CPU socket: Difference between revisions
m Fixing broken anchor: Incorrect capitalization/spaced section title #Ryzen 8000 series→List of AMD Ryzen processors#Ryzen 8000 series |
No edit summary Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit Disambiguation links added |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
In [[computer hardware]], a '''CPU socket''' or '''CPU slot''' contains one or more mechanical components providing mechanical and electrical connections between a [[microprocessor]] and a [[printed circuit board]] (PCB). This allows for placing and replacing the [[central processing unit]] (CPU) without soldering. |
In [[computer hardware]], a '''CPU socket''' or '''CPU slot''' contains one or more mechanical components providing mechanical and electrical connections between a [[microprocessor]] and a [[printed circuit board]] (PCB). This allows for placing and replacing the [[central processing unit]] (CPU) without soldering. |
||
Common sockets have retention clips that apply a constant force, which must be overcome when a device is inserted. For chips with many pins, [[zero insertion force]] (ZIF) sockets are preferred. Common sockets include [[Pin grid array|Pin Grid Array]] (PGA) or [[Land grid array|Land Grid Array]] (LGA). These designs apply a [[compression (physics)|compression force]] once either a handle (PGA type) or a surface plate (LGA type) is put into place. This provides superior mechanical retention while avoiding the risk of bending [[Lead (electronics)|pins]] when inserting the chip into the socket. Certain devices use [[Ball grid array|Ball Grid Array]] (BGA) sockets, although these require soldering and are generally not considered user replaceable. |
Common sockets have retention clips that apply a constant force, which must be overcome when a device is inserted. For chips with many pins, [[zero insertion force]] (ZIF) sockets are preferred. Common sockets include [[Pin grid array|Pin Grid Array]] (PGA) or [[Land grid array|Land Grid Array]] (LGA). These designs apply a [[compression (physics)|compression force]] once either a handle (PGA type) or a surface plate (LGA type) is put into place. This provides superior mechanical retention while avoiding the risk of bending [[Lead (electronics)|pins]] when inserting the chip into the [[socket]]. Certain devices use [[Ball grid array|Ball Grid Array]] (BGA) sockets, although these require soldering and are generally not considered user replaceable. |
||
CPU sockets are used on the [[motherboard]] in [[desktop computer|desktop]] and [[server (computing)|server]] computers. Because they allow easy swapping of components, they are also used for prototyping new circuits. [[Laptop]]s typically use [[surface-mount technology|surface-mount]] CPUs, which take up less space on the motherboard than a socketed part. |
CPU sockets are used on the [[motherboard]] in [[desktop computer|desktop]] and [[server (computing)|server]] computers. Because they allow easy swapping of components, they are also used for prototyping new circuits. [[Laptop]]s typically use [[surface-mount technology|surface-mount]] CPUs, which take up less space on the motherboard than a socketed part. |
||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
! style="text-align:left;| [[Socket 2]] |
! style="text-align:left;| [[Socket 2]] |
||
| ? |
| ? |
||
| Intel [[80486]]<br />Intel Pentium |
| Intel [[80486]]<br />Intel [[Pentium OverDrive]] (P24T)<br />Intel DX4<br />AMD 486<br />AMD 5x86<br />Cyrix 486<br />Cyrix 5x86 |
||
| |
| |
||
| [[Pin grid array|PGA]] |
| [[Pin grid array|PGA]] |
||
| Line 86: | Line 86: | ||
! style="text-align:left;"| [[Socket 3]] |
! style="text-align:left;"| [[Socket 3]] |
||
| 1991 |
| 1991 |
||
| Intel [[80486]]<br />Intel Pentium |
| Intel [[80486]]<br />Intel [[Pentium OverDrive]] (P24T)<br />Intel DX4<br />AMD 486<br />AMD 5x86<br />Cyrix 486<br />Cyrix 5x86<br />IBM Blue Lightning |
||
| |
| |
||
| [[Pin grid array|PGA]] |
| [[Pin grid array|PGA]] |
||
| Line 163: | Line 163: | ||
| 66–133 MHz |
| 66–133 MHz |
||
| Celeron (Covington, Mendocino)<br />Pentium II (Klamath, Deschutes)<br />Pentium III (Katmai)- all versions<br />Pentium III (coppermine) |
| Celeron (Covington, Mendocino)<br />Pentium II (Klamath, Deschutes)<br />Pentium III (Katmai)- all versions<br />Pentium III (coppermine) |
||
|- valign="top" |
|||
|- style="vertical-align:top;" |
