Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase: Difference between revisions
→Further reading: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)36222-5 |
Citation bot (talk | contribs) Alter: title, template type. Add: series, chapter, doi-access. Removed parameters. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by AManWithNoPlan | #UCB_toolbar |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Mammalian protein found in Homo sapiens}} |
|||
{{Infobox_gene}} |
{{Infobox_gene}} |
||
'''Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase''' ('''APRTase''') is an [[enzyme]] encoded by the ''APRT'' [[gene]], found in [[humans]] on [[chromosome 16]].<ref name = "Valaperta_2014">{{cite journal | vauthors = Valaperta R, Rizzo V, Lombardi F, Verdelli C, Piccoli M, Ghiroldi A, Creo P, Colombo A, Valisi M, Margiotta E, Panella R, Costa E | title = Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase (APRT) deficiency: identification of a novel nonsense mutation | journal = BMC Nephrology | volume = 15 | pages = 102 | date = 1 July 2014 | pmid = 24986359 | doi = 10.1186/1471-2369-15-102 | pmc=4094445}}</ref> It is part of the Type I PRTase family and is involved in the [[nucleotide salvage]] pathway, which provides an alternative to [[nucleotide]] biosynthesis de novo in humans and most other animals.<ref name = "Silva_2008"/> In parasitic [[protozoa]] such as [[giardia]], APRTase provides the sole mechanism by which |
'''Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase''' ('''APRTase''') is an [[enzyme]] encoded by the ''APRT'' [[gene]], found in [[humans]] on [[chromosome 16]].<ref name = "Valaperta_2014">{{cite journal | vauthors = Valaperta R, Rizzo V, Lombardi F, Verdelli C, Piccoli M, Ghiroldi A, Creo P, Colombo A, Valisi M, Margiotta E, Panella R, Costa E | title = Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase (APRT) deficiency: identification of a novel nonsense mutation | journal = BMC Nephrology | volume = 15 | pages = 102 | date = 1 July 2014 | pmid = 24986359 | doi = 10.1186/1471-2369-15-102 | pmc=4094445 | doi-access = free }}</ref> It is part of the Type I PRTase family and is involved in the [[nucleotide salvage]] pathway, which provides an alternative to [[nucleotide]] biosynthesis de novo in humans and most other animals.<ref name = "Silva_2008"/> In parasitic [[protozoa]] such as [[giardia]], APRTase provides the sole mechanism by which AMP can be produced.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Sarver AE, Wang CC | title = The adenine phosphoribosyltransferase from Giardia lamblia has a unique reaction mechanism and unusual substrate binding properties | journal = The Journal of Biological Chemistry | volume = 277 | issue = 42 | pages = 39973–80 | date = Oct 2002 | pmid = 12171924 | doi = 10.1074/jbc.M205595200 | doi-access = free }}</ref> APRTase deficiency contributes to the formation of kidney stones ([[urolithiasis]]) and to potential [[renal failure|kidney failure]].<ref name ="Shi_2001">{{cite journal | vauthors = Shi W, Tanaka KS, Crother TR, Taylor MW, Almo SC, Schramm VL | title = Structural analysis of adenine phosphoribosyltransferase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae | journal = Biochemistry | volume = 40 | issue = 36 | pages = 10800–9 | date = Sep 2001 | pmid = 11535055 | doi=10.1021/bi010465h}}</ref> |
||
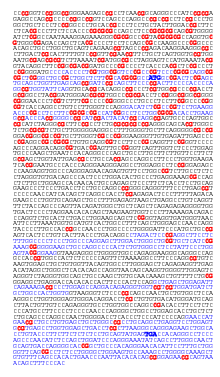
[[File:APRT-CpG.svg|thumb|The APRT gene is constituted by 5 exons (in blue). The start (ATG) and stop (TGA) codons are indicated (bold blue). CpG dinucleotides are emphasized in red. They are more abundant in the upstream region of the gene where they form a [[CpG island]].]] |
|||
== Function == |
== Function == |
||
| Line 10: | Line 13: | ||
[[File:ARPTase Reaction Scheme.png|frame|center|ARPTase catalyzes a phosphoribosyl transfer from PRPP to adenine, forming AMP and releasing pyrophosphate (PPi).]] |
[[File:ARPTase Reaction Scheme.png|frame|center|ARPTase catalyzes a phosphoribosyl transfer from PRPP to adenine, forming AMP and releasing pyrophosphate (PPi).]] |
||
In organisms that can synthesize [[purines]] de novo, the nucleotide salvage pathway provides an alternative that is energetically more efficient. It can salvage adenine from the [[polyamine]] biosynthetic pathway or from dietary sources of purines.<ref name="Silva_2008">{{cite journal | vauthors = Silva CH, Silva M, Iulek J, Thiemann OH | title = Structural complexes of human adenine phosphoribosyltransferase reveal novel features of the APRT catalytic mechanism | journal = Journal of Biomolecular Structure & Dynamics | volume = 25 | issue = 6 | pages = 589–97 | date = Jun 2008 | pmid = 18399692 | doi = 10.1080/07391102.2008.10507205 }}</ref> Although APRTase is functionally redundant in these organisms, it becomes more important during periods of rapid growth, such as embryogenesis and tumor growth.<ref name="Bashor_2002"/> It is constitutively expressed in all mammalian tissue.<ref name = "Silva_2004"/> |
In organisms that can synthesize [[purines]] de novo, the nucleotide salvage pathway provides an alternative that is energetically more efficient. It can salvage adenine from the [[polyamine]] biosynthetic pathway or from dietary sources of purines.<ref name="Silva_2008">{{cite journal | vauthors = Silva CH, Silva M, Iulek J, Thiemann OH | title = Structural complexes of human adenine phosphoribosyltransferase reveal novel features of the APRT catalytic mechanism | journal = Journal of Biomolecular Structure & Dynamics | volume = 25 | issue = 6 | pages = 589–97 | date = Jun 2008 | pmid = 18399692 | doi = 10.1080/07391102.2008.10507205 | s2cid = 40788077 }}</ref> Although APRTase is functionally redundant in these organisms, it becomes more important during periods of rapid growth, such as embryogenesis and tumor growth.<ref name="Bashor_2002"/> It is constitutively expressed in all mammalian tissue.<ref name = "Silva_2004"/> |
||
In [[protozoan]] parasites, the nucleotide salvage pathway provides the sole means for nucleotide synthesis. Since the consequences of APRTase deficiency in humans is comparatively mild and treatable, it may be possible to treat certain [[parasitic infections]] by targeting APRTase function.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Shi W, Sarver AE, Wang CC, Tanaka KS, Almo SC, Schramm VL | title = Closed site complexes of adenine phosphoribosyltransferase from Giardia lamblia reveal a mechanism of ribosyl migration | journal = The Journal of Biological Chemistry | volume = 277 | issue = 42 | pages = 39981–8 | date = Oct 2002 | pmid = 12171925 | doi = 10.1074/jbc.M205596200 }}</ref> |
