | Line 239: | ||
===Slovak forces during the campaign against Poland (1939)=== |
===Slovak forces during the campaign against Poland (1939)=== |
||
{{Main|Slovak invasion of Poland|Invasion of Poland}} |
{{Main|Slovak invasion of Poland|Invasion of Poland}} |
||
[[File:Ferdinand Čatloš decorates ethnic German soldiers in the Slovak army 2.png|thumb|Slovak Minister of Defence [[Ferdinand Čatloš]] decorates [[Volksdeutsche|ethnic Germans]] in the Slovak Army after invasion in Poland]] |
[[File:Ferdinand Čatloš decorates ethnic German soldiers in the Slovak army 2.png|thumb|Slovak Minister of Defence [[Ferdinand Čatloš]] decorates [[Volksdeutsche|ethnic Germans]] in the Slovak Army after the invasion in Poland]] |
||
Slovakia was the only Axis nation other than [[Nazi Germany|Germany]] to take part in the [[Invasion of Poland]]. With the impending invasion planned for September 1939, the [[Oberkommando der Wehrmacht]] (OKW) requested the assistance of Slovakia. Although the Slovak military was only six months old, it formed a small mobile [[Field Army Bernolák|combat group]] consisting of |
Slovakia was the only Axis nation other than [[Nazi Germany|Germany]] to take part in the [[Invasion of Poland]]. With the impending invasion planned for September 1939, the [[Oberkommando der Wehrmacht]] (OKW) requested the assistance of Slovakia. Although the Slovak military was only six months old, it formed a small mobile [[Field Army Bernolák|combat group]] consisting of several infantry and artillery battalions. Two combat groups were created for the campaign in Poland alongside the Germans. The first group was a brigade-sized formation that consisted of six infantry battalions, two artillery battalions, and a company of [[combat engineer]]s, all commanded by Antonín Pulanich. The second group was a mobile formation that consisted of two battalions of combined cavalry and motorcycle recon troops along with nine motorized artillery batteries, all commanded by Gustav Malár. The two groups reported to the headquarters of the [[1st Infantry Division (Slovak Republic)|1st]] and 3rd Slovak Infantry Divisions. The two combat groups fought while pushing through the [[Nowy Sącz]] and [[Dukla Pass|Dukla Mountain Passes]], advancing towards [[Dębica]] and [[Tarnów]] in the region of southern Poland. |
||
===Slovak forces during the campaign against the Soviet Union (1941–1944)=== |
===Slovak forces during the campaign against the Soviet Union (1941–1944)=== |
||
| Line 247: | Line 247: | ||
The Slovak military participated in the war on the [[Eastern Front (World War II)|Eastern Front]] against the Soviet Union. The [[Slovak Expeditionary Army Group]] of about 45,000 entered the Soviet Union shortly after the [[Operation Barbarossa|German attack]]. This army lacked logistic and transportation support, so a much smaller unit, the Slovak Mobile Command (Pilfousek Brigade), was formed from units selected from this force; the rest of the Slovak army was relegated to rear-area security duty. The Slovak Mobile Command was attached to the [[17th Army (Wehrmacht)|German 17th Army]] (as was the Hungarian [[Gyorshadtest|Carpathian Group]] also) and shortly thereafter given over to direct German command, the Slovaks lacking the command infrastructure to exercise effective operational control. This unit fought with the 17th Army through July 1941, including at the [[Battle of Uman]].<ref name=Felgrau>{{cite web |url=https://www.feldgrau.com/WW2-Slovakian-Axis-Forces/ |title=Slovak Axis Forces in WWII |author=Jason Pipes |work=Feldgrau |access-date=10 November 2014}}</ref> |
The Slovak military participated in the war on the [[Eastern Front (World War II)|Eastern Front]] against the Soviet Union. The [[Slovak Expeditionary Army Group]] of about 45,000 entered the Soviet Union shortly after the [[Operation Barbarossa|German attack]]. This army lacked logistic and transportation support, so a much smaller unit, the Slovak Mobile Command (Pilfousek Brigade), was formed from units selected from this force; the rest of the Slovak army was relegated to rear-area security duty. The Slovak Mobile Command was attached to the [[17th Army (Wehrmacht)|German 17th Army]] (as was the Hungarian [[Gyorshadtest|Carpathian Group]] also) and shortly thereafter given over to direct German command, the Slovaks lacking the command infrastructure to exercise effective operational control. This unit fought with the 17th Army through July 1941, including at the [[Battle of Uman]].<ref name=Felgrau>{{cite web |url=https://www.feldgrau.com/WW2-Slovakian-Axis-Forces/ |title=Slovak Axis Forces in WWII |author=Jason Pipes |work=Feldgrau |access-date=10 November 2014}}</ref> |
||
At the beginning of August 1941, the Slovak Mobile Command was dissolved and instead two infantry divisions were formed from the Slovak Expeditionary Army Group. The Slovak 2nd Division was a [[Security Division (Wehrmacht)|security division]], but the Slovak 1st Division was a front-line unit that fought in the campaigns of 1941 and 1942, reaching the [[Battle of the Caucasus|Caucasus area]] with [[Army Group B]]. The Slovak 1st Division then shared the fate of the German southern forces, losing their heavy equipment in the [[Kuban bridgehead]], then being badly mangled near [[Melitopol]] in southern Ukraine. In June 1944, the remnant of the division, no longer considered fit for combat due to low morale, was disarmed and the personnel assigned to construction work |
At the beginning of August 1941, the Slovak Mobile Command was dissolved, and instead, two infantry divisions were formed from the Slovak Expeditionary Army Group. The Slovak 2nd Division was a [[Security Division (Wehrmacht)|security division]], but the Slovak 1st Division was a front-line unit that fought in the campaigns of 1941 and 1942, reaching the [[Battle of the Caucasus|Caucasus area]] with [[Army Group B]]. The Slovak 1st Division then shared the fate of the German southern forces, losing their heavy equipment in the [[Kuban bridgehead]], then being badly mangled near [[Melitopol]] in southern Ukraine. In June 1944, the remnant of the division, no longer considered fit for combat due to low morale, was disarmed, and the personnel were assigned to construction work. This fate had already befallen the Slovak 2nd Division earlier for the same reason.<ref name=Felgrau/> |
||
===Slovak National Uprising (1944)=== |
===Slovak National Uprising (1944)=== |
||
| Line 254: | Line 254: | ||
In 1944, during the Slovak National Uprising, many Slovak units sided with the Slovak resistance and rebelled against Tiso's collaborationist government, while others helped German forces put the uprising down. |
In 1944, during the Slovak National Uprising, many Slovak units sided with the Slovak resistance and rebelled against Tiso's collaborationist government, while others helped German forces put the uprising down. |
||
This resistance movement was represented mainly by members of the [[Democratic Party (Slovakia, 1944)|Democratic Party]], [[Czech Social Democratic Party|social democrat]]s, and [[Communist Party of Slovakia (1939)|communists]]. It was launched on 29 August 1944 from [[Banská Bystrica]] in an attempt to resist German troops that had occupied Slovak territory and to overthrow the [[collaborationist]] government of [[Jozef Tiso]].<ref>{{Cite web |title=The Slovak National Uprising |url=https://enrs.eu/article/the-slovak-national-uprising |website=ENRS}}</ref> Although |
This resistance movement was represented mainly by members of the [[Democratic Party (Slovakia, 1944)|Democratic Party]], [[Czech Social Democratic Party|social democrat]]s, and [[Communist Party of Slovakia (1939)|communists]]. It was launched on 29 August 1944 from [[Banská Bystrica]] in an attempt to resist German troops that had occupied Slovak territory and to overthrow the [[collaborationist]] government of [[Jozef Tiso]].<ref>{{Cite web |title=The Slovak National Uprising |url=https://enrs.eu/article/the-slovak-national-uprising |website=ENRS}}</ref> Although German forces largely defeated the resistance, guerrilla operations continued their efforts in the mountains. |
||
In retaliation, [[Einsatzgruppe H]] and the [[Hlinka Guard Emergency Divisions]] executed many Slovaks suspected of aiding the rebels as well as Jews who had avoided deportation until then, and destroyed 93 villages on suspicion of [[collaboration]]. Several villages were burned to the ground and all their inhabitants were murdered, as in [[Ostrý Grúň]] and [[Kľak]] (21 January 1945) or [[Kalište (Slovakia)|Kalište]] (18 March 1945). A later estimate of the death toll was 5,304 and authorities discovered 211 [[mass grave]]s that resulted from those atrocities. The largest executions occurred in [[Kremnička]] (747 killed, mostly Jews and Roma) and [[Nemecká]] (900 killed). |
In retaliation, [[Einsatzgruppe H]] and the [[Hlinka Guard Emergency Divisions]] executed many Slovaks suspected of aiding the rebels as well as Jews who had avoided deportation until then, and destroyed 93 villages on suspicion of [[collaboration]]. Several villages were burned to the ground, and all their inhabitants were murdered, as in [[Ostrý Grúň]] and [[Kľak]] (21 January 1945) or [[Kalište (Slovakia)|Kalište]] (18 March 1945). A later estimate of the death toll was 5,304, and authorities discovered 211 [[mass grave]]s that resulted from those atrocities. The largest executions occurred in [[Kremnička]] (747 killed, mostly Jews and Roma) and [[Nemecká]] (900 killed). |
||
==Hlinka Guard== |
==Hlinka Guard== |
||
| Line 262: | Line 262: | ||
[[File:Member of the Hlinka Guard.jpg|thumb|170px|left|Hlinka Guard flag bearer]] |
[[File:Member of the Hlinka Guard.jpg|thumb|170px|left|Hlinka Guard flag bearer]] |
||
The Hlinka Guard was a paramilitary organization of the [[Hlinka's Slovak People's Party]]. It was created in 1938 and it was built according to the Nazi model. Even though there was an attempt to establish it as an organization with |
The Hlinka Guard was a paramilitary organization of the [[Hlinka's Slovak People's Party]]. It was created in 1938, and it was built according to the Nazi model. Even though there was an attempt to establish it as an organization with compulsory membership for all adult citizens (except Jews) in 1939, this idea was soon changed, and membership in the Guard was voluntary. |
||
The Hlinka Guard |
The Hlinka Guard was Slovakia's state police and most willingly helped Hitler with his plans. It operated against [[Jew]]s, [[Czech people|Czech]]s, [[Hungarian people|Hungarian]]s, the [[Left-wing politics|Left]], and the opposition. By a [[decree]] issued on October 29, 1938, the Hlinka Guard was designated as the only body authorized to give its members [[paramilitary]] training, and it was this decree that established its formal status in the country. Hlinka guardsmen wore black uniforms and a cap shaped like a boat, with a woolen pompom on top, and they used the raised-arm salute. The official salute was "[[Na stráž]]!" ("On guard!"). |
||
{{Multiple image |
{{Multiple image |
||
| Line 277: | Line 277: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
A small group called Náš Boj (Our Struggle), which operated under SS auspices, was the most radical element in the guard. Throughout its |
A small group called Náš Boj (Our Struggle), which operated under SS auspices, was the most radical element in the guard. Throughout its existence, the Hlinka Guard competed with the Hlinka party for primacy in ruling the country. After the anti-Nazi [[Slovak National Uprising]] was crushed in August 1944, the SS took over and shaped the Hlinka Guard to suit its purposes. Special units of the guard ([[Hlinka Guard Emergency Divisions]] – POHG) were employed against partisans and Jews. |
||
The Hlinka Guard was known for its participation in the Holocaust in Slovakia |
The Hlinka Guard was known for its participation in the Holocaust in Slovakia; its members appropriated Jewish property and rounded up Jews for deportation. In 1942, the guard was involved in the [[List of Holocaust transports from Slovakia|deportation of almost 60,000 Slovak Jews to occupied Poland]]. |
||
The Hlinka Youth was also an |
The Hlinka Youth was also an organization subordinated to the Hlinka's Slovak People's Party. It was formed as a single nationwide organization in 1938. Initially, it was just for boys, but later, there was also a chapter for girls. |
||
==The Holocaust== |
==The Holocaust== |
||
{{Main|The Holocaust in Slovakia}} |
{{Main|The Holocaust in Slovakia}} |
||
[[File:"Nebuď služobníkom žida"—Slovak propaganda poster.jpg|thumb|170px|left|A Slovak propaganda poster, "Do not be a servant to the Jew"]] |
[[File:"Nebuď služobníkom žida"—Slovak propaganda poster.jpg|thumb|170px|left|A Slovak propaganda poster, "Do not be a servant to the Jew"]] |
||
Soon after independence and along with the mass exile and deportation of Czechs, the Slovak Republic began a series of measures aimed against the Jews in the country. The Hlinka's Guard began to attack Jews, and the "[[Anti-Jewish laws#Slovakia|Jewish Code]]" was passed in September 1941. Resembling the [[Nuremberg Laws]], the code required Jews to wear a [[Yellow badge|yellow armband]] |
Soon after independence and along with the mass exile and deportation of Czechs, the Slovak Republic began a series of measures aimed against the Jews in the country. The Hlinka's Guard began to attack Jews, and the "[[Anti-Jewish laws#Slovakia|Jewish Code]]" was passed in September 1941. Resembling the [[Nuremberg Laws]], the code required Jews to wear a [[Yellow badge|yellow armband]] and banned them from intermarriage and many jobs. By October 1941, the Slovak Republic had expelled 15,000 Jews from Bratislava, sending many to labor camps. |
||
The Slovak Republic was one of the countries that agreed to deport its Jews as part of the Nazi [[Final Solution]]. |
The Slovak Republic was one of the countries that agreed to deport its Jews as part of the Nazi [[Final Solution]]. Initially, the Slovak government tried to make a deal with Germany in October 1941 to deport its Jews as a substitute for providing Slovak workers to help the war effort. After the [[Wannsee Conference]], the Germans agreed to the Slovak proposal, and a deal was reached where the Slovak Republic would pay for each Jew deported, and, in return, Germany promised that the Jews would never return to the republic. The initial terms were for "20,000 young, strong Jews", but the Slovak government quickly agreed to a German proposal to deport the entire population for "evacuation to territories in the East" meaning to [[Auschwitz-Birkenau]].<ref name="HEART">{{cite web |url=http://www.holocaustresearchproject.org/nazioccupation/slovakjews.html |publisher=Holocaust Research Project.org |title=The Fate of the Slovak Jews |author1=Branik Ceslav |author2=Carmelo Lisciotto |website=Holocaust Education & Archive Research Team |year=2008 |access-date=20 January 2016}}</ref> |
||
[[File:Alexander Mach Slovakia1.jpg|thumb|[[Hlinka Guard]]]] |
[[File:Alexander Mach Slovakia1.jpg|thumb|[[Hlinka Guard]]]] |
||
The deportations of Jews from Slovakia started on 25 March 1942 |
The deportations of Jews from Slovakia started on 25 March 1942 but halted on 20 October 1942 after a group of Jewish citizens, led by [[Gisi Fleischmann]] and Rabbi [[Michael Ber Weissmandl]], built a coalition of concerned officials from the [[Roman Curia|Vatican]] and the government, and, through a mix of bribery and negotiation, was able to stop the process. By then, however, some 58,000 Jews had already been deported, primarily to [[Auschwitz concentration camp|Auschwitz]]. Slovak government officials filed complaints against Germany when it became clear that Germany had gassed many of the previously deported Slovak Jews in mass executions.<ref name="HEART"/> |