|- style="vertical-align:top;" |
||
! style="text-align:left;| [[Super Socket 7]] |
! style="text-align:left;| [[Super Socket 7]] |
||
| Line 484: | Line 483: | ||
| 5.7 GT/s |
| 5.7 GT/s |
||
| used for Intel 2nd generation, 3rd generation processors. |
| used for Intel 2nd generation, 3rd generation processors. |
||
Sandy Bridge supports 20 [[PCI Express|PCIe]] 2.0 lanes.<br />Ivy Bridge supports 40 [[PCI Express|PCIe]] 3.0 lanes.<br />Intel Mainstream Socket. |
Sandy Bridge supports 20 [[PCI Express|PCIe]] 2.0 lanes.<br />Ivy Bridge supports 40 [[PCI Express|PCIe]] 3.0 lanes.<br />Intel Mainstream Socket. |
||
| Line 527: | Line 525: | ||
| 3.2 GT/s |
| 3.2 GT/s |
||
| used for 1st generation Mobile APUs |
| used for 1st generation Mobile APUs |
||
|- |
|||
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" |
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" |
||
! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket AM3+]] |
! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket AM3+]] |
||
| 2011 |
| 2011 |
||
| AMD [[Bulldozer (processor)#2nd Generation Piledriver core|FX Vishera]]<br />AMD [[Bulldozer (microarchitecture)|FX Zambezi]]<br />AMD [[Phenom II]]<br />AMD [[Athlon II]]<br />AMD [[Sempron]] |
| AMD [[Bulldozer (processor)#2nd Generation Piledriver core|FX Vishera]]{{Broken anchor|date=2024-09-19|bot=User:Cewbot/log/20201008/configuration|target_link=Bulldozer (processor)#2nd Generation Piledriver core|reason= The anchor (2nd Generation Piledriver core) [[Special:Diff/546495333|has been deleted]].}}<br />AMD [[Bulldozer (microarchitecture)|FX Zambezi]]<br />AMD [[Phenom II]]<br />AMD [[Athlon II]]<br />AMD [[Sempron]] |
||
| Desktop |
| Desktop |
||
| [[Pin grid array|PGA]] |
| [[Pin grid array|PGA]] |
||
| Line 538: | Line 535: | ||
| 3.2 GT/s |
| 3.2 GT/s |
||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|||
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" |
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" |
||
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 1356]]/<br />[[Socket B2]] |
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 1356]]/<br />[[Socket B2]] |
||
| Line 549: | Line 545: | ||
| 3.2–4.0 GT/s |
| 3.2–4.0 GT/s |
||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|||
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" |
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" |
||
! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket FM2]] |
! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket FM2]] |
||
| Line 560: | Line 555: | ||
| ? |
| ? |
||
| used for 2nd generation APUs |
| used for 2nd generation APUs |
||
|- |
|||
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" |
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" |
||
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 1150]]/<br />[[Socket H3]] |
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 1150]]/<br />[[Socket H3]] |
||
| Line 571: | Line 565: | ||
| ? |
| ? |
||
| used for Intel's 4th generation (Haswell/Haswell Refresh), the handful of intel 5th generation processors |
| used for Intel's 4th generation (Haswell/Haswell Refresh), the handful of intel 5th generation processors |
||
|- |
|||
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" |
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" |
||
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[rPGA 946B/947]]/<br />[[Intel Socket G3|Socket G3]] |
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[rPGA 946B/947]]/<br />[[Intel Socket G3|Socket G3]] |
||
| Line 582: | Line 575: | ||
| 5.0 GT/s |
| 5.0 GT/s |
||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|||
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" |
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" |
||
! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket FM2+]] |
! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket FM2+]] |
||
| Line 593: | Line 585: | ||
| ? |
| ? |
||
| Compatible with [[AMD APU]]s such as "[[AMD Accelerated Processing Unit#Richland|Richland" and "Trinity]]" |
| Compatible with [[AMD APU]]s such as "[[AMD Accelerated Processing Unit#Richland|Richland" and "Trinity]]" |
||
|- |
|||
|- |
|||
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" |
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" |
||
! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket AM1]] |
! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket AM1]] |