In [[protozoan]] parasites, the nucleotide salvage pathway provides the sole means for nucleotide synthesis. Since the consequences of APRTase deficiency in humans is comparatively mild and treatable, it may be possible to treat certain [[parasitic infections]] by targeting APRTase function.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Shi W, Sarver AE, Wang CC, Tanaka KS, Almo SC, Schramm VL | title = Closed site complexes of adenine phosphoribosyltransferase from Giardia lamblia reveal a mechanism of ribosyl migration | journal = The Journal of Biological Chemistry | volume = 277 | issue = 42 | pages = 39981–8 | date = Oct 2002 | pmid = 12171925 | doi = 10.1074/jbc.M205596200 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
||
In [[plants]], as in other organisms, ARPTase functions primarily for the synthesis of [[adenylate]]. It has the unique ability to metabolize [[cytokinins]]—a [[plant hormone]] that can exist as a [[base (chemistry)|base]], [[nucleotide]], or [[nucleoside]]—into adenylate nucleotides.<ref name = "Allen_2002">{{cite journal | vauthors = Allen M, Qin W, Moreau F, Moffatt B | title = Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase isoforms of Arabidopsis and their potential contributions to adenine and cytokinin metabolism | journal = Physiologia Plantarum | volume = 115 | issue = 1 | pages = 56–68 | date = May 2002 | pmid = 12010467 | doi=10.1034/j.1399-3054.2002.1150106.x}}</ref> |
In [[plants]], as in other organisms, ARPTase functions primarily for the synthesis of [[adenylate]]. It has the unique ability to metabolize [[cytokinins]]—a [[plant hormone]] that can exist as a [[base (chemistry)|base]], [[nucleotide]], or [[nucleoside]]—into adenylate nucleotides.<ref name = "Allen_2002">{{cite journal | vauthors = Allen M, Qin W, Moreau F, Moffatt B | title = Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase isoforms of Arabidopsis and their potential contributions to adenine and cytokinin metabolism | journal = Physiologia Plantarum | volume = 115 | issue = 1 | pages = 56–68 | date = May 2002 | pmid = 12010467 | doi=10.1034/j.1399-3054.2002.1150106.x}}</ref> |
||
| Line 28: | Line 31: | ||
[[File:Human APRTase, adenine binding site.png|thumb|right|Residues A131, L159, V25, and R27 are important for purine specificity in human APRTase.]] |
[[File:Human APRTase, adenine binding site.png|thumb|right|Residues A131, L159, V25, and R27 are important for purine specificity in human APRTase.]] |
||
The core is highly conserved across many PRTases. The hood, which contains the [[adenine]] [[binding site]], has more variability within the family of enzymes. A 13-residue motif comprises the [[Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate|PRPP]] binding region and involves two adjacent [[acidic]] residues and at least one surrounding [[hydrophobic]] residue.<ref name = "Liu_1990">{{cite journal | vauthors = Liu Q, Hirono S, Moriguchi I | title = Quantitative structure-activity relationships for calmodulin inhibitors | journal = Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin | volume = 38 | issue = 8 | pages = 2184–9 | date = Aug 1990 | pmid = 2279281 | doi=10.1248/cpb.38.2184}}</ref> |
The core is highly conserved across many PRTases. The hood, which contains the [[adenine]] [[binding site]], has more variability within the family of enzymes. A 13-residue motif comprises the [[Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate|PRPP]] binding region and involves two adjacent [[acidic]] residues and at least one surrounding [[hydrophobic]] residue.<ref name = "Liu_1990">{{cite journal | vauthors = Liu Q, Hirono S, Moriguchi I | title = Quantitative structure-activity relationships for calmodulin inhibitors | journal = Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin | volume = 38 | issue = 8 | pages = 2184–9 | date = Aug 1990 | pmid = 2279281 | doi=10.1248/cpb.38.2184| doi-access = free }}</ref> |
||
The enzyme's specificity for adenine involves hydrophobic residues [[Alanine|Ala131]] and [[Leucine|Leu159]] in the core domain. In humans, two residues in the hood domain [[hydrogen bond]] with the purine for further specificity: [[Valine|Val25]] with the [[hydrogen]]s on N6, and [[Arginine|Arg27]] with N1. Although the flexible loop does not interact with the hood during purine recognition, it is thought to close over the [[active site]] and sequester the reaction from [[solvents]].<ref name = "Silva_2004">{{cite journal | vauthors = Silva M, Silva CH, Iulek J, Thiemann OH | title = Three-dimensional structure of human adenine phosphoribosyltransferase and its relation to DHA-urolithiasis | journal = Biochemistry | volume = 43 | issue = 24 | pages = 7663–71 | date = Jun 2004 | pmid = 15196008 | doi = 10.1021/bi0360758 }}</ref> |
The enzyme's specificity for adenine involves hydrophobic residues [[Alanine|Ala131]] and [[Leucine|Leu159]] in the core domain. In humans, two residues in the hood domain [[hydrogen bond]] with the purine for further specificity: [[Valine|Val25]] with the [[hydrogen]]s on N6, and [[Arginine|Arg27]] with N1. Although the flexible loop does not interact with the hood during purine recognition, it is thought to close over the [[active site]] and sequester the reaction from [[solvents]].<ref name = "Silva_2004">{{cite journal | vauthors = Silva M, Silva CH, Iulek J, Thiemann OH | title = Three-dimensional structure of human adenine phosphoribosyltransferase and its relation to DHA-urolithiasis | journal = Biochemistry | volume = 43 | issue = 24 | pages = 7663–71 | date = Jun 2004 | pmid = 15196008 | doi = 10.1021/bi0360758 }}</ref> |
||
| Line 44: | Line 47: | ||
When APRTase has reduced or nonexistent activity, [[adenine]] accumulates from other pathways. It is degraded by [[xanthine dehydrogenase]] to [[2,8-dihydroxyadenine]] (DHA). Although DHA is protein-bound in [[blood plasma|plasma]], it has poor [[solubility]] in [[urine]] and gradually precipitates in [[nephrons|kidney tubules]], leading to the formation of kidney stones ([[urolithiasis]]). If left untreated, the condition can eventually produce [[renal failure|kidney failure]].<ref name ="Shi_2001"/> |