||
Jewish deportations resumed on 30 September 1944, when the Republic lost independence to a complete German occupation due to the Nazis' concern that the [[Soviet Union|Soviet]] army had reached the Slovak border, and the [[Slovak National Uprising]] began. During the German occupation, another 13,500 Jews were deported and 5,000 were imprisoned. Deportations continued until 31 March 1945. In all, German and Slovak authorities deported about 70,000 Jews from Slovakia; about 65,000 of them were murdered or died in concentration camps. The overall figures are inexact, partly because many Jews did not identify themselves |
Jewish deportations resumed on 30 September 1944, when the Republic lost independence to a complete German occupation due to the Nazis' concern that the [[Soviet Union|Soviet]] army had reached the Slovak border, and the [[Slovak National Uprising]] began. During the German occupation, another 13,500 Jews were deported, and 5,000 were imprisoned. Deportations continued until 31 March 1945. In all, German and Slovak authorities deported about 70,000 Jews from Slovakia; about 65,000 of them were murdered or died in concentration camps. The overall figures are inexact, partly because many Jews did not identify themselves. Still, one 2006 estimate is that approximately 105,000 Slovak Jews, or 77% of their pre-war population, died during the war.<ref>{{cite web|author=Rebekah Klein-Pejšová|title=An overview of the history of Jews in Slovakia|work=Slovak Jewish Heritage|publisher=Synagoga Slovaca|year=2006|url=http://www.slovak-jewish-heritage.org/history-of-jews-in-slovakia.php|access-date=2007-08-02}}</ref> |
||
==End== |
==End== |
||
| Line 307: | Line 307: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
Bratislava |
Bratislava was often bombarded by the [[Allies of World War II|Allies]]. Major air raids included the bombing of Bratislava and its refinery [[Slovnaft|Apollo]] on June 16, 1944, by American [[Consolidated B-24 Liberator|B-24 bombers]] of the [[Fifteenth Air Force#World War II|Fifteenth Air Force]] with 181 victims.<ref>{{cite web |title=Bratislava in World War 2|date=August 23, 2016 |url=https://www.bratislavashootingclub.com/bratislava-in-world-war-2/|publisher=Bratislava Shooting Club|access-date=2020-07-21}}</ref> [[Bombardment group]] attacked in four waves with overall 158 planes. |
||
After the anti-Nazi [[Slovak National Uprising]] in August 1944, the Germans occupied the country (from October 1944), which thereby lost much of its independence. The German troops were gradually pushed out by the [[Red Army]], by [[Romania]]n and by Czechoslovak |
After the anti-Nazi [[Slovak National Uprising]] in August 1944, the Germans occupied the country (from October 1944), which thereby lost much of its independence. The German troops were gradually pushed out by the [[Red Army]], by [[Romania]]n, and by Czechoslovak soldiers coming from the east. The liberated territories again became ''[[de facto]]'' part of Czechoslovakia. |
||
The First Slovak Republic ceased to exist ''de facto'' on 4 April 1945 when the [[Red Army|Soviet Red Army]] [[2nd Ukrainian Front]] captured Bratislava during [[Bratislava–Brno offensive]] and occupied all of Slovakia.<ref name="WWII">{{cite web|publisher=City of Bratislava |url=http://www.visit.bratislava.sk/en/vismo/dokumenty2.asp?id_org=700014&id=1014&p1=1578 |title=History – Wartime Bratislava |year=2005 |access-date=May 15, 2007 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070224024210/http://www.visit.bratislava.sk/en/vismo/dokumenty2.asp?id_org=700014&id=1014&p1=1578 |archive-date=February 24, 2007}}</ref><ref>Kováč et al., "Kronika Slovenska 2", p. 300</ref> ''[[De jure]]'' it ceased to exist when the exiled Slovak government capitulated to General [[Walton Walker]] leading the [[XX Corps (United States)|XX Corps]] of the [[3rd US Army]] on 8 May 1945 in the [[Austria]]n town of [[Kremsmünster]]. In summer 1945, the captured former president and members of the former government were handed over to Czechoslovak authorities. |
The First Slovak Republic ceased to exist ''de facto'' on 4 April 1945 when the [[Red Army|Soviet Red Army]] [[2nd Ukrainian Front]] captured Bratislava during [[Bratislava–Brno offensive]] and occupied all of Slovakia.<ref name="WWII">{{cite web|publisher=City of Bratislava |url=http://www.visit.bratislava.sk/en/vismo/dokumenty2.asp?id_org=700014&id=1014&p1=1578 |title=History – Wartime Bratislava |year=2005 |access-date=May 15, 2007 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070224024210/http://www.visit.bratislava.sk/en/vismo/dokumenty2.asp?id_org=700014&id=1014&p1=1578 |archive-date=February 24, 2007}}</ref><ref>Kováč et al., "Kronika Slovenska 2", p. 300</ref> ''[[De jure]]'' it ceased to exist when the exiled Slovak government capitulated to General [[Walton Walker]] leading the [[XX Corps (United States)|XX Corps]] of the [[3rd US Army]] on 8 May 1945 in the [[Austria]]n town of [[Kremsmünster]]. In the summer of 1945, the captured former president and members of the former government were handed over to Czechoslovak authorities. |
||
Several prominent Slovak politicians escaped to [[Neutral powers during World War II|neutral countries]]. Following his captivity, the deposed president Jozef Tiso authorized the former foreign minister [[Ferdinand Ďurčanský]] as his successor. Ďurčanský, Tiso's personal secretary Karol Murín, and cousin Fraňo Tiso were appointed by ex-president Tiso as the representatives of the Slovak nation |
Several prominent Slovak politicians escaped to [[Neutral powers during World War II|neutral countries]]. Following his captivity, the deposed president Jozef Tiso authorized the former foreign minister [[Ferdinand Ďurčanský]] as his successor. Ďurčanský, Tiso's personal secretary Karol Murín, and cousin Fraňo Tiso were appointed by ex-president Tiso as the representatives of the Slovak nation; however, they failed to create a [[government-in-exile]] as no country recognized them. In the 1950s, fellow Slovak nationalists established the Slovak Action Committee (later Slovak Liberation Committee), which unsuccessfully advocated the restoration of the independent Slovak State and the renewal of war against the Soviet Union. After the [[dissolution of Czechoslovakia]] and the creation of the modern [[Slovakia|Slovak republic]], the Slovak Liberation Committee proclaimed Tiso's authorization as obsolete. |
||
[[File:Nastupeni povstalci.jpg|thumb|Troops of Slovak anti-Nazi [[resistance movement]] during the [[Slovak National Uprising]] in 1944]] |
[[File:Nastupeni povstalci.jpg|thumb|Troops of Slovak anti-Nazi [[resistance movement]] during the [[Slovak National Uprising]] in 1944]] |
||
At the end of the war, Vojtech Tuka suffered a stroke which confined him to a wheelchair |
At the end of the war, Vojtech Tuka suffered a stroke which confined him to a wheelchair; he emigrated together with his wife, nursing attendants, and personal doctor to [[Austria]], where he was arrested by Allied troops following the capitulation of Germany and handed over to the officials of the renewed Czechoslovakia. Following a brief trial, Vojtech Tuka was executed by hanging on 20 August 1946. |
||
Jozef Tiso was sentenced to death, |
Jozef Tiso was sentenced to death, deprivation of his civil rights, and confiscation of all of his property.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://karolveres.szm.com/DEJ/pramene/procesza3.htm|title=Proces s dr.J Tisom - VÝPIS Z ROZSUDKU spracovaný obhajcom E. Zabkayom|website=karolveres.szm.com|access-date=20 February 2017}}</ref> Tiso appealed to the Czechoslovak president [[Edvard Beneš]] and expected a reprieve; his prosecutor had recommended clemency. However, no reprieve was forthcoming.{{sfn|Ward|2013|pp=264–5}} Wearing his clerical outfit, Tiso was [[hanging|hanged]] in [[Bratislava]] on 18 April 1947. The Czechoslovak government buried him secretly to avoid having his grave become a shrine,{{sfn|Ward|2013|p=266}} but far-right followers of Tiso soon identified the grave in the St Martin cemetery in Bratislava as his. Decades later, after a DNA test in April 2008 that confirmed it, the body of Tiso was exhumed and buried in [[St. Emmeram's Cathedral, Nitra|St Emmeram's Cathedral]] in [[Nitra]], in accordance with canon law.<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://www.cas.sk/clanok/93932/jozefa-tisa-pochovali-v-hrobke-na-nitrianskom-hrade/|title=Jozefa Tisa pochovali v hrobke na Nitrianskom hrade|newspaper=Nový Čas|access-date=20 February 2017|language=sk}} https://www.vatican.va/archive/cod-iuris-canonici/eng/documents/cic_lib4-cann1166-1190_en.html</ref> |
||
==Legacy== |
==Legacy== |
||
Some Slovak nationalists, such as the [[People's Party Our Slovakia]], celebrate March 14 as the anniversary of Slovak independence |
Some Slovak nationalists, such as the [[People's Party Our Slovakia]], celebrate March 14 as the anniversary of Slovak independence. However, January 1 (the date of the [[Velvet Divorce]]) is the official independence day of modern [[Slovak Republic]].<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Nedelsky |first1=Nadya |title="The Struggle for the Memory of the Nation": Post-Communist Slovakia and its World War II Past |journal=Human Rights Quarterly |date=November 10, 2016 |volume=38 |issue=4 |pages=969–992 |doi=10.1353/hrq.2016.0053 |s2cid=151419238 |url=https://muse.jhu.edu/article/636566 |language=en |issn=1085-794X}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=Kotleba: Slovak Extremist Who Made Far Right Fashionable |url=https://balkaninsight.com/2020/02/26/kotleba-slovak-extremist-who-made-far-right-fashionable/ |access-date=19 April 2020 |work=Balkan Insight |date=26 February 2020}}</ref> The issue of March 14 commemorations divided the [[Christian Democratic Movement]] in the early 1990s.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Cohen |first1=Shari J. |title=Politics without a Past: The Absence of History in Postcommunist Nationalism |date=1999 |publisher=Duke University Press |isbn=978-0-8223-9067-1 |page=238 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=f7stDlDUUYcC&q=14+March+commemoration+slovakia&pg=PA238 |language=en}}</ref> |
||
Members of the far-right in admiration of Tiso created a memorial grave in [[National Cemetery in Martin|Martin cemetery]] in October of 2008 to commemorate Tiso.<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://www.cas.sk/clanok/109519/skupina-ludi-spominala-na-slovensky-stat-pri-tisovom-hrobe/|title=Skupina ľudí spomínala na Slovenský štát pri Tisovom hrobe|last=Azet.sk|newspaper=Nový Čas|access-date=20 February 2017|language=sk}}</ref> It has since been used as an occasional gathering place for many far-right groups, including the [[People's Party Our Slovakia]]. Ultranationalist propaganda proclaims Tiso as a "[[martyr]]" who "sacrificed his life for his belief and nation" |
Members of the far-right in admiration of Tiso created a memorial grave in [[National Cemetery in Martin|Martin cemetery]] in October of 2008 to commemorate Tiso.<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://www.cas.sk/clanok/109519/skupina-ludi-spominala-na-slovensky-stat-pri-tisovom-hrobe/|title=Skupina ľudí spomínala na Slovenský štát pri Tisovom hrobe|last=Azet.sk|newspaper=Nový Čas|access-date=20 February 2017|language=sk}}</ref> It has since been used as an occasional gathering place for many far-right groups, including the [[People's Party Our Slovakia]]. Ultranationalist propaganda proclaims Tiso as a "[[martyr]]" who "sacrificed his life for his belief and nation" and so tries to paint him as an innocent victim of communism and a saint.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.jozeftiso.sk/|title=Jozef Tiso. Mučeník viery katolíckej a národa slovenského - Jozef Tiso. Mučeník viery katolíckej a národa slovenského|website=www.jozeftiso.sk|access-date=20 February 2017}}</ref> |
||
== See also == |
== See also == |
||
Revision as of 20:01, 16 May 2024
Slovak Republic Slovenská republika | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1939–1945 | |||||||||
| Motto: Verní sebe, svorne napred! (English: "Faithful to Ourselves, Together Ahead!") | |||||||||
| Anthem: Hej, Slováci (English: "Hey, Slovaks") | |||||||||
 The Slovak Republic in 1942 | |||||||||
| Status | Client state of Germany [a] | ||||||||
| Capital and largest city | Bratislava 48°09′N 17°07′E / 48.150°N 17.117°E | ||||||||
| Common languages | Slovak, German | ||||||||
| Ethnic groups | |||||||||
| Religion | Roman Catholicism (state religion)[5] | ||||||||
| Demonym(s) | Slovak | ||||||||
| Government | Clerical fascist one-party corporate state[6] under a totalitarian dictatorship | ||||||||
| President | |||||||||
• 1939–1945 | Jozef Tiso | ||||||||
| Prime Minister | |||||||||
• 1939 | Jozef Tiso | ||||||||
• 1939–1944 | Vojtech Tuka | ||||||||
• 1944–1945 | Štefan Tiso | ||||||||
| Historical era | World War II | ||||||||
| 14 March 1939 | |||||||||
| 23–31 March 1939 | |||||||||
| 21 July 1939 | |||||||||
| 1–16 September 1939 | |||||||||
| 28 July 1940 | |||||||||
| 24 November 1940 | |||||||||
| 22 June 1941 | |||||||||
| 29 August 1944 | |||||||||
| 4 April 1945 | |||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
• Total | 38,055[7] km2 (14,693 sq mi) | ||||||||
| Population | |||||||||
• Estimate | 2,655,053[8] | ||||||||
| Currency | Slovak koruna (Ks) | ||||||||
| Driving side | right | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | Slovakia Poland | ||||||||
The (First) Slovak Republic (Slovak: (Prvá) Slovenská republika), otherwise known as the Slovak State (Slovenský štát), was a partially-recognized client state of Nazi Germany which existed between 14 March 1939 and 4 April 1945 in Central Europe. The Slovak part of Czechoslovakia declared independence with German support one day before the German occupation of Bohemia and Moravia. It controlled most of the territory of present-day Slovakia, without its current southern parts, which were ceded by Czechoslovakia to Hungary in 1938. Slovakia had been a formally independent state for the first time in history. Bratislava was declared the capital city.
A one-party state governed by the far-right Hlinka's Slovak People's Party, the Slovak Republic is primarily known for its collaboration with Nazi Germany, which included sending troops to the invasion of Poland in September 1939 and the Soviet Union in 1941. In 1940, the country joined the Axis when its leaders signed the Tripartite Pact.
In 1942, the country deported 58,000 Jews (two-thirds of the Slovak Jewish population) to German-occupied Poland, paying Germany 500 Reichsmarks each. After an increase in the activity of anti-Nazi Slovak partisans, Germany invaded Slovakia, triggering a significant uprising. The Slovak Republic was abolished after the Soviet occupation in 1945, and its territory was reintegrated into the recreated Third Czechoslovak Republic.
The current Slovak Republic does not consider itself a successor state of the wartime Slovak Republic, instead a successor to the Czechoslovak Federal Republic. However, some nationalists celebrate 14 March as a day of independence.
Name
The official name of the country was the Slovak State (Slovak: Slovenský štát) from 14 March to 21 July 1939 (until the adoption of the Constitution), and the Slovak Republic (Slovak: Slovenská Republika) from 21 July 1939 to its end in April 1945.
The country is often referred to historically as the First Slovak Republic (Slovak: prvá Slovenská Republika) to distinguish it from the contemporary (Second) Slovak Republic, Slovakia, which is not considered its legal successor state. "Slovak State" was used colloquially, but "First Slovak Republic" was used even in encyclopedias written during the post-war Communist period.[9][10]
Creation

