Berlepsch's tinamou: Difference between revisions
m added explanation of name |
m Moving Category:Birds of the Tumbes-Chocó-Magdalena to Category:Birds of Tumbes-Chocó-Magdalena per Wikipedia:Categories for discussion/Speedy |
||
| (40 intermediate revisions by 28 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Species of bird}} |
|||
{{Taxobox |
|||
{{Speciesbox |
|||
| name = Berlepsch's Tinamou |
|||
| image = Crypturellus berlepschi 1897.jpg |
| image = Crypturellus berlepschi 1897.jpg |
||
| image_caption = Berlepsch's |
| image_caption = Berlepsch's tinamou is the bird in the center. The bird on the left is another species. |
||
| status = LC |
| status = LC |
||
| status_system = IUCN3.1 |
| status_system = IUCN3.1 |
||
| status_ref = <ref name= |
| status_ref = <ref name="iucn status 12 November 2021">{{cite iucn |author=BirdLife International |date=2016 |title=''Crypturellus berlepschi'' |volume=2016 |page=e.T22678163A92759082 |doi=10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22678163A92759082.en |access-date=12 November 2021}}</ref> |
||
| |
| genus = Crypturellus |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| phylum = [[Chordate|Chordata]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| classis = [[bird|Aves]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ordo = [[Tinamiformes]] |
|||
| familia = [[Tinamidae]] |
|||
| subfamilia = [[Tinaminae]] |
|||
| genus = ''[[Crypturellus]]'' |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| binomial = ''Crypturellus berlepschi'' |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| range_map_width = 250px |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Berlepsch's tinamou''' ('''''Crypturellus berlepschi''''') is a type of ground bird found in [[Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests|moist forest]]<ref name="BLI">BirdLife International (2008)</ref> in northwestern [[Colombia]] and northwestern [[Ecuador]].<ref name="Clements">Clements, J (2007)</ref> |
|||
The common name and Latin binomial of the bird commemorate the German ornithologist and collector [[Hans von Berlepsch]].<ref>{{cite book|last=Boelens|first=Bo|title=Whose Bird? Men and Women Commemorated in the Common Names of Birds|year=2003|publisher=Christopher Helm|location=London|page=50|coauthors=Michael Watkins}}</ref> |
|||
==Taxonomy== |
==Taxonomy== |
||
The Berlepsch's |
The Berlepsch's tinamou is a monotypic species.<ref name="Clements">Clements, J (2007)</ref> All tinamou are from the family Tinamidae, and in the larger scheme are also [[ratite]]s. Unlike other ratites, tinamous can fly, although in general, they are not strong fliers. All ratites evolved from prehistoric flying birds, and tinamous are the closest living relative of these birds.<ref name="Davies">Davies, S. J. J. F. (2003)</ref> Until the mid 20th century, this species was considered a sub-species of the [[cinereous tinamou]], but due to its bill size, its ratio of toe and tarsus length and the fact that its plumage has conspicuous differences from that of the cinereous tinamou created enough of a question for the new species to be named.<ref name=Cabot>{{cite encyclopedia|last1=Cabot| first1=J. |last2= Carboneras| first2= C.| last3= Folch| first3= A. |last4=de Juanca| first4= E. |last5=Llimona|first5=F. |last6=Matheu|first6=E.|year=1992 |editor-first=J.|editor-last=del Hoyo |publisher=Lynx Edicions |location= Barcelona, Spain| volume= I: Ostrich to Ducks| encyclopedia= Handbook of the Birds of the World|title= Tinamiformes}}</ref> |
||
==Etymology== |
==Etymology== |
||
''Crypturellus'' is formed from three [[Latin]] or [[Greek language|Greek]] words. ''kruptos'' meaning '''covered''' or '''hidden''', ''oura'' meaning '''tail''', and ''ellus'' meaning '''diminutive'''. Therefore ''Crypturellus'' means small hidden tail.<ref>Gotch, A. F. (1195)</ref> ''berlepschi'' comes |
''Crypturellus'' is formed from three [[Latin]] or [[Greek language|Greek]] words. ''kruptos'' meaning '''covered''' or '''hidden''', ''oura'' meaning '''tail''', and ''ellus'' meaning '''diminutive'''. Therefore, ''Crypturellus'' means small hidden tail.<ref>Gotch, A. F. (1195)</ref> ''berlepschi'' comes from the [[Latin]] form of Berlepsch to commemorate the German ornithologist and collector [[Hans von Berlepsch]].<ref>{{cite book|last=Boelens|first=Bo|title=Whose Bird? Men and Women Commemorated in the Common Names of Birds|year=2003|publisher=Christopher Helm|location=London|page=50|author2=Michael Watkins}}</ref> |