||
| Line 605: | Line 595: | ||
| ? |
| ? |
||
| Compatible with [[AMD APU]]s such as "[[AMD Accelerated Processing Unit#Kabini|Kabini]]" |
| Compatible with [[AMD APU]]s such as "[[AMD Accelerated Processing Unit#Kabini|Kabini]]" |
||
|- |
|||
|- |
|||
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" |
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" |
||
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;" | [[LGA 2011-v3]] |
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;" | [[LGA 2011-v3]] |
||
| Line 637: | Line 625: | ||
| ? |
| ? |
||
| used for Intel's Xeon Phi x200 and Xeon Scalable processors |
| used for Intel's Xeon Phi x200 and Xeon Scalable processors |
||
|- |
|||
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" |
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" |
||
! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket AM4]] |
! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket AM4]] |
||
| Line 663: | Line 650: | ||
| Depends on DDR4 speed |
| Depends on DDR4 speed |
||
| compatible with AMD [[Ryzen]] 9, [[Ryzen]] 7, [[Ryzen]] 5 & [[Ryzen]] 3 Zen based processors |
| compatible with AMD [[Ryzen]] 9, [[Ryzen]] 7, [[Ryzen]] 5 & [[Ryzen]] 3 Zen based processors |
||
|- |
|||
|- |
|||
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" |
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" |
||
! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket SP3]] |
! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket SP3]] |
||
| Line 675: | Line 660: | ||
| Depends on DDR4 speed |
| Depends on DDR4 speed |
||
| compatible with AMD Epyc processors |
| compatible with AMD Epyc processors |
||
|- |
|||
|- |
|||
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" |
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" |
||
! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket TR4]]/<br />Socket SP3r2 |
! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket TR4]]/<br />Socket SP3r2 |
||
| Line 687: | Line 670: | ||
| Depends on DDR4 speed |
| Depends on DDR4 speed |
||
| compatible with AMD Ryzen Threadripper processors |
| compatible with AMD Ryzen Threadripper processors |
||
|- |
|||
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" |
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" |
||
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 2066]]/<br />[[Socket R4]] |
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 2066]]/<br />[[Socket R4]] |
||
| Line 698: | Line 680: | ||
| ? |
| ? |
||
| Used for Intel's 7th generation (Skylake-X & Kaby Lake-X & Cascade Lake-X) series of Core-X processors |
| Used for Intel's 7th generation (Skylake-X & Kaby Lake-X & Cascade Lake-X) series of Core-X processors |
||
|- |
|||
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" |
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" |
||
! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket sTRX4]]/<br />Socket SP3r3 |
! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket sTRX4]]/<br />Socket SP3r3 |
||
| Line 709: | Line 690: | ||
| Depends on DDR4 speed |
| Depends on DDR4 speed |
||
| compatible with 3rd generation AMD Ryzen Threadripper processors |
| compatible with 3rd generation AMD Ryzen Threadripper processors |
||
|- |
|||
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" |
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" |
||
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 4189]] |
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 4189]] |
||
| Line 720: | Line 700: | ||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|||
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" |
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" |
||
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 1200]] |
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 1200]] |
||
| Line 731: | Line 710: | ||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|||
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" |
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" |
||
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 1700]] |
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 1700]] |
||
| Line 743: | Line 721: | ||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|||
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" |
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" |
||
! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket sWRX8]] |
! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket sWRX8]] |
||
| Line 751: | Line 728: | ||
| [[Land grid array|LGA]] |
| [[Land grid array|LGA]] |
||
| 4094 |
| 4094 |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 773: | Line 750: | ||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
|Used for Epyc Genoa and Milan |
| Used for Epyc Genoa and Milan |
||
|- |
|||
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" |
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" |
||
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 4677]] |
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 4677]] |
||
| Line 795: | Line 771: | ||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| ⚫ | |||
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" |
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" |
||
! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket sTR5]] |
! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket sTR5]] |
||
| Line 806: | Line 781: | ||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 1851]] |
|||
| 2024 |
|||
| Intel [[Meteor Lake]]-PS (Core Ultra Series 1)<br>Intel [[Arrow Lake (microprocessor)|Arrow Lake]] (Core Ultra 200S Series)<br>{{abbr|TBA|to be announced}} |
|||
| Desktop |
|||
| [[Land grid array|LGA]] |
|||
| 1851 |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" |
|- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" |
||
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 7529]] |
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 7529]] |
||
| Line 814: | Line 798: | ||
| [[Land grid array|LGA]] |
| [[Land grid array|LGA]] |
||
| 7529 |
| 7529 |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
! |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 968: | Line 942: | ||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
* [http://www.cpushack.net/SocketID.html Socket ID Guide] |
* [http://www.cpushack.net/SocketID.html Socket ID Guide up to 2005] |
||
* [http://pclinks.xtreemhost.com/ CPU Sockets Chart] - A fairly detailed table listing x86 Sockets and associated attributes. |
* [http://pclinks.xtreemhost.com/ CPU Sockets Chart] - A fairly detailed table listing x86 Sockets and associated attributes. |
||
* [http://www.techpowerup.com/cpudb/ techPowerUp! CPU Database] |
* [http://www.techpowerup.com/cpudb/ techPowerUp! CPU Database] |
||
Latest revision as of 16:11, 3 November 2024
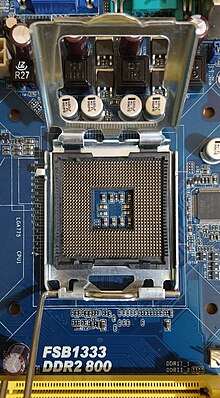

In computer hardware, a CPU socket or CPU slot contains one or more mechanical components providing mechanical and electrical connections between a microprocessor and a printed circuit board (PCB). This allows for placing and replacing the central processing unit (CPU) without soldering.
Common sockets have retention clips that apply a constant force, which must be overcome when a device is inserted. For chips with many pins, zero insertion force (ZIF) sockets are preferred. Common sockets include Pin Grid Array (PGA) or Land Grid Array (LGA). These designs apply a compression force once either a handle (PGA type) or a surface plate (LGA type) is put into place. This provides superior mechanical retention while avoiding the risk of bending pins when inserting the chip into the socket. Certain devices use Ball Grid Array (BGA) sockets, although these require soldering and are generally not considered user replaceable.
CPU sockets are used on the motherboard in desktop and server computers. Because they allow easy swapping of components, they are also used for prototyping new circuits. Laptops typically use surface-mount CPUs, which take up less space on the motherboard than a socketed part.
As the pin density increases in modern sockets, increasing demands are placed on the printed circuit board fabrication technique, which permits the large number of signals to be successfully routed to nearby components. Likewise, within the chip carrier, the wire bonding technology also becomes more demanding with increasing pin counts and pin densities. Each socket technology will have specific reflow soldering requirements. As CPU and memory frequencies increase, above 30 MHz or thereabouts, electrical signalling increasingly shifts to differential signaling over parallel buses, bringing a new set of signal integrity challenges. The evolution of the CPU socket amounts to a coevolution of all these technologies in tandem.