When APRTase has reduced or nonexistent activity, [[adenine]] accumulates from other pathways. It is degraded by [[xanthine dehydrogenase]] to [[2,8-dihydroxyadenine]] (DHA). Although DHA is protein-bound in [[blood plasma|plasma]], it has poor [[solubility]] in [[urine]] and gradually precipitates in [[nephrons|kidney tubules]], leading to the formation of kidney stones ([[urolithiasis]]). If left untreated, the condition can eventually produce [[renal failure|kidney failure]].<ref name ="Shi_2001"/> |
||
ARPTase deficiency was first diagnosed in the [[UK]] in 1976. Since then, two categories of APRTase deficiency have been defined in humans.<ref name = "Cassidy_2004">{{cite journal | vauthors = Cassidy MJ, McCulloch T, Fairbanks LD, Simmonds HA | title = Diagnosis of adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency as the underlying cause of renal failure in a renal transplant recipient | journal = Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation | volume = 19 | issue = 3 | pages = 736–8 | date = Mar 2004 | pmid = 14767036 | doi=10.1093/ndt/gfg562}}</ref> |
ARPTase deficiency was first diagnosed in the [[UK]] in 1976. Since then, two categories of APRTase deficiency have been defined in humans.<ref name = "Cassidy_2004">{{cite journal | vauthors = Cassidy MJ, McCulloch T, Fairbanks LD, Simmonds HA | title = Diagnosis of adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency as the underlying cause of renal failure in a renal transplant recipient | journal = Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation | volume = 19 | issue = 3 | pages = 736–8 | date = Mar 2004 | pmid = 14767036 | doi=10.1093/ndt/gfg562| doi-access = free }}</ref> |
||
Type I deficiency results in a complete loss of APRTase activity and can occur in patients that are [[homozygous]] or [[compound heterozygous]] for various [[mutations]].<ref name = "Bollée_2012">{{cite journal | vauthors = Bollée G, Harambat J, Bensman A, Knebelmann B, Daudon M, Ceballos-Picot I | title = Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency | journal = Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology | volume = 7 | issue = 9 | pages = 1521–7 | date = Sep 2012 | pmid = 22700886 | doi = 10.2215/CJN.02320312 }}</ref> [[Sequencing]] has revealed many different mutations that can account for Type 1, including [[missense mutations]], [[nonsense mutations]], a duplicated set of 4 [[base pairs]] in [[exon]] 3,<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Kamatani N, Hakoda M, Otsuka S, Yoshikawa H, Kashiwazaki S | title = Only three mutations account for almost all defective alleles causing adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency in Japanese patients | journal = The Journal of Clinical Investigation | volume = 90 | issue = 1 | pages = 130–5 | date = Jul 1992 | pmid = 1353080 | doi = 10.1172/JCI115825 | pmc=443071}}</ref> and a single [[thymine]] [[Insertion (genetics)|insertion]] in [[intron]] 4.<ref name = "Bollée_2010">{{cite journal | vauthors = Bollée G, Dollinger C, Boutaud L, Guillemot D, Bensman A, Harambat J, Deteix P, Daudon M, Knebelmann B, Ceballos-Picot I | title = Phenotype and genotype characterization of adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency | journal = Journal of the American Society of Nephrology | volume = 21 | issue = 4 | pages = 679–88 | date = Apr 2010 | pmid = 20150536 | doi = 10.1681/ASN.2009080808 | pmc=2844298}}</ref> These mutations cause effects that are clustered into three main areas: in the binding of PRPP's |
Type I deficiency results in a complete loss of APRTase activity and can occur in patients that are [[homozygous]] or [[compound heterozygous]] for various [[mutations]].<ref name = "Bollée_2012">{{cite journal | vauthors = Bollée G, Harambat J, Bensman A, Knebelmann B, Daudon M, Ceballos-Picot I | title = Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency | journal = Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology | volume = 7 | issue = 9 | pages = 1521–7 | date = Sep 2012 | pmid = 22700886 | doi = 10.2215/CJN.02320312 | doi-access = free }}</ref> [[Sequencing]] has revealed many different mutations that can account for Type 1, including [[missense mutations]], [[nonsense mutations]], a duplicated set of 4 [[base pairs]] in [[exon]] 3,<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Kamatani N, Hakoda M, Otsuka S, Yoshikawa H, Kashiwazaki S | title = Only three mutations account for almost all defective alleles causing adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency in Japanese patients | journal = The Journal of Clinical Investigation | volume = 90 | issue = 1 | pages = 130–5 | date = Jul 1992 | pmid = 1353080 | doi = 10.1172/JCI115825 | pmc=443071}}</ref> and a single [[thymine]] [[Insertion (genetics)|insertion]] in [[intron]] 4.<ref name = "Bollée_2010">{{cite journal | vauthors = Bollée G, Dollinger C, Boutaud L, Guillemot D, Bensman A, Harambat J, Deteix P, Daudon M, Knebelmann B, Ceballos-Picot I | title = Phenotype and genotype characterization of adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency | journal = Journal of the American Society of Nephrology | volume = 21 | issue = 4 | pages = 679–88 | date = Apr 2010 | pmid = 20150536 | doi = 10.1681/ASN.2009080808 | pmc=2844298}}</ref> These mutations cause effects that are clustered into three main areas: in the binding of PRPP's |
||
Type I deficiency has been observed in various ethnic groups but studied predominately among [[White people|White]] populations.<ref name = "Bollée_2010"/> |
Type I deficiency has been observed in various ethnic groups but studied predominately among [[White people|White]] populations.<ref name = "Bollée_2010"/> |
||
Type II deficiency causes APRTase to have a reduced affinity for PRPP, resulting in a tenfold increase in the K<sub>M</sub> value.<ref name = "Silva_2008"/> It has been observed and studied primarily in [[Japan]].<ref name = "Bollée_2010"/> |
Type II deficiency causes APRTase to have a reduced affinity for PRPP, resulting in a tenfold increase in the K<sub>M</sub> value.<ref name = "Silva_2008"/> It has been observed and studied primarily in [[Japan]].<ref name = "Bollée_2010"/> |
||