After the Munich Betrayal, Slovakia gained autonomy inside Czecho-Slovakia (as former Czechoslovakia had been renamed) and lost its southern territories to Hungary under the First Vienna Award. As Hitler was preparing a mobilization into Czech territory and the creation of the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia, he had various plans for Slovakia. The Hungarians initially misinformed German officials that the Slovaks wanted to join Hungary. Germany decided to make Slovakia a separate puppet state under German influence and a potential strategic base for German attacks on Poland and other regions.
On 13 March 1939, Hitler invited Monsignor Jozef Tiso (the Slovak ex-prime minister who had been deposed by Czechoslovak troops several days earlier) to Berlin and urged him to proclaim Slovakia's independence. Hitler added that if Tiso had not consented, he would have allowed events in Slovakia to take place effectively, leaving it to the mercies of Hungary and Poland. During the meeting, Joachim von Ribbentrop passed on a report claiming that Hungarian troops were approaching the Slovak borders. Tiso refused to make such a decision himself, after which he was allowed by Hitler to organize a meeting of the Slovak parliament ("Diet of the Slovak Land"), which would approve Slovakia's independence.

On 14 March, the Slovak parliament convened and heard Tiso's report on his discussion with Hitler and a possible declaration of independence. Some of the deputies were skeptical of making such a move, among other reasons, because some worried that the Slovak state would be too small and with a strong Hungarian minority.[11] The debate was quickly brought to a head when Franz Karmasin, leader of the German minority in Slovakia, said that any delay in declaring independence would result in Slovakia being divided between Hungary and Germany. Under these circumstances, Parliament unanimously voted to secede from Czecho-Slovakia, thus creating the first Slovak state in history.[11] Jozef Tiso was appointed the first Prime Minister of the new republic. The next day, Tiso sent a telegram (composed the previous day in Berlin) announcing Slovakia's independence, asking the Reich to take over the protection of the newly minted state. The request was readily accepted.[12]
Diplomatic recognition
Germany and Italy immediately recognized the emergent Slovak state a few weeks later. Britain and France refused to do so; in March 1939, both powers sent diplomatic notes to Berlin protesting developments in former Czechoslovakia as a breach of the Munich agreement and pledged not to acknowledge the territorial changes. Similar notes – though without reference to Munich – were sent by the USSR and the USA. Some non-Axis states, like Switzerland, Poland, and the Vatican, recognized Slovakia in March and April 1939.
The Great Powers soon changed their position. In May, British diplomacy asked for (and received) a new exequatur for its former consul in Bratislava, which marked de facto recognition of Slovakia. France followed suit in July 1939. However, Czechoslovak legations kept operating in London and Paris. Some international organizations like the League of Nations or the International Labour Union still considered Czechoslovakia their member, but some – like the Universal Postal Union – admitted Slovakia.