Modern CPU sockets are almost always designed in conjunction with a heat sink mounting system, or in lower power devices, other thermal considerations.
Function
[edit]A CPU socket is made of plastic, and often comes with a lever or latch, and with metal contacts for each of the pins or lands on the CPU. Many packages are keyed to ensure the proper insertion of the CPU. CPUs with a PGA (pin grid array) package are inserted into the socket and, if included, the latch is closed. CPUs with an LGA (land grid array) package are inserted into the socket, the latch plate is flipped into position atop the CPU, and the lever is lowered and locked into place, pressing the CPU's contacts firmly against the socket's lands and ensuring a good connection, as well as increased mechanical stability.
List
[edit]80x86
[edit]Table legend:
| Socket name |
Year of introduction | CPU families supported | Computer type | Package | Pin count | Pin pitch (mm) |
Bus clock & transfers |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIP | 1970s | Intel 8086 Intel 8088 |
DIP | 40 | 2.54 | 5/10 MHz | ||
| PLCC | ? | Intel 80186 Intel 80286 Intel 80386 |
PLCC | 68 to 132 | 1.27 | 6–40 MHz | ||
| PGA 168 | ? | Intel 80486 AMD 486 Cyrix 486 |
PGA | 168 | 2.54 | 16–50 MHz | Sometimes referred to as Socket 0 or Socket 486 | |
| Socket 1 | 1989 | Intel 80486 AMD 486 AMD 5x86 Cyrix 486 Cyrix 5x86 |
PGA | 169 | 2.54 | 16–50 MHz | ||
| Socket 2 | ? | Intel 80486 Intel Pentium OverDrive (P24T) Intel DX4 AMD 486 AMD 5x86 Cyrix 486 Cyrix 5x86 |
PGA | 238 | 2.54 | 16–50 MHz | ||
| Socket 3 | 1991 | Intel 80486 Intel Pentium OverDrive (P24T) Intel DX4 AMD 486 AMD 5x86 Cyrix 486 Cyrix 5x86 IBM Blue Lightning |
PGA | 237 | 2.54 | 16–50 MHz[a] | ||
| Socket 4 | 1993 | Intel Pentium | PGA | 273 | ? | 60–100 MHz | ||
| Socket 5 | 1994 | Intel Pentium AMD K5 Cyrix 6x86 IDT WinChip C6 IDT WinChip 2 |
PGA | 320 | ? | 50–100 MHz | ||
| Socket 6 | ? | Intel 80486 | PGA | 235 | ? | ? | Designed but not used | |
| Socket 463/ Socket NexGen |
1994 | NexGen Nx586 | PGA | 463 | ? | 37.5–66 MHz | ||
| Socket 7 | 1994 | Intel Pentium Intel Pentium MMX AMD K6 |
PGA | 321 | ? | 50–66 MHz | It is possible to use Socket 7 processors in a Socket 5. An adapter is required, or if one is careful, a socket 7 can be pulled off its pins and put onto a socket 5 board, allowing the use of socket 7 processors. | |
| Socket 8 | 1995 | Intel Pentium Pro | PGA | 387 | ? | 60–66 MHz | ||
| Slot 1 | 1997 | Intel Pentium II Intel Pentium III |