||
==Description== |
==Description== |
||
Berlepsch's |
Berlepsch's tinamou is a medium-sized bird, about {{convert|29.6|-|32|cm|in}}, with the male weighing {{convert|430|-|537|g|oz}} and the female weighing {{convert|512|-|615|g|oz}}.<ref name=Cabot/> The plumage of this bird varies somewhat; however there are some features that can be quantified, such as, in general the color is a brownish black to a deep sooty brown. Also, the head and throat tend to be darker than the rest of the body, with a reddish tinge to its crown and nape. The legs and feet are pink and the bill has a dark upper mandible and a pinkish lower mandible. Its bill is longer and heavier than that of the cinereous tinamou. Finally, its iris is red.<ref name=Cabot/> |
||
The juvenile form of the bird is similar in coloring to the adult; however it does have barring on its under-parts and also on its wings with a cinnamon tinge to them.<ref name=Cabot/> |
The juvenile form of the bird is similar in coloring to the adult; however it does have barring on its under-parts and also on its wings with a cinnamon tinge to them.<ref name=Cabot/> |
||
==Range and habitat== |
==Range and habitat== |
||
Its range is |
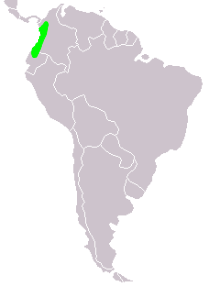
Its range is extreme northern coastal [[Ecuador]] north into coastal [[Colombia]],<ref name="Clements" /> as far north as [[Utria National Park]] ([[Bahia de Capica]]).<ref name="iucn status 12 November 2021" /> This tinamou lives in lowland moist forest in sub-tropical to tropical regions, and will also choose to live in a mature secondary forest.<ref name=Cabot/> It has also proven that it can survive in forests that have been logged.<ref name="BLI" /> In Colombia it will choose the coastal lowlands and hills up to {{convert|500|m|ft}}, although it has been found as high as {{convert|900|m|ft}}.<ref name=Cabot/> |
||
The only 2 documented sightings are at Playa de oro reserva de los tigrillos, which is in Ecuador about {{convert|20|km|miles}} north of [[Cotacachi Cayapas Ecological Reserve]] and at [[Milipe Bird Sanctuary]] about {{convert|15|km|miles}} west of [[Maquipucuna]], also in [[Ecuador]].<ref name=eBird>{{cite web|url=http://ebird.org/ebird/map/bertin1?neg=true&env.minX=-83.01161719768254&env.minY=-4.792892862650885&env.maxX=-40.82411719768254&env.maxY=13.48825266723504&zh=true&gp=true&mr=1-12&bmo=1&emo=12&yr=1900-2013&byr=1900&eyr=2013|work=eBird|title = Berlepsch's Tinamou|date=2013-04-13}}</ref> |
|||
==Behavior== |
==Behavior== |
||
The Berlepsch's |
The Berlepsch's tinamou is considered a sedentary bird. |
||
===Feeding=== |
===Feeding=== |
||
There is little species specific information on Berlepsch's |
There is little species specific information on Berlepsch's tinamou, so scientists believe that like other members of ''[[Crypturellus]]'' its diet focus is on fleshy fruit, which it prefers to eat off the ground, but will pick it off lower hanging branches. Like other tinamous, the Berlepsch's also eat small amounts of [[invertebrates]], flower buds, tender leaves, seeds, and roots. |
||
===Breeding=== |
===Breeding=== |
||
They breed in February in Colombia.<ref name=Cabot/> As a forest species, they would choose the months of plentiful food and that would mean the summer. |
|||
The male, like other |
The male, like other tinamou, incubates the eggs which may come from as many as 4 different females, and then will raise them until they are ready to be on their own, usually 2–3 weeks. The nest is located on the ground in dense brush or between raised root buttresses.<ref name="Davies" /> |
||
==Conservation== |
==Conservation== |
||
The [[IUCN]] classifies the Berlepshch's |
The [[IUCN]] classifies the Berlepshch's tinamou as [[Least Concern]],<ref name="iucn status 12 November 2021" /> and it has an occurrence range of {{convert|60000|km2|sqmi|abbr=on}}.<ref name="BLI" /> |
||
==Footnotes== |
==Footnotes== |
||
{{ |
{{Reflist}} |
||
==References== |
==References== |
||