A diagnosis of APRTase deficiency can be made by analyzing [[kidney stones]], measuring DHA concentrations in urine, or analyzing APRTase activity in [[erythrocytes]]. It is treatable with regular doses of [[allopurinol]] or [[febuxostat]], which inhibit xanthine dehydrogenase activity to prevent the accumulation and precipitation of DHA.<ref name = "Edvardsson_1993">{{cite journal | vauthors = Edvardsson VO, Palsson R, Sahota A | veditors = Pagon RA, Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, Bean LJ, Bird TD, Fong CT, Mefford HC, Smith RJ, Stephens K | journal = SourceGeneReviews |
A diagnosis of APRTase deficiency can be made by analyzing [[kidney stones]], measuring DHA concentrations in urine, or analyzing APRTase activity in [[erythrocytes]]. It is treatable with regular doses of [[allopurinol]] or [[febuxostat]], which inhibit xanthine dehydrogenase activity to prevent the accumulation and precipitation of DHA.<ref name = "Edvardsson_1993">{{cite journal | vauthors = Edvardsson VO, Palsson R, Sahota A | veditors = Pagon RA, Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, Bean LJ, Bird TD, Fong CT, Mefford HC, Smith RJ, Stephens K | journal = SourceGeneReviews | title = Adenine Phosphoribosyltransferase Deficiency | date = 1993 | pmid = 22934314 }}</ref> The condition can also be attenuated with a low-purine diet and high fluid intake.<ref name = "Cassidy_2004"/> |
||
== References == |
== References == |
||
| Line 59: | Line 62: | ||
== Further reading == |
== Further reading == |
||
{{refbegin|33em}} |
{{refbegin|33em}} |
||
* {{cite |
* {{cite book | vauthors = Tischfield JA, Engle SJ, Gupta PK, Bye S, Boyadjiev S, Shao C, O'Neill P, Albertini RJ, Stambrook PJ, Sahota AS | title = Purine and Pyrimidine Metabolism in Man VIII | chapter = Germline and Somatic Mutation at the APRT Locus of Mice and Man | series = Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology | volume = 370 | pages = 661–4 | year = 1995 | pmid = 7660991 | doi = 10.1007/978-1-4615-2584-4_137 | isbn = 978-1-4613-6105-3 }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Takeuchi H, Kaneko Y, Fujita J, Yoshida O | title = A case of a compound heterozygote for adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency (APRT*J/APRT*Q0) leading to 2,8-dihydroxyadenine urolithiasis: review of the reported cases with 2,8-dihydroxyadenine stones in Japan | journal = The Journal of Urology | volume = 149 | issue = 4 | pages = 824–6 | date = Apr 1993 | pmid = 8455250 | doi = 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)36222-5 }} |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Takeuchi H, Kaneko Y, Fujita J, Yoshida O | title = A case of a compound heterozygote for adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency (APRT*J/APRT*Q0) leading to 2,8-dihydroxyadenine urolithiasis: review of the reported cases with 2,8-dihydroxyadenine stones in Japan | journal = The Journal of Urology | volume = 149 | issue = 4 | pages = 824–6 | date = Apr 1993 | pmid = 8455250 | doi = 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)36222-5 }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Ludwig H, Kuzmits R, Pietschmann H, Müller MM | title = Enzymes of the purine interconversion system in chronic lymphatic leukemia: decreased purine nucleoside phosphorylase and adenosine deaminase activity | journal = Blut | volume = 39 | issue = 5 | pages = 309–15 | date = Nov 1979 | pmid = 116697 | doi = 10.1007/BF01014193 }} |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Ludwig H, Kuzmits R, Pietschmann H, Müller MM | title = Enzymes of the purine interconversion system in chronic lymphatic leukemia: decreased purine nucleoside phosphorylase and adenosine deaminase activity | journal = Blut | volume = 39 | issue = 5 | pages = 309–15 | date = Nov 1979 | pmid = 116697 | doi = 10.1007/BF01014193 | s2cid = 6283377 }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Johnson LA, Gordon RB, Emmerson BT | title = Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase: a simple spectrophotometric assay and the incidence of mutation in the normal population | journal = Biochemical Genetics | volume = 15 | issue = |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Johnson LA, Gordon RB, Emmerson BT | title = Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase: a simple spectrophotometric assay and the incidence of mutation in the normal population | journal = Biochemical Genetics | volume = 15 | issue = 3–4 | pages = 265–72 | date = Apr 1977 | pmid = 869896 | doi = 10.1007/BF00484458 | s2cid = 41264715 }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Kamatani N, Hakoda M, Otsuka S, Yoshikawa H, Kashiwazaki S | title = Only three mutations account for almost all defective alleles causing adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency in Japanese patients | journal = The Journal of Clinical Investigation | volume = 90 | issue = 1 | pages = 130–5 | date = Jul 1992 | pmid = 1353080 | pmc = 443071 | doi = 10.1172/JCI115825 }} |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Kamatani N, Hakoda M, Otsuka S, Yoshikawa H, Kashiwazaki S | title = Only three mutations account for almost all defective alleles causing adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency in Japanese patients | journal = The Journal of Clinical Investigation | volume = 90 | issue = 1 | pages = 130–5 | date = Jul 1992 | pmid = 1353080 | pmc = 443071 | doi = 10.1172/JCI115825 }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Chen J, Sahota A, Laxdal T, Scrine M, Bowman S, Cui C, Stambrook PJ, Tischfield JA | title = Identification of a single missense mutation in the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase (APRT) gene from five Icelandic patients and a British patient | journal = American Journal of Human Genetics | volume = 49 | issue = 6 | pages = 1306–11 | date = Dec 1991 | pmid = 1746557 | pmc = 1686459 |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Chen J, Sahota A, Laxdal T, Scrine M, Bowman S, Cui C, Stambrook PJ, Tischfield JA | title = Identification of a single missense mutation in the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase (APRT) gene from five Icelandic patients and a British patient | journal = American Journal of Human Genetics | volume = 49 | issue = 6 | pages = 1306–11 | date = Dec 1991 | pmid = 1746557 | pmc = 1686459 }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Mimori A, Hidaka Y, Wu VC, Tarlé SA, Kamatani