Desktop | Slot | 242 | ? | 66–133 MHz | Celeron (Covington, Mendocino) Pentium II (Klamath, Deschutes) Pentium III (Katmai)- all versions Pentium III (coppermine) |
| Super Socket 7 | 1998 | AMD K6-2 AMD K6-III Rise mP6 Cyrix MII |
PGA | 321 | ? | 66–100 MHz | Backward compatible with Socket 5 and Socket 7 processors. | |
| Slot 2 | 1998 | Intel Pentium II Xeon Intel Pentium III Xeon |
Server | Slot | 330 | ? | 100–133 MHz | |
| Socket 615 | 1999 | Intel Mobile Pentium II Intel Mobile Celeron |
Notebook | PGA | 615 | ? | 66 MHz | |
| Slot A | 1999 | AMD Athlon | Desktop | Slot | 242 | ? | 100 MHz | |
| Socket 370 | 1999 | Intel Pentium III Intel Celeron VIA Cyrix III VIA C3 |
Desktop | PGA | 370 | 1.27[1] | 66–133 MHz | |
| Socket A/ Socket 462 |
2000 | AMD Athlon AMD Duron AMD Athlon XP AMD Athlon XP-M AMD Athlon MP AMD Sempron |
Desktop | PGA | 462 | ? | 100–200 MHz 400 MT/s[b] |
|
| Socket 423 | 2000 | Intel Pentium 4 | Desktop | PGA | 423 | 1[2] | 100 MHz 400 MT/s |
Willamette core only. Can accept some of Socket 478 CPU with an adapter |
| Socket 495 | 2000 | Intel Celeron Intel Pentium III |
Notebook | PGA | 495 | 1.27[3] | 66–133 MHz | |
| Socket 603 | 2001 | Intel Xeon | Server | PGA | 603 | 1.27[4] | 100–133 MHz 400–533 MT/s |
|
| Socket 478/ Socket N |
2001 | Intel Pentium 4 Intel Celeron Intel Pentium 4 EE Intel Pentium 4 M |
Desktop | PGA | 478 | 1.27[5] | 100–200 MHz 400–800 MT/s |
|
| Socket 563 | 2002 | AMD Athlon XP-M | Notebook | PGA | 563 | ? | 333 MHz | |
| Socket 604 | 2002 | Intel Xeon | Server | PGA | 604 | 1.27[4] | 100–266 MHz 400–1066 MT/s |
|
| Socket 754 | 2003 | AMD Athlon 64 AMD Sempron AMD Turion 64 |
Desktop | PGA | 754 | 1.27[6] | 200–800 MHz | |
| Socket 940 | 2003 | AMD Opteron AMD Athlon 64 FX |
Desktop Server |
PGA | 940 | 1.27[7] | 200–1000 MHz | |
| Socket 479 | 2003 | Intel Pentium M Intel Celeron M |
Notebook | PGA | 479[8] | ? | 100–133 MHz 400–533 MT/s |
|
| Socket 939 | 2004 | AMD Athlon 64 AMD Athlon 64 FX AMD Athlon 64 X2 AMD Opteron |
Desktop | PGA | 939 | 1.27[9] | 200–1000 MHz | Support of Athlon 64 FX to 1 GHz Support of Opteron limited to 100-series only |
| LGA 775/ Socket T |
2004 | Intel Pentium 4 Intel Pentium D Intel Celeron Intel Celeron D Intel Pentium XE Intel Core 2 Duo Intel Core 2 Quad Intel Xeon |
Desktop | LGA | 775 | 1.09 x 1.17[10] | 1600 MHz | Can accept LGA 771 CPU with slight modification and use of an adapter |
| Socket M | 2006 | Intel Core Solo Intel Core Duo Intel Dual-Core Xeon Intel Core 2 Duo |