Following the outbreak of the Second World War, the British and French consulates in Slovakia were closed, and the territory was declared under occupation. However, in September 1939, the USSR recognized Slovakia, admitted a Slovak representative, and closed the hitherto operational Czechoslovak legation in Moscow. Official Soviet-Slovak diplomatic relations were maintained until the outbreak of the German-Soviet war in 1941, when Slovakia joined the invasion on Germany's side, and the USSR recognized the Czechoslovak government-in-exile; Britain recognized it one year earlier.
In all, 27 states either de iure or de facto recognized Slovakia. They were either Axis countries (like Romania, Finland, Hungary) or Axis-dominated semi-independent states (like Vichy France, Manchukuo)[13] or neutral countries like Lithuania, the Netherlands, and Sweden, as well as some beyond Europe (like Ecuador, Costa Rica, Liberia). In some cases, Czechoslovak legations were closed (e.g., in Switzerland), but some countries opted for a somewhat ambiguous stand. The states that maintained their independence ceased recognizing Slovakia in the late stages of World War II. However, some (e.g., Spain) permitted operations of semi-diplomatic representation until the late 1950s.[14]
The United States never recognized Slovak independence. It remained consistent in their initial approach, as they never recognized the Munich Agreement, the extinction of Czechoslovakia, or any territorial changes made to Czechoslovak territory in the period 1938 – 1939.[15]
International relations