N, Kelley WN, Pallela TD | title = A mutant allele common to the type I adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency in Japanese subjects | journal = American Journal of Human Genetics | volume = 48 | issue = 1 | pages = 103–7 | date = Jan 1991 | pmid = 1985452 | pmc = 1682758 |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Mimori A, Hidaka Y, Wu VC, Tarlé SA, Kamatani N, Kelley WN, Pallela TD | title = A mutant allele common to the type I adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency in Japanese subjects | journal = American Journal of Human Genetics | volume = 48 | issue = 1 | pages = 103–7 | date = Jan 1991 | pmid = 1985452 | pmc = 1682758 }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Chen J, Sahota A, Stambrook PJ, Tischfield JA | title = Polymerase chain reaction amplification and sequence analysis of human mutant adenine phosphoribosyltransferase genes: the nature and frequency of errors caused by Taq DNA polymerase | journal = Mutation Research | volume = 249 | issue = 1 | pages = 169–76 | date = Jul 1991 | pmid = 2067530 | doi = 10.1016/0027-5107(91)90143-C }} |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Chen J, Sahota A, Stambrook PJ, Tischfield JA | title = Polymerase chain reaction amplification and sequence analysis of human mutant adenine phosphoribosyltransferase genes: the nature and frequency of errors caused by Taq DNA polymerase | journal = Mutation Research | volume = 249 | issue = 1 | pages = 169–76 | date = Jul 1991 | pmid = 2067530 | doi = 10.1016/0027-5107(91)90143-C }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Gathof BS, Sahota A, Gresser U, Chen J, Stambrook PJ, Tischfield JA, Zöllner N | title = Identification of a splice mutation at the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus in a German family | journal = Klinische Wochenschrift | volume = 69 | issue = 24 | pages = 1152–5 | date = Dec 1990 | pmid = 2135300 | doi = 10.1007/BF01815434 }} |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Gathof BS, Sahota A, Gresser U, Chen J, Stambrook PJ, Tischfield JA, Zöllner N | title = Identification of a splice mutation at the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus in a German family | journal = Klinische Wochenschrift | volume = 69 | issue = 24 | pages = 1152–5 | date = Dec 1990 | pmid = 2135300 | doi = 10.1007/BF01815434 | s2cid = 11791868 }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Kamatani N, Kuroshima S, Hakoda M, Palella TD, Hidaka Y | title = Crossovers within a short DNA sequence indicate a long evolutionary history of the APRT*J mutation | journal = Human Genetics | volume = 85 | issue = 6 | pages = 600–4 | date = Oct 1990 | pmid = 2227951 | doi = 10.1007/BF00193582 }} |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Kamatani N, Kuroshima S, Hakoda M, Palella TD, Hidaka Y | title = Crossovers within a short DNA sequence indicate a long evolutionary history of the APRT*J mutation | journal = Human Genetics | volume = 85 | issue = 6 | pages = 600–4 | date = Oct 1990 | pmid = 2227951 | doi = 10.1007/BF00193582 | url = https://deepblue.lib.umich.edu/bitstream/2027.42/47628/1/439_2004_Article_BF00193582.pdf | hdl = 2027.42/47628 | s2cid = 10595601 | hdl-access = free }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Kamatani N, Kuroshima S, Terai C, Hidaka Y, Palella TD, Nishioka K | title = Detection of an amino acid substitution in the mutant enzyme for a special type of adenine phosphoribosyltransferase (APRT) deficiency by sequence-specific protein cleavage | journal = American Journal of Human Genetics | volume = 45 | issue = 2 | pages = 325–31 | date = Aug 1989 | pmid = 2502918 | pmc = 1683345 |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Kamatani N, Kuroshima S, Terai C, Hidaka Y, Palella TD, Nishioka K | title = Detection of an amino acid substitution in the mutant enzyme for a special type of adenine phosphoribosyltransferase (APRT) deficiency by sequence-specific protein cleavage | journal = American Journal of Human Genetics | volume = 45 | issue = 2 | pages = 325–31 | date = Aug 1989 | pmid = 2502918 | pmc = 1683345 }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Hidaka Y, Tarlé SA, Fujimori S, Kamatani N, Kelley WN, Palella TD | title = Human adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency. Demonstration of a single mutant allele common to the Japanese | journal = The Journal of Clinical Investigation | volume = 81 | issue = 3 | pages = 945–50 | date = Mar 1988 | pmid = 3343350 | pmc = 442550 | doi = 10.1172/JCI113408 }} |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Hidaka Y, Tarlé SA, Fujimori S, Kamatani N, Kelley WN, Palella TD | title = Human adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency. Demonstration of a single mutant allele common to the Japanese | journal = The Journal of Clinical Investigation | volume = 81 | issue = 3 | pages = 945–50 | date = Mar 1988 | pmid = 3343350 | pmc = 442550 | doi = 10.1172/JCI113408 }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Wilson JM, O'Toole TE, Argos P, Shewach DS, Daddona PE, Kelley WN | title = Human adenine phosphoribosyltransferase. Complete amino acid sequence of the erythrocyte enzyme | journal = The Journal of Biological Chemistry | volume = 261 | issue = 29 | pages = 13677–83 | date = Oct 1986 | pmid = 3531209 | doi = }} |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Wilson JM, O'Toole TE, Argos P, Shewach DS, Daddona PE, Kelley WN | title = Human adenine phosphoribosyltransferase. Complete amino acid sequence of the erythrocyte enzyme | journal = The Journal of Biological Chemistry | volume = 261 | issue = 29 | pages = 13677–83 | date = Oct 1986 | doi = 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)67074-7 | pmid = 3531209 | doi-access = free }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Broderick TP, Schaff DA, Bertino AM, Dush MK, Tischfield JA, Stambrook PJ | title = Comparative anatomy of the human APRT gene and enzyme: nucleotide sequence divergence and conservation of a nonrandom CpG dinucleotide arrangement | journal = Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America | volume = 84 | issue = 10 | pages = 3349–53 | date = May 1987 | pmid = 3554238 | pmc = 304867 | doi = 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3349 }} |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Broderick