Notebook | PGA | 478 | ? | 133–166 MHz 533–667 MT/s |
Replaces Socket 479 |
| LGA 771/ Socket J |
2006 | Intel Xeon | Server | LGA | 771 | 1.09 x 1.17[11] | 1600 MHz | See LGA 775/Socket T above |
| Socket S1 | 2006 | AMD Turion 64 X2 | Notebook | PGA | 638 | 1.27[12] | 200–800 MHz | |
| Socket AM2 | 2006 | AMD Athlon 64 AMD Athlon 64 X2 |
Desktop | PGA | 940 | 1.27[9] | 200–1000 MHz | Replaces Socket 754 and Socket 939 |
| Socket F/ Socket L (Socket 1207FX) |
2006 | AMD Athlon 64 FX AMD Opteron (Socket L only support Athlon 64 FX) |
Desktop Server |
LGA | 1207 | 1.1[13] | Socket L: 1000 MHz in Single CPU mode, 2000 MHz in Dual CPU mode |
Replaces Socket 940 Socket L was intended for enthusiasts who wanted server power in a desktop PC. It is just a re-branded Socket F that doesn't need special RAM, and may have only been used in the Asus L1N64-SLI WS Motherboard. |
| Socket AM2+ | 2007 | AMD Athlon 64 AMD Athlon X2 AMD Phenom AMD Phenom II |
Desktop | PGA | 940 | 1.27[9] | 200–2600 MHz | Separated power planes Replaces Socket AM2 AM2+ Pkg. CPUs can work in Socket AM2 AM2 Pkg. CPUs can work in Socket AM2+ |
| Socket P | 2007 | Intel Core 2 | Notebook | PGA | 478 | ? | 133–266 MHz 533–1066 MT/s |
Replaces Socket M |
| LGA 1366/ Socket B |
2008 | Intel Core i7 (900 series) Intel Xeon (35xx, 36xx, 55xx, 56xx series) |
Desktop Server |
LGA | 1366 | ? | 4.8–6.4 GT/s | Replaces Socket J (LGA 771) in the entry level. |
| Socket AM3 | 2009 | AMD Phenom II AMD Athlon II AMD Sempron AMD Opteron (1300 series) |
Desktop | PGA | 941[14] or 940[15] | 1.27[9] | 200–3200 MHz | Separated power planes Replaces Socket AM2+ AM3 Pkg. CPUs can work in Socket AM2/AM2+ Sempron 140 only |
| rPGA 988A/ Socket G1 |
2009 | Intel Clarksfield Intel Arrandale |
Notebook | rPGA | 988 | 1 | 2.5 GT/s | Replaces Socket P |
| LGA 1156/ Socket H |
2009 | Intel Nehalem (1st gen) Intel Westmere |
Desktop | LGA | 1156 | ? | 2.5 GT/s | DMI bus is a (perhaps modified) PCIe x4 v1.1 interface |
| Socket G34 | 2010 | AMD Opteron (6000 series) | Server | LGA | 1974 | ? | 200–3200 MHz | Replaces Socket F |
| Socket C32 | 2010 | AMD Opteron (4000 series) | Server | LGA | 1207 | ? | 200–3200 MHz | Replaces Socket F, Socket AM3 |
| LGA 1567/ Socket LS |
2010 | Intel Xeon 6500/7500-series | Server | LGA | 1567 | ? | 4.8–6.4 GT/s | |
| LGA 1155/ Socket H2 |
2011/Q1 2011.01.09 |
Intel Sandy Bridge (2nd gen) Intel Ivy Bridge (3rd gen) |
Desktop | LGA | 1155 | ? | 5.7 GT/s | used for Intel 2nd generation, 3rd generation processors.