From the beginning, the Slovak Republic was under the influence of Germany. The so-called "protection treaty" (Treaty on the protective relationship between Germany and the Slovak State), signed on 23 March 1939, partially subordinated its foreign, military, and economic policy to that of Germany.[16] The German Wehrmacht established the so-called "Protective Zone" (German: Schutzzone) in Western Slovakia in August 1939.[citation needed]

Following Slovak participation in the invasion of Poland in September 1939, border adjustments increased the Slovak Republic's geographical extent in the areas of Orava and Spiš, absorbing previously Polish-controlled territory.[17]
In July 1940, at the Salzburg Conference, the Germans forced a reshuffle of the Slovak cabinet by threatening to withdraw their protection guarantees.[18]
On 24 November 1940, Slovakia joined the Axis when its leaders signed the Tripartite Pact.
The Slovak-Soviet Treaty of Commerce and Navigation was signed at Moscow on 6 December 1940.[19]
The Croatian–Romanian–Slovak friendship proclamation was created in May 1942 to stop further Hungarian expansion. It can be compared to the Little Entente.[20]
The state's most difficult foreign policy problem involved relations with Hungary, which had annexed one-third of Slovakia's territory by the First Vienna Award of 2 November 1938. Slovakia tried to achieve a revision of the Vienna Award, but Germany did not allow it.[citation needed] There were also constant quarrels concerning Hungary's treatment of Slovaks living in Hungary.
Characteristics
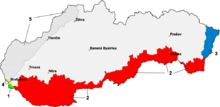
2.6 million people lived within the 1939 borders of the Slovak State, and 85 percent had declared Slovak nationality on the 1938 census. Minorities included Germans (4.8 percent), Czechs (2.9 percent), Rusyns (2.6 percent), Hungarians (2.1 percent), Jews (1.1 percent), and Romani people (0.9 percent).[21] Seventy-five percent of Slovaks were Catholics. Most of the remainder belonged to the Lutheran and Greek Catholic churches.[22] 50% of the population were employed in agriculture. The state was divided in six counties (župy), 58 districts (okresy) and 2659 municipalities. The capital, Bratislava, had over 140,000 inhabitants.
The state continued the legal system of Czechoslovakia, which was modified only gradually. According to the Constitution of 1939, the "President" (Jozef Tiso) was the head of the state, the "Assembly/Diet of the Slovak Republic" elected for five years, was the highest legislative body (no general elections took place, however), and the "State Council" performed the duties of a senate. The government, which had eight ministries, was the executive body.

The Slovak Republic was an authoritarian regime where German pressure resulted in the adoption of many elements of Nazism. Some historians characterized Tiso's regime as clerical fascism. The government issued many antisemitic laws prohibiting the Jews from participation in public life and later supported their deportation to concentration camps erected by Germany on occupied Polish territory.
The only political parties permitted were the dominant Hlinka's Slovak People's Party and two smaller openly fascist parties, these being the Hungarian National Party which represented the Hungarian minority and the German Party which represented the German minority. However, those two parties formed part of a coalition with the Hlinka's Slovak People's Party; for all intents and purposes, Slovakia was a one-party state.
The state advocated excluding women from the public sphere and politics. While promoting "natural" maternal duties of women, the regime aimed to restrict women's space to the privacy of family life.[23] Slovakia's pro-natalist programs limited access to previously available birth-control methods and introduced harsher punishments for already criminalized abortions.[24]
Leaders and politicians
 President
President
- Jozef Tiso (26 October 1939 – 4 April 1945)
 Prime Ministers
Prime Ministers
- Jozef Tiso (14 March 1939 – 26 October 1939)
- Vojtech Tuka (26 October 1939 – 5 September 1944)
- Štefan Tiso (5 September 1944 – 4 April 1945)
 Commanders of German occupation forces
Commanders of German occupation forces
- Ogruf. Gottlob Christian Berger (29 August 1944 – 20 September 1944)
- Ogruf. Hermann Höfle (20 September 1944 – 3 April 1945)
 Commanders of Soviet occupation forces
Commanders of Soviet occupation forces
- G.A. Ivan Yefimovich Petrov (6 August 1944 – 24 March 1945)
- G.A. Andrey Ivanovich Yeryomenko (25 April 1945 – July 1945)
Administrative divisions