* {{cite web| url=http://www.birdlife.org/datazone/species/index.html?action=SpcHTMDetails.asp&sid=19&m=0 | title=Berlepsch's Tinamou - BirdLife Species Factsheet | |
* {{cite web| url=http://www.birdlife.org/datazone/species/index.html?action=SpcHTMDetails.asp&sid=19&m=0 | title=Berlepsch's Tinamou - BirdLife Species Factsheet | access-date=8 Feb 2009 | author=BirdLife International | year=2008| work=Data Zone}} |
||
* {{cite web| url= |
* {{cite web | url=http://taxonomicon.taxonomy.nl/TaxonTree.aspx?id=51330&src=0 | title=Taxon: Species ''Crypturellus berlepschi'' | access-date=25 July 2017 | editor-last=Brands | editor-first=Sheila | publisher=The Taxonomicon |website=taxonomicon.taxonomy.nl}} |
||
* {{cite book |last1=Clements |first1=James |title=The Clements Checklist of the Birds of the World |edition= |
* {{cite book |last1=Clements |first1=James |title=The Clements Checklist of the Birds of the World |edition=6th |year=2007 |publisher= Cornell University Press|location=Ithaca, NY |isbn=978-0-8014-4501-9 }} |
||
* {{cite encyclopedia |last=Davies |first=S.J.J.F.|editor1-first=Michael |editor1-last= Hutchins|encyclopedia=Grzimek's Animal Life Encyclopedia |title=Tinamous |edition= |
* {{cite encyclopedia |last=Davies |first=S.J.J.F.|editor1-first=Michael |editor1-last= Hutchins|encyclopedia=Grzimek's Animal Life Encyclopedia |title=Tinamous |edition=2nd |year=2003 |publisher=Gale Group|volume=8 Birds I Tinamous and Ratites to Hoatzins |location=Farmington Hills, MI|isbn=0-7876-5784-0 |pages=57–59}} |
||
* {{cite book |last1=Gotch |first1=A. F. |title=Latin Names Explained. A Guide to the Scientific Classifications of Reptiles, Birds & Mammals|year= 1995 | |
* {{cite book |last1=Gotch |first1=A. F. |title=Latin Names Explained. A Guide to the Scientific Classifications of Reptiles, Birds & Mammals|year= 1995 |orig-year=1979 |publisher=Facts on File |location=New York, NY|isbn=0-8160-3377-3|page=183|chapter=Tinamous}} |
||
{{Tinamous}} |
{{Tinamous}} |
||
{{Taxonbar|from=Q793573}} |
|||
[[Category:Crypturellus]] |
[[Category:Crypturellus|Berlepsch's tinamou]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Tinamous of South America|Berlepsch's tinamou]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Birds of Colombia]] |
||
[[Category:Birds of Ecuador |
[[Category:Birds of Ecuador]] |
||
[[Category:Birds of |
[[Category:Birds of Tumbes-Chocó-Magdalena]] |
||
[[Category:Birds described in 1897|Berlepsch's tinamou]] |
|||
{{Tinamiformes-stub}} |
|||
Latest revision as of 21:53, 25 February 2024
| Berlepsch's tinamou | |
|---|---|

| |
| Berlepsch's tinamou is the bird in the center. The bird on the left is another species. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Infraclass: | Palaeognathae |
| Order: | Tinamiformes |
| Family: | Tinamidae |
| Genus: | Crypturellus |
| Species: | C. berlepschi
|
| Binomial name | |
| Crypturellus berlepschi (Rothschild, 1897)[2]
| |
| |
Berlepsch's tinamou (Crypturellus berlepschi) is a type of ground bird found in moist forest[3] in northwestern Colombia and northwestern Ecuador.[4]
Taxonomy[edit]
The Berlepsch's tinamou is a monotypic species.[4] All tinamou are from the family Tinamidae, and in the larger scheme are also ratites. Unlike other ratites, tinamous can fly, although in general, they are not strong fliers. All ratites evolved from prehistoric flying birds, and tinamous are the closest living relative of these birds.[5] Until the mid 20th century, this species was considered a sub-species of the cinereous tinamou, but due to its bill size, its ratio of toe and tarsus length and the fact that its plumage has conspicuous differences from that of the cinereous tinamou created enough of a question for the new species to be named.[6]
Etymology[edit]
Crypturellus is formed from three Latin or Greek words. kruptos meaning covered or hidden, oura meaning tail, and ellus meaning diminutive. Therefore, Crypturellus means small hidden tail.[7] berlepschi comes from the Latin form of Berlepsch to commemorate the German ornithologist and collector Hans von Berlepsch.[8]
Description[edit]