TP, Schaff DA, Bertino AM, Dush MK, Tischfield JA, Stambrook PJ | title = Comparative anatomy of the human APRT gene and enzyme: nucleotide sequence divergence and conservation of a nonrandom CpG dinucleotide arrangement | journal = Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America | volume = 84 | issue = 10 | pages = 3349–53 | date = May 1987 | pmid = 3554238 | pmc = 304867 | doi = 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3349 | bibcode = 1987PNAS...84.3349B | doi-access = free }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Hidaka Y, Palella TD, O'Toole TE, Tarlé SA, Kelley WN | title = Human adenine phosphoribosyltransferase. Identification of allelic mutations at the nucleotide level as a cause of complete deficiency of the enzyme | journal = The Journal of Clinical Investigation | volume = 80 | issue = 5 | pages = 1409–15 | date = Nov 1987 | pmid = 3680503 | pmc = 442397 | doi = 10.1172/JCI113219 }} |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Hidaka Y, Palella TD, O'Toole TE, Tarlé SA, Kelley WN | title = Human adenine phosphoribosyltransferase. Identification of allelic mutations at the nucleotide level as a cause of complete deficiency of the enzyme | journal = The Journal of Clinical Investigation | volume = 80 | issue = 5 | pages = 1409–15 | date = Nov 1987 | pmid = 3680503 | pmc = 442397 | doi = 10.1172/JCI113219 }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Hidaka Y, Tarlé SA, O'Toole TE, Kelley WN, Palella TD | title = Nucleotide sequence of the human APRT gene | journal = Nucleic Acids Research | volume = 15 | issue = 21 | pages = 9086 | date = Nov 1987 | pmid = 3684585 | pmc = 306432 | doi = 10.1093/nar/15.21.9086 }} |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Hidaka Y, Tarlé SA, O'Toole TE, Kelley WN, Palella TD | title = Nucleotide sequence of the human APRT gene | journal = Nucleic Acids Research | volume = 15 | issue = 21 | pages = 9086 | date = Nov 1987 | pmid = 3684585 | pmc = 306432 | doi = 10.1093/nar/15.21.9086 }} |
||
| Line 87: | Line 90: | ||
{{Glycosyltransferases}} |
{{Glycosyltransferases}} |
||
{{Enzymes}} |
{{Enzymes}} |
||
{{Portal bar| |
{{Portal bar|Biology|border=no}} |
||
[[Category:EC 2.4.2]] |
[[Category:EC 2.4.2]] |
||
Latest revision as of 19:32, 2 September 2023
| APRT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | APRT, AMP, APRTD, adenine phosphoribosyltransferase | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 102600; MGI: 88061; HomoloGene: 413; GeneCards: APRT; OMA:APRT - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase (APRTase) is an enzyme encoded by the APRT gene, found in humans on chromosome 16.[5] It is part of the Type I PRTase family and is involved in the nucleotide salvage pathway, which provides an alternative to nucleotide biosynthesis de novo in humans and most other animals.[6] In parasitic protozoa such as giardia, APRTase provides the sole mechanism by which AMP can be produced.[7] APRTase deficiency contributes to the formation of kidney stones (urolithiasis) and to potential kidney failure.[8]
Function[edit]
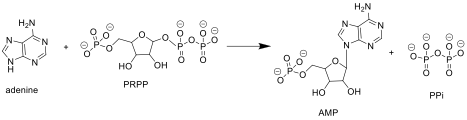
APRTase catalyzes the following reaction in the purine nucleotide salvage pathway:
Adenine + Phosphoribosyl Pyrophosphate (PRPP) → Adenylate (AMP) + Pyrophosphate (PPi)
In organisms that can synthesize purines de novo, the nucleotide salvage pathway provides an alternative that is energetically more efficient. It can salvage adenine from the polyamine biosynthetic pathway or from dietary sources of purines.[6] Although APRTase is functionally redundant in these organisms, it becomes more important during periods of rapid growth, such as embryogenesis and tumor growth.[9] It is constitutively expressed in all mammalian tissue.[10]
In protozoan parasites, the nucleotide salvage pathway provides the sole means for nucleotide synthesis. Since the consequences of APRTase deficiency in humans is comparatively mild and treatable, it may be possible to treat certain parasitic infections by targeting APRTase function.[11]
In plants, as in other organisms, ARPTase functions primarily for the synthesis of adenylate. It has the unique ability to metabolize cytokinins—a plant hormone that can exist as a base, nucleotide, or nucleoside—into adenylate nucleotides.[12]
APRT is functionally related to hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HPRT).
Structure[edit]
APRTase is a homodimer, with 179 amino acid residues per monomer. Each monomer contains the following regions:
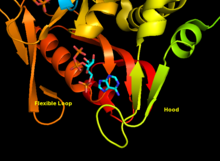
- "Core" domain (residues 33-169) with five parallel
β -sheets - "Hood" domain (residues 5-34) with 2
α -helices and 2β -sheets - "Flexible loop" domain (residues 95-113) with 2 antiparallel
β -sheets[10]
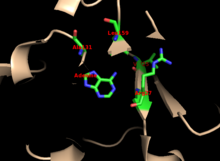
The core is highly conserved across many PRTases. The hood, which contains the adenine binding site, has more variability within the family of enzymes. A 13-residue motif comprises the PRPP binding region and involves two adjacent acidic residues and at least one surrounding hydrophobic residue.[13]
The enzyme's specificity for adenine involves hydrophobic residues Ala131 and Leu159 in the core domain. In humans, two residues in the hood domain hydrogen bond with the purine for further specificity: Val25 with the hydrogens on N6, and Arg27 with N1. Although the flexible loop does not interact with the hood during purine recognition, it is thought to close over the active site and sequester the reaction from solvents.[10]
Most research on APRTase reports that Mg2+ is essential for phosphoribosyl transfer, and this is conserved across Type I PRTases.[12] However, a recent effort to resolve the structure of human APRTase was unable to locate a single site for Mg2+, but did find evidence to suggest a Cl− atom near Trp98. Despite the difficulty of placing Mg2+, it is generally accepted that the catalytic mechanism is dependent on this ion.[6]
Mechanism[edit]
APRTase proceeds via a bi bi ordered sequential mechanism, involving the formation of a ternary complex. The enzyme first binds PRPP, followed by adenine. After the phosphoribosyl transfer occurs, pyrophosphate leaves first, followed by AMP. Kinetic studies indicate that the phosphoribosyl transfer is relatively fast, while the product release (particularly the release of AMP) is rate-limiting.[9]