The Slovak Republic was divided into 6 counties and 58 districts.[25] The extant population records are from the same time:
- Bratislava county (Bratislavská župa), 3,667 km2, with 455,728 inhabitants, and 6 districts: Bratislava, Malacky, Modra, Senica, Skalica, and Trnava.
- Nitra county (Nitrianska župa), 3,546 km2, with 335,343 inhabitants, and 5 districts: Hlohovec, Nitra, Prievidza, Topoľčany, and Zlaté Moravce.
- Trenčín county (Trenčianska župa), 5,592 km2, with 516,698 inhabitants, and 12 districts: Bánovce nad Bebravou, Čadca, Ilava, Kysucké Nové Mesto, Myjava, Nové Mesto nad Váhom, Piešťany, Považská Bystrica, Púchov, Trenčín, Veľká Bytča, and Žilina.
- Tatra county (Tatranská župa), 9,222 km2, with 463,286 inhabitants, and 13 districts: Dolný Kubín, Gelnica, Kežmarok, Levoča, Liptovský Svätý Mikuláš, Námestovo, Poprad, Ružomberok, Spišská Nová Ves, Spišská Stará Ves, Stará Ľubovňa, Trstená, and Turčiansky Svätý Martin.
- Šariš-Zemplín county (Šarišsko-zemplínska župa), 7,390 km2, with 440,372 inhabitants, and 10 districts: Bardejov, Giraltovce, Humenné, Medzilaborce, Michalovce, Prešov, Sabinov, Stropkov, Trebišov, and Vranov nad Topľou.
- Hron county (Pohronská župa), 8,587 km2, with 443,626 inhabitants, and 12 districts: Banská Bystrica, Banská Štiavnica, Brezno nad Hronom, Dobšiná, Hnúšťa, Kremnica, Krupina, Lovinobaňa, Modrý Kameň, Nová Baňa, Revúca, and Zvolen.
SS plans for Slovakia

Although the official policy of the Nazi regime was in favor of an independent Slovak state dependent on Germany and opposed to any annexations of Slovak territory, Heinrich Himmler's SS considered ambitious population policy options concerning the German minority of Slovakia, which numbered circa 130,000 people.[26]
In 1940, Günther Pancke, head of the SS RuSHA ("Race and Settlement Office"), undertook a study trip in Slovak lands where ethnic Germans were present and reported to Himmler that the Slovak Germans were in danger of disappearing.[26] Pancke recommended that action should be taken to fuse the racially valuable part of the Slovaks into the German minority and remove the Romani and Jewish populations.[26] He stated that this would be possible by "excluding" the Hungarian minority of the country and by settling some 100,000 ethnic German families in Slovakia.[26] The racial core of this Germanization policy was to be gained from the Hlinka Guard, which was to be further integrated into the SS shortly.[26]
Slovak military

War with Hungary (1939)
On 23 March 1939, Hungary, having already occupied Carpatho-Ukraine, attacked from there, and the newly established Slovak Republic was forced to cede 1,697 square kilometres (655 sq mi) of territory with about 70,000 people to Hungary before the onset of World War II.
Slovak forces during the campaign against Poland (1939)

Slovakia was the only Axis nation other than Germany to take part in the Invasion of Poland. With the impending invasion planned for September 1939, the Oberkommando der Wehrmacht (OKW) requested the assistance of Slovakia. Although the Slovak military was only six months old, it formed a small mobile combat group consisting of several infantry and artillery battalions. Two combat groups were created for the campaign in Poland alongside the Germans. The first group was a brigade-sized formation that consisted of six infantry battalions, two artillery battalions, and a company of combat engineers, all commanded by Antonín Pulanich. The second group was a mobile formation that consisted of two battalions of combined cavalry and motorcycle recon troops along with nine motorized artillery batteries, all commanded by Gustav Malár. The two groups reported to the headquarters of the 1st and 3rd Slovak Infantry Divisions. The two combat groups fought while pushing through the Nowy Sącz and Dukla Mountain Passes, advancing towards Dębica and Tarnów in the region of southern Poland.
Slovak forces during the campaign against the Soviet Union (1941–1944)

The Slovak military participated in the war on the Eastern Front against the Soviet Union. The Slovak Expeditionary Army Group of about 45,000 entered the Soviet Union shortly after the German attack. This army lacked logistic and transportation support, so a much smaller unit, the Slovak Mobile Command (Pilfousek Brigade), was formed from units selected from this force; the rest of the Slovak army was relegated to rear-area security duty. The Slovak Mobile Command was attached to the German 17th Army (as was the Hungarian Carpathian Group also) and shortly thereafter given over to direct German command, the Slovaks lacking the command infrastructure to exercise effective operational control. This unit fought with the 17th Army through July 1941, including at the Battle of Uman.[27]
At the beginning of August 1941, the Slovak Mobile Command was dissolved, and instead, two infantry divisions were formed from the Slovak Expeditionary Army Group. The Slovak 2nd Division was a security division, but the Slovak 1st Division was a front-line unit that fought in the campaigns of 1941 and 1942, reaching the Caucasus area with Army Group B. The Slovak 1st Division then shared the fate of the German southern forces, losing their heavy equipment in the Kuban bridgehead, then being badly mangled near Melitopol in southern Ukraine. In June 1944, the remnant of the division, no longer considered fit for combat due to low morale, was disarmed, and the personnel were assigned to construction work. This fate had already befallen the Slovak 2nd Division earlier for the same reason.[27]
Slovak National Uprising (1944)

In 1944, during the Slovak National Uprising, many Slovak units sided with the Slovak resistance and rebelled against Tiso's collaborationist government, while others helped German forces put the uprising down.
This resistance movement was represented mainly by members of the Democratic Party, social democrats, and communists. It was launched on 29 August 1944 from Banská Bystrica in an attempt to resist German troops that had occupied Slovak territory and to overthrow the collaborationist government of Jozef Tiso.[28] Although German forces largely defeated the resistance, guerrilla operations continued their efforts in the mountains.
In retaliation, Einsatzgruppe H and the Hlinka Guard Emergency Divisions executed many Slovaks suspected of aiding the rebels as well as Jews who had avoided deportation until then, and destroyed 93 villages on suspicion of collaboration. Several villages were burned to the ground, and all their inhabitants were murdered, as in Ostrý Grúň and Kľak (21 January 1945) or Kalište (18 March 1945). A later estimate of the death toll was 5,304, and authorities discovered 211 mass graves that resulted from those atrocities. The largest executions occurred in Kremnička (747 killed, mostly Jews and Roma) and Nemecká (900 killed).
Hlinka Guard

The Hlinka Guard was a paramilitary organization of the Hlinka's Slovak People's Party. It was created in 1938, and it was built according to the Nazi model. Even though there was an attempt to establish it as an organization with compulsory membership for all adult citizens (except Jews) in 1939, this idea was soon changed, and membership in the Guard was voluntary.
The Hlinka Guard was Slovakia's state police and most willingly helped Hitler with his plans. It operated against Jews, Czechs, Hungarians, the Left, and the opposition. By a decree issued on October 29, 1938, the Hlinka Guard was designated as the only body authorized to give its members paramilitary training, and it was this decree that established its formal status in the country. Hlinka guardsmen wore black uniforms and a cap shaped like a boat, with a woolen pompom on top, and they used the raised-arm salute. The official salute was "Na stráž!" ("On guard!").
A small group called Náš Boj (Our Struggle), which operated under SS auspices, was the most radical element in the guard. Throughout its existence, the Hlinka Guard competed with the Hlinka party for primacy in ruling the country. After the anti-Nazi Slovak National Uprising was crushed in August 1944, the SS took over and shaped the Hlinka Guard to suit its purposes. Special units of the guard (Hlinka Guard Emergency Divisions – POHG) were employed against partisans and Jews.
The Hlinka Guard was known for its participation in the Holocaust in Slovakia; its members appropriated Jewish property and rounded up Jews for deportation. In 1942, the guard was involved in the deportation of almost 60,000 Slovak Jews to occupied Poland.
The Hlinka Youth was also an organization subordinated to the Hlinka's Slovak People's Party. It was formed as a single nationwide organization in 1938. Initially, it was just for boys, but later, there was also a chapter for girls.
The Holocaust