Berlepsch's tinamou is a medium-sized bird, about 29.6–32 centimetres (11.7–12.6 in), with the male weighing 430–537 grams (15.2–18.9 oz) and the female weighing 512–615 grams (18.1–21.7 oz).[6] The plumage of this bird varies somewhat; however there are some features that can be quantified, such as, in general the color is a brownish black to a deep sooty brown. Also, the head and throat tend to be darker than the rest of the body, with a reddish tinge to its crown and nape. The legs and feet are pink and the bill has a dark upper mandible and a pinkish lower mandible. Its bill is longer and heavier than that of the cinereous tinamou. Finally, its iris is red.[6]
The juvenile form of the bird is similar in coloring to the adult; however it does have barring on its under-parts and also on its wings with a cinnamon tinge to them.[6]
Range and habitat[edit]
Its range is extreme northern coastal Ecuador north into coastal Colombia,[4] as far north as Utria National Park (Bahia de Capica).[1] This tinamou lives in lowland moist forest in sub-tropical to tropical regions, and will also choose to live in a mature secondary forest.[6] It has also proven that it can survive in forests that have been logged.[3] In Colombia it will choose the coastal lowlands and hills up to 500 metres (1,600 ft), although it has been found as high as 900 metres (3,000 ft).[6]
The only 2 documented sightings are at Playa de oro reserva de los tigrillos, which is in Ecuador about 20 kilometres (12 mi) north of Cotacachi Cayapas Ecological Reserve and at Milipe Bird Sanctuary about 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) west of Maquipucuna, also in Ecuador.[9]
Behavior[edit]
The Berlepsch's tinamou is considered a sedentary bird.
Feeding[edit]
There is little species specific information on Berlepsch's tinamou, so scientists believe that like other members of Crypturellus its diet focus is on fleshy fruit, which it prefers to eat off the ground, but will pick it off lower hanging branches. Like other tinamous, the Berlepsch's also eat small amounts of invertebrates, flower buds, tender leaves, seeds, and roots.
Breeding[edit]
They breed in February in Colombia.[6] As a forest species, they would choose the months of plentiful food and that would mean the summer.
The male, like other tinamou, incubates the eggs which may come from as many as 4 different females, and then will raise them until they are ready to be on their own, usually 2–3 weeks. The nest is located on the ground in dense brush or between raised root buttresses.[5]
Conservation[edit]
The IUCN classifies the Berlepshch's tinamou as Least Concern,[1] and it has an occurrence range of 60,000 km2 (23,000 sq mi).[3]
Footnotes[edit]
- ^ a b c BirdLife International (2016). "Crypturellus berlepschi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22678163A92759082. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22678163A92759082.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ^ Brands, S. (2008)
- ^ a b c BirdLife International (2008)
- ^ a b c Clements, J (2007)
- ^ a b Davies, S. J. J. F. (2003)
- ^ a b c d e f g Cabot, J.; Carboneras, C.; Folch, A.; de Juanca, E.; Llimona, F.; Matheu, E. (1992). "Tinamiformes". In del Hoyo, J. (ed.). Handbook of the Birds of the World. Vol. I: Ostrich to Ducks. Barcelona, Spain: Lynx Edicions.
- ^ Gotch, A. F. (1195)
- ^ Boelens, Bo; Michael Watkins (2003). Whose Bird? Men and Women Commemorated in the Common Names of Birds. London: Christopher Helm. p. 50.
- ^ "Berlepsch's Tinamou". eBird. 2013-04-13.
References[edit]
- BirdLife International (2008). "Berlepsch's Tinamou - BirdLife Species Factsheet". Data Zone. Retrieved 8 Feb 2009.
- Brands, Sheila (ed.). "Taxon: Species Crypturellus berlepschi". taxonomicon.taxonomy.nl. The Taxonomicon. Retrieved 25 July 2017.
- Clements, James (2007). The Clements Checklist of the Birds of the World (6th ed.). Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press. ISBN 978-0-8014-4501-9.
- Davies, S.J.J.F. (2003). "Tinamous". In Hutchins, Michael (ed.). Grzimek's Animal Life Encyclopedia. Vol. 8 Birds I Tinamous and Ratites to Hoatzins (2nd ed.). Farmington Hills, MI: Gale Group. pp. 57–59. ISBN 0-7876-5784-0.
- Gotch, A. F. (1995) [1979]. "Tinamous". Latin Names Explained. A Guide to the Scientific Classifications of Reptiles, Birds & Mammals. New York, NY: Facts on File. p. 183. ISBN 0-8160-3377-3.