In human APRTase, it is thought that adenine's N9 proton is abstracted by Glu104 to form an oxacarbenium transition state. This functions as the nucleophile to attack the anomeric carbon of PRPP, forming AMP and displacing pyrophosphate from PRPP. The mechanism of APRTase is generally consistent with that of other PRTases, which conserve the function of displacing PRPP's
Deficiency[edit]
When APRTase has reduced or nonexistent activity, adenine accumulates from other pathways. It is degraded by xanthine dehydrogenase to 2,8-dihydroxyadenine (DHA). Although DHA is protein-bound in plasma, it has poor solubility in urine and gradually precipitates in kidney tubules, leading to the formation of kidney stones (urolithiasis). If left untreated, the condition can eventually produce kidney failure.[8]
ARPTase deficiency was first diagnosed in the UK in 1976. Since then, two categories of APRTase deficiency have been defined in humans.[14]
Type I deficiency results in a complete loss of APRTase activity and can occur in patients that are homozygous or compound heterozygous for various mutations.[15] Sequencing has revealed many different mutations that can account for Type 1, including missense mutations, nonsense mutations, a duplicated set of 4 base pairs in exon 3,[16] and a single thymine insertion in intron 4.[17] These mutations cause effects that are clustered into three main areas: in the binding of PRPP's
Type II deficiency causes APRTase to have a reduced affinity for PRPP, resulting in a tenfold increase in the KM value.[6] It has been observed and studied primarily in Japan.[17]
A diagnosis of APRTase deficiency can be made by analyzing kidney stones, measuring DHA concentrations in urine, or analyzing APRTase activity in erythrocytes. It is treatable with regular doses of allopurinol or febuxostat, which inhibit xanthine dehydrogenase activity to prevent the accumulation and precipitation of DHA.[18] The condition can also be attenuated with a low-purine diet and high fluid intake.[14]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000198931 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000006589 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Valaperta R, Rizzo V, Lombardi F, Verdelli C, Piccoli M, Ghiroldi A, Creo P, Colombo A, Valisi M, Margiotta E, Panella R, Costa E (1 July 2014). "Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase (APRT) deficiency: identification of a novel nonsense mutation". BMC Nephrology. 15: 102. doi:10.1186/1471-2369-15-102. PMC 4094445. PMID 24986359.
- ^ a b c d e Silva CH, Silva M, Iulek J, Thiemann OH (Jun 2008). "Structural complexes of human adenine phosphoribosyltransferase reveal novel features of the APRT catalytic mechanism". Journal of Biomolecular Structure & Dynamics. 25 (6): 589–97. doi:10.1080/07391102.2008.10507205. PMID 18399692. S2CID 40788077.
- ^ Sarver AE, Wang CC (Oct 2002). "The adenine phosphoribosyltransferase from Giardia lamblia has a unique reaction mechanism and unusual substrate binding properties". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (42): 39973–80. doi:10.1074/jbc.M205595200. PMID 12171924.
- ^ a b Shi W, Tanaka KS, Crother TR, Taylor MW, Almo SC, Schramm VL (Sep 2001). "Structural analysis of adenine phosphoribosyltransferase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae". Biochemistry. 40 (36): 10800–9. doi:10.1021/bi010465h. PMID 11535055.
- ^ a b Bashor C, Denu JM, Brennan RG, Ullman B (Mar 2002). "Kinetic mechanism of adenine phosphoribosyltransferase from Leishmania donovani". Biochemistry. 41 (12): 4020–31. doi:10.1021/bi0158730. PMID 11900545.
- ^ a b c d Silva M, Silva CH, Iulek J, Thiemann OH (Jun 2004). "Three-dimensional structure of human adenine phosphoribosyltransferase and its relation to DHA-urolithiasis". Biochemistry. 43 (24): 7663–71. doi:10.1021/bi0360758. PMID 15196008.
- ^ Shi W, Sarver AE, Wang CC, Tanaka KS, Almo SC, Schramm VL (Oct 2002). "Closed site complexes of adenine phosphoribosyltransferase from Giardia lamblia reveal a mechanism of ribosyl migration". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (42): 39981–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M205596200. PMID 12171925.
- ^ a b Allen M, Qin W, Moreau F, Moffatt B (May 2002). "Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase isoforms of Arabidopsis and their potential contributions to adenine and cytokinin metabolism". Physiologia Plantarum. 115 (1): 56–68. doi:10.1034/j.1399-3054.2002.1150106.x. PMID 12010467.
- ^ Liu Q, Hirono S, Moriguchi I (Aug 1990). "Quantitative structure-activity relationships for calmodulin inhibitors". Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 38 (8): 2184–9. doi:10.1248/cpb.38.2184. PMID 2279281.
- ^ a b Cassidy MJ, McCulloch T, Fairbanks LD, Simmonds HA (Mar 2004). "Diagnosis of adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency as the underlying cause of renal failure in a renal transplant recipient". Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation. 19 (3): 736–8. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfg562. PMID 14767036.
- ^ Bollée G, Harambat J, Bensman A, Knebelmann B, Daudon M, Ceballos-Picot I (Sep 2012). "Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency". Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. 7 (9): 1521–7. doi:10.2215/CJN.02320312. PMID 22700886.
- ^ Kamatani N, Hakoda M, Otsuka S, Yoshikawa H, Kashiwazaki S (Jul 1992). "Only three mutations account for almost all defective alleles causing adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency in Japanese patients". The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 90 (1): 130–5. doi:10.1172/JCI115825. PMC 443071. PMID 1353080.
- ^ a b c Bollée G, Dollinger C, Boutaud L, Guillemot D, Bensman A, Harambat J, Deteix P, Daudon M, Knebelmann B, Ceballos-Picot I (Apr 2010). "Phenotype and genotype characterization of adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency". Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. 21 (4): 679–88. doi:10.1681/ASN.2009080808. PMC 2844298. PMID 20150536.
- ^ Edvardsson VO, Palsson R, Sahota A (1993). Pagon RA, Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, Bean LJ, Bird TD, Fong CT, Mefford HC, Smith RJ, Stephens K (eds.). "Adenine Phosphoribosyltransferase Deficiency". SourceGeneReviews. PMID 22934314.