Soon after independence and along with the mass exile and deportation of Czechs, the Slovak Republic began a series of measures aimed against the Jews in the country. The Hlinka's Guard began to attack Jews, and the "Jewish Code" was passed in September 1941. Resembling the Nuremberg Laws, the code required Jews to wear a yellow armband and banned them from intermarriage and many jobs. By October 1941, the Slovak Republic had expelled 15,000 Jews from Bratislava, sending many to labor camps.
The Slovak Republic was one of the countries that agreed to deport its Jews as part of the Nazi Final Solution. Initially, the Slovak government tried to make a deal with Germany in October 1941 to deport its Jews as a substitute for providing Slovak workers to help the war effort. After the Wannsee Conference, the Germans agreed to the Slovak proposal, and a deal was reached where the Slovak Republic would pay for each Jew deported, and, in return, Germany promised that the Jews would never return to the republic. The initial terms were for "20,000 young, strong Jews", but the Slovak government quickly agreed to a German proposal to deport the entire population for "evacuation to territories in the East" meaning to Auschwitz-Birkenau.[29]

The deportations of Jews from Slovakia started on 25 March 1942 but halted on 20 October 1942 after a group of Jewish citizens, led by Gisi Fleischmann and Rabbi Michael Ber Weissmandl, built a coalition of concerned officials from the Vatican and the government, and, through a mix of bribery and negotiation, was able to stop the process. By then, however, some 58,000 Jews had already been deported, primarily to Auschwitz. Slovak government officials filed complaints against Germany when it became clear that Germany had gassed many of the previously deported Slovak Jews in mass executions.[29]
Jewish deportations resumed on 30 September 1944, when the Republic lost independence to a complete German occupation due to the Nazis' concern that the Soviet army had reached the Slovak border, and the Slovak National Uprising began. During the German occupation, another 13,500 Jews were deported, and 5,000 were imprisoned. Deportations continued until 31 March 1945. In all, German and Slovak authorities deported about 70,000 Jews from Slovakia; about 65,000 of them were murdered or died in concentration camps. The overall figures are inexact, partly because many Jews did not identify themselves. Still, one 2006 estimate is that approximately 105,000 Slovak Jews, or 77% of their pre-war population, died during the war.[30]
End
Bratislava was often bombarded by the Allies. Major air raids included the bombing of Bratislava and its refinery Apollo on June 16, 1944, by American B-24 bombers of the Fifteenth Air Force with 181 victims.[31] Bombardment group attacked in four waves with overall 158 planes.
After the anti-Nazi Slovak National Uprising in August 1944, the Germans occupied the country (from October 1944), which thereby lost much of its independence. The German troops were gradually pushed out by the Red Army, by Romanian, and by Czechoslovak soldiers coming from the east. The liberated territories again became de facto part of Czechoslovakia.
The First Slovak Republic ceased to exist de facto on 4 April 1945 when the Soviet Red Army 2nd Ukrainian Front captured Bratislava during Bratislava–Brno offensive and occupied all of Slovakia.[32][33] De jure it ceased to exist when the exiled Slovak government capitulated to General Walton Walker leading the XX Corps of the 3rd US Army on 8 May 1945 in the Austrian town of Kremsmünster. In the summer of 1945, the captured former president and members of the former government were handed over to Czechoslovak authorities.
Several prominent Slovak politicians escaped to neutral countries. Following his captivity, the deposed president Jozef Tiso authorized the former foreign minister Ferdinand Ďurčanský as his successor. Ďurčanský, Tiso's personal secretary Karol Murín, and cousin Fraňo Tiso were appointed by ex-president Tiso as the representatives of the Slovak nation; however, they failed to create a government-in-exile as no country recognized them. In the 1950s, fellow Slovak nationalists established the Slovak Action Committee (later Slovak Liberation Committee), which unsuccessfully advocated the restoration of the independent Slovak State and the renewal of war against the Soviet Union. After the dissolution of Czechoslovakia and the creation of the modern Slovak republic, the Slovak Liberation Committee proclaimed Tiso's authorization as obsolete.