Further reading[edit]
- Tischfield JA, Engle SJ, Gupta PK, Bye S, Boyadjiev S, Shao C, O'Neill P, Albertini RJ, Stambrook PJ, Sahota AS (1995). "Germline and Somatic Mutation at the APRT Locus of Mice and Man". Purine and Pyrimidine Metabolism in Man VIII. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Vol. 370. pp. 661–4. doi:10.1007/978-1-4615-2584-4_137. ISBN 978-1-4613-6105-3. PMID 7660991.
- Takeuchi H, Kaneko Y, Fujita J, Yoshida O (Apr 1993). "A case of a compound heterozygote for adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency (APRT*J/APRT*Q0) leading to 2,8-dihydroxyadenine urolithiasis: review of the reported cases with 2,8-dihydroxyadenine stones in Japan". The Journal of Urology. 149 (4): 824–6. doi:10.1016/s0022-5347(17)36222-5. PMID 8455250.
- Ludwig H, Kuzmits R, Pietschmann H, Müller MM (Nov 1979). "Enzymes of the purine interconversion system in chronic lymphatic leukemia: decreased purine nucleoside phosphorylase and adenosine deaminase activity". Blut. 39 (5): 309–15. doi:10.1007/BF01014193. PMID 116697. S2CID 6283377.
- Johnson LA, Gordon RB, Emmerson BT (Apr 1977). "Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase: a simple spectrophotometric assay and the incidence of mutation in the normal population". Biochemical Genetics. 15 (3–4): 265–72. doi:10.1007/BF00484458. PMID 869896. S2CID 41264715.
- Kamatani N, Hakoda M, Otsuka S, Yoshikawa H, Kashiwazaki S (Jul 1992). "Only three mutations account for almost all defective alleles causing adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency in Japanese patients". The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 90 (1): 130–5. doi:10.1172/JCI115825. PMC 443071. PMID 1353080.
- Chen J, Sahota A, Laxdal T, Scrine M, Bowman S, Cui C, Stambrook PJ, Tischfield JA (Dec 1991). "Identification of a single missense mutation in the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase (APRT) gene from five Icelandic patients and a British patient". American Journal of Human Genetics. 49 (6): 1306–11. PMC 1686459. PMID 1746557.
- Mimori A, Hidaka Y, Wu VC, Tarlé SA, Kamatani N, Kelley WN, Pallela TD (Jan 1991). "A mutant allele common to the type I adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency in Japanese subjects". American Journal of Human Genetics. 48 (1): 103–7. PMC 1682758. PMID 1985452.
- Chen J, Sahota A, Stambrook PJ, Tischfield JA (Jul 1991). "Polymerase chain reaction amplification and sequence analysis of human mutant adenine phosphoribosyltransferase genes: the nature and frequency of errors caused by Taq DNA polymerase". Mutation Research. 249 (1): 169–76. doi:10.1016/0027-5107(91)90143-C. PMID 2067530.
- Gathof BS, Sahota A, Gresser U, Chen J, Stambrook PJ, Tischfield JA, Zöllner N (Dec 1990). "Identification of a splice mutation at the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus in a German family". Klinische Wochenschrift. 69 (24): 1152–5. doi:10.1007/BF01815434. PMID 2135300. S2CID 11791868.
- Kamatani N, Kuroshima S, Hakoda M, Palella TD, Hidaka Y (Oct 1990). "Crossovers within a short DNA sequence indicate a long evolutionary history of the APRT*J mutation" (PDF). Human Genetics. 85 (6): 600–4. doi:10.1007/BF00193582. hdl:2027.42/47628. PMID 2227951. S2CID 10595601.
- Kamatani N, Kuroshima S, Terai C, Hidaka Y, Palella TD, Nishioka K (Aug 1989). "Detection of an amino acid substitution in the mutant enzyme for a special type of adenine phosphoribosyltransferase (APRT) deficiency by sequence-specific protein cleavage". American Journal of Human Genetics. 45 (2): 325–31. PMC 1683345. PMID 2502918.
- Hidaka Y, Tarlé SA, Fujimori S, Kamatani N, Kelley WN, Palella TD (Mar 1988). "Human adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency. Demonstration of a single mutant allele common to the Japanese". The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 81 (3): 945–50. doi:10.1172/JCI113408. PMC 442550. PMID 3343350.
- Wilson JM, O'Toole TE, Argos P, Shewach DS, Daddona PE, Kelley WN (Oct 1986). "Human adenine phosphoribosyltransferase. Complete amino acid sequence of the erythrocyte enzyme". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 261 (29): 13677–83. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)67074-7. PMID 3531209.
- Broderick TP, Schaff DA, Bertino AM, Dush MK, Tischfield JA, Stambrook PJ (May 1987). "Comparative anatomy of the human APRT gene and enzyme: nucleotide sequence divergence and conservation of a nonrandom CpG dinucleotide arrangement". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 84 (10): 3349–53. Bibcode:1987PNAS...84.3349B. doi:10.1073/pnas.84.10.3349. PMC 304867. PMID 3554238.
- Hidaka Y, Palella TD, O'Toole TE, Tarlé SA, Kelley WN (Nov 1987). "Human adenine phosphoribosyltransferase. Identification of allelic mutations at the nucleotide level as a cause of complete deficiency of the enzyme". The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 80 (5): 1409–15. doi:10.1172/JCI113219. PMC 442397. PMID 3680503.
- Hidaka Y, Tarlé SA, O'Toole TE, Kelley WN, Palella TD (Nov 1987). "Nucleotide sequence of the human APRT gene". Nucleic Acids Research. 15 (21): 9086. doi:10.1093/nar/15.21.9086. PMC 306432. PMID 3684585.
- Chen J, Sahota A, Martin GF, Hakoda M, Kamatani N, Stambrook PJ, Tischfield JA (Jun 1993). "Analysis of germline and in vivo somatic mutations in the human adenine phosphoribosyltransferase gene: mutational hot spots at the intron 4 splice donor site and at codon 87". Mutation Research. 287 (2): 217–25. doi:10.1016/0027-5107(93)90014-7. PMID 7685481.
- Sahota A, Chen J, Boyadjiev SA, Gault MH, Tischfield JA (May 1994). "Missense mutation in the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase gene causing 2,8-dihydroxyadenine urolithiasis". Human Molecular Genetics. 3 (5): 817–8. doi:10.1093/hmg/3.5.817. PMID 7915931.
External links[edit]
- Adenine+phosphoribosyltransferase at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Human APRT genome location and APRT gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.