At the end of the war, Vojtech Tuka suffered a stroke which confined him to a wheelchair; he emigrated together with his wife, nursing attendants, and personal doctor to Austria, where he was arrested by Allied troops following the capitulation of Germany and handed over to the officials of the renewed Czechoslovakia. Following a brief trial, Vojtech Tuka was executed by hanging on 20 August 1946.
Jozef Tiso was sentenced to death, deprivation of his civil rights, and confiscation of all of his property.[34] Tiso appealed to the Czechoslovak president Edvard Beneš and expected a reprieve; his prosecutor had recommended clemency. However, no reprieve was forthcoming.[35] Wearing his clerical outfit, Tiso was hanged in Bratislava on 18 April 1947. The Czechoslovak government buried him secretly to avoid having his grave become a shrine,[36] but far-right followers of Tiso soon identified the grave in the St Martin cemetery in Bratislava as his. Decades later, after a DNA test in April 2008 that confirmed it, the body of Tiso was exhumed and buried in St Emmeram's Cathedral in Nitra, in accordance with canon law.[37]
Legacy
Some Slovak nationalists, such as the People's Party Our Slovakia, celebrate March 14 as the anniversary of Slovak independence. However, January 1 (the date of the Velvet Divorce) is the official independence day of modern Slovak Republic.[38][39] The issue of March 14 commemorations divided the Christian Democratic Movement in the early 1990s.[40]
Members of the far-right in admiration of Tiso created a memorial grave in Martin cemetery in October of 2008 to commemorate Tiso.[41] It has since been used as an occasional gathering place for many far-right groups, including the People's Party Our Slovakia. Ultranationalist propaganda proclaims Tiso as a "martyr" who "sacrificed his life for his belief and nation" and so tries to paint him as an innocent victim of communism and a saint.[42]
See also
| History of Czechoslovakia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- Slovakia
- Slovakia during World War II
- The Holocaust in Slovakia
- Slovak National Uprising
- Axis powers
- Czechoslovak government-in-exile
- Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia
- Occupation of Czechoslovakia (1938–1945)
- Croatian–Romanian–Slovak friendship proclamation
Notes
- ^ Views differ on Slovakia's relation to Germany. István Deák writes, "Despite the claims of some historians, [Slovakia] functioned not as a puppet state but as Nazi Germany’s first but not last Slavic-speaking military ally".[1] Tatjana Tönsmeyer, who maintains that the puppet-state narrative overstates German influence and understates Slovakia's autonomy, notes that Slovak authorities frequently avoided implementing measures pushed by the Germans when such measures did not suit Slovak priorities. According to German historian Barbara Hutzelmann, "Although the country was not independent, in the full sense of the word, it would be too simplistic to see this German-protected state (Schutzstaat) simply as a 'puppet regime'."[2] Ivan Kamenec, however, emphasizes German influence on Slovak internal and external politics and describes it as a "German satellite".[3]
References
- ^ Deák 2015, pp. 35–36.
- ^ Hutzelmann 2016, p. 168.
- ^ Kamenec 2011a, pp. 180–182.
- ^ "Slovensko v rokoch 1938 – 1945". Museum of the Slovak National Uprising. 1 May 2024.
- ^ Doe, Norman (4 August 2011). Law and Religion in Europe: A Comparative Introduction. OUP Oxford. ISBN 978-0-19-960401-2 – via Google Books.
- ^
Badie, Bertrand; Berg-Schlosser, Dirk; Morlino, Leonardo, eds. (7 September 2011). International Encyclopedia of Political Science. SAGE Publications (published 2011). ISBN 9781483305394. Retrieved 9 September 2020.
... fascist Italy ... developed a state structure known as the corporate state with the ruling party acting as a mediator between 'corporations' making up the body of the nation. Similar designs were quite popular elsewhere in the 1930s. The most prominent examples were Estado Novo in Portugal (1933–1974) and Brazil (1937–1945), the Austrian Standestaat (1934–1938), and authoritarian experiments in Estonia, Romania, and some other countries of East and East-Central Europe,
- ^ "Slovensko v rokoch 1938 – 1945". Museum of the Slovak National Uprising. 1 May 2024.
- ^ "Slovensko v rokoch 1938 – 1945". Museum of the Slovak National Uprising. 1 May 2024.
- ^ Vladár, J. (Ed.), Encyklopédia Slovenska V. zväzok R – Š. Bratislava, Veda, 1981, pp. 330–331
- ^ Plevza, V. (Ed.) Dejiny Slovenského národného povstania 1944 5. zväzok. Bratislava, Nakladateľstvo Pravda, 1985, pp. 484–487
- ^ a b Dominik Jůn interviewing Professor Jan Rychlík (2016). "Czechs and Slovaks - more than just neighbours". Radio Prague. Retrieved 28 October 2016.
- ^ William Shirer, The Rise and Fall of the Third Reich (Touchstone Edition) (New York: Simon & Schuster, 1990)
- ^ Pavol Petruf, Vichy France and the diplomatic recognition of the Slovak Republic, [in:] Historický Časopis 48 (2000), pp. 131-152
- ^ Michal Považan, Slovakia 1939-1945: Statehood and International Recognition, [in:] UNISCI Discussion Papers 36 (2014), pp. 75-78
- ^ "Slovakia 1939 – 1945: Statehood and International Recognition (de iure or de facto statehood?)". Dialnet. 1 May 2024.
- ^ Noack, David X. (4 October 2012). Slowakei – Der mühsame Weg nach Westen. Brennpunkt Osteuropa. Vienna: Promedia (published 2012). pp. 48–50. ISBN 9783853718025. Retrieved 19 April 2022.
- ^ Piotrowski, Tadeusz (1998). Poland's Holocaust: Ethnic Strife, Collaboration with Occupying Forces and Genocide in the Second Republic, 1918-1947. Science Publications. Jefferson, NC: McFarland. p. 294. ISBN 9780786403714. Retrieved 9 February 2017.
Between 1920 and 1924, some areas of Orawa and Spisz fell to Poland, others to Slovakia. With Germany's support, on the basis of the November 1 and 30, 1938 agreements between Poland and Czechoslovakia, Poland annexed 226 square kilometers (and 4,280 people) of Orawa and Spisz. The following year, on the basis of an agreement (November 21, 1939) between Germany and Slovakia, these territories, along with some previously Polish sections of Orawa and Spisz (a total of 752 square kilometers of land with 30,000 people) were transferred to Slovakia.
- ^ Ward 2013, pp. 211–212.
- ^ National Archives, document reference FO 371/24856
- ^ Third Axis Fourth Ally: Romanian Armed Forces in the European War, 1941–1945, by Mark Axworthy, Cornel Scafeş and Cristian Crăciunoiu, page 73
- ^ Kamenec 2011a, p. 175.
- ^ Rothkirchen 2001, p. 596.
- ^ Nešťáková, Denisa (2023). Be Fruitful and Multiply. Slovakia's Family Planning Under Three Regimes (1918-1965), Marburg. https://bam-mr.buchkatalog.de/be-fruitful-and-multiply-9783879694853
- ^ Denisa Nešťáková (2023) In the Name of Helping Women: Women Against the Family Policy of the Slovak State, Central Europe, 21:2, 78-96, DOI: 10.1080/14790963.2023.2294409
- ^ "Slovensko v rokoch 1938 – 1945". Museum of the Slovak National Uprising. 1 May 2024.
- ^ a b c d e Longerich, P. (2008), Heinrich Himmler, p. 458, ISBN 0-19-161989-2
- ^ a b Jason Pipes. "Slovak Axis Forces in WWII". Feldgrau. Retrieved 10 November 2014.
- ^ "The Slovak National Uprising". ENRS.
- ^ a b Branik Ceslav; Carmelo Lisciotto (2008). "The Fate of the Slovak Jews". Holocaust Education & Archive Research Team. Holocaust Research Project.org. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- ^ Rebekah Klein-Pejšová (2006). "An overview of the history of Jews in Slovakia". Slovak Jewish Heritage. Synagoga Slovaca. Retrieved 2 August 2007.
- ^ "Bratislava in World War 2". Bratislava Shooting Club. 23 August 2016. Retrieved 21 July 2020.
- ^ "History – Wartime Bratislava". City of Bratislava. 2005. Archived from the original on 24 February 2007. Retrieved 15 May 2007.
- ^ Kováč et al., "Kronika Slovenska 2", p. 300
- ^ "Proces s dr.J Tisom - VÝPIS Z ROZSUDKU spracovaný obhajcom E. Zabkayom". karolveres.szm.com. Retrieved 20 February 2017.
- ^ Ward 2013, pp. 264–5.
- ^ Ward 2013, p. 266.
- ^ "Jozefa Tisa pochovali v hrobke na Nitrianskom hrade". Nový Čas (in Slovak). Retrieved 20 February 2017. https://www.vatican.va/archive/cod-iuris-canonici/eng/documents/cic_lib4-cann1166-1190_en.html
- ^ Nedelsky, Nadya (10 November 2016). ""The Struggle for the Memory of the Nation": Post-Communist Slovakia and its World War II Past". Human Rights Quarterly. 38 (4): 969–992. doi:10.1353/hrq.2016.0053. ISSN 1085-794X. S2CID 151419238.
- ^ "Kotleba: Slovak Extremist Who Made Far Right Fashionable". Balkan Insight. 26 February 2020. Retrieved 19 April 2020.
- ^ Cohen, Shari J. (1999). Politics without a Past: The Absence of History in Postcommunist Nationalism. Duke University Press. p. 238. ISBN 978-0-8223-9067-1.
- ^ Azet.sk. "Skupina ľudí spomínala na Slovenský štát pri Tisovom hrobe". Nový Čas (in Slovak). Retrieved 20 February 2017.
- ^ "Jozef Tiso. Mučeník viery katolíckej a národa slovenského - Jozef Tiso. Mučeník viery katolíckej a národa slovenského". www.jozeftiso.sk. Retrieved 20 February 2017.
- Sources
- Deák, István (2015) [2013]. Europe on Trial: The Story of Collaboration, Resistance, and Retribution during World War II. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-8133-4790-5.
- Hutzelmann, Barbara (2016). "Slovak Society and the Jews: Attitudes and Patterns of Behaviour". In Bajohr, Frank; Löw, Andrea (eds.). The Holocaust and European Societies: Social Processes and Social Dynamics. London: Springer. pp. 167–185. ISBN 978-1-137-56984-4.
- Kamenec, Ivan (2011). "The Slovak state, 1939–1945". In Teich, Mikuláš; Kováč, Dušan; Brown, Martin D. (eds.). Slovakia in History. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 175–192. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511780141. ISBN 978-1-139-49494-6.
Further reading
- Nedelsky, Nadya (7 January 2003). "The wartime Slovak state: a case study in the relationship between ethnic nationalism and authoritarian patterns of governance". Nations and Nationalism. 7 (2): 215–234. doi:10.1111/1469-8219.00013.
External links
- Client states of Nazi Germany
- Slovakia during World War II
- Slovak National Uprising
- Former countries in Europe
- Former republics
- 1939 in Slovakia
- 1940s in Slovakia
- Military history of Czechoslovakia during World War II
- Eastern European theatre of World War II
- States and territories established in 1939
- States and territories disestablished in 1945
- 20th century in Slovakia
- Politics of Czechoslovakia
- Axis powers
- Christian states
- Totalitarian states
- Fascist states