Sandy Bridge supports 20 PCIe 2.0 lanes. |
| LGA 2011/ Socket R |
2011/Q3 2011.11.14 |
Intel Core i7 3xxx Sandy Bridge-E Intel Core i7 4xxx Ivy Bridge-E Intel Xeon E5 2xxx/4xxx (Sandy Bridge EP) (2/4S) Intel Xeon E5-2xxx/4xxx v2 (Ivy Bridge EP) (2/4S) |
Desktop Server |
LGA | 2011 | ? | 4.8–6.4 GT/s | Sandy Bridge-E/EP and Ivy Bridge-E/EP both support 40 PCIe 3.0 lanes. Using the Xeon focused 2011 socket gives also 4 memory Channels. |
| rPGA 988B/ Socket G2 |
2011 | Intel Core i7 Intel Core i5 Intel Core i3 (2000, 3000 series) |
Notebook | rPGA | 988 | 1 | 2.5 GT/s, 4.8 GT/s | |
| Socket FM1 | 2011 | AMD Llano Processors | Desktop | PGA | 905 | 1.27 | 5.2 GT/s | used for 1st generation APUs |
| Socket FS1 | 2011 | AMD Llano Processors | Notebook | PGA | 722 | 1.27 | 3.2 GT/s | used for 1st generation Mobile APUs |
| Socket AM3+ | 2011 | AMD FX Vishera[broken anchor] AMD FX Zambezi AMD Phenom II AMD Athlon II AMD Sempron |
Desktop | PGA | 942 (CPU 71pin) | 1.27 | 3.2 GT/s | |
| LGA 1356/ Socket B2 |
2012 | Intel Xeon (E5 1400 & 2400 series) | Server | LGA | 1356 | ? | 3.2–4.0 GT/s | |
| Socket FM2 | 2012 | AMD Trinity Processors | Desktop | PGA | 904 | 1.27 | ? | used for 2nd generation APUs |
| LGA 1150/ Socket H3 |
2013 | Intel Haswell (4th gen) Intel Haswell Refresh Intel Broadwell (5th gen) |
Desktop | LGA | 1150 | ? | ? | used for Intel's 4th generation (Haswell/Haswell Refresh), the handful of intel 5th generation processors |
| rPGA 946B/947/ Socket G3 |
2013 | Intel Haswell | Notebook | rPGA | 946 | 1 | 5.0 GT/s | |
| Socket FM2+ | 2014 | AMD Kaveri AMD Godavari |
Desktop | PGA | 906 | 1.27 | ? | Compatible with AMD APUs such as "Richland" and "Trinity" |
| Socket AM1 | 2014 | AMD Athlon AMD Sempron |
Desktop | PGA | 721 | 1.27 | ? | Compatible with AMD APUs such as "Kabini" |
| LGA 2011-v3 | 2014 (August and September) |
Haswell-E Haswell-EP |
Desktop | LGA | 2011 | ? | Up to 68 GB/sec. Depends on DDR4 speed and channel count. |
Up to 40 PCIe 3.0 lanes. Up to 4 memory Channels. |
| LGA 1151/ Socket H4 |
2015 | Intel Skylake (6th gen) Intel Kaby Lake (7th gen) Intel Coffee Lake (8th gen) Intel Coffee Lake Refresh (9th gen) |
Desktop | LGA | 1151 | ? | 5 GT/s - 8 GT/s | used for Intel's 6th generation (Skylake), 7th generation (Kaby Lake), 8th generation (Coffee Lake) processors, and 9th generation (Coffee Lake Refresh) processors |
| LGA 3647 | 2016 | Intel Xeon Phi Intel Skylake-SP |
Server | LGA | 3647 | ? | ? | used for Intel's Xeon Phi x200 and Xeon Scalable processors |
| Socket AM4 | 2016 |
AMD Athlon Bristol Ridge
|
Desktop | PGA | 1331 | 1 | Depends on DDR4 speed | compatible with AMD Ryzen 9, Ryzen 7, Ryzen 5 & Ryzen 3 Zen based processors |
| Socket SP3 | 2017 | AMD Epyc Naples AMD Epyc Rome AMD Epyc Milan |
Server | LGA | 4094 | ? | Depends on DDR4 speed | compatible with AMD Epyc processors |
| Socket TR4/ Socket SP3r2 |
2017 | AMD Ryzen Threadripper (1000 series) AMD Ryzen Threadripper (2000 series) |
Desktop | LGA | 4094 | ? | Depends on DDR4 speed | compatible with AMD Ryzen Threadripper processors |
| LGA 2066/ Socket R4 |
2017 | Intel Skylake-X Intel Kaby Lake-X Intel Cascade Lake-X |
Desktop Server |
LGA | 2066 | ? | ? | Used for Intel's 7th generation (Skylake-X & Kaby Lake-X & Cascade Lake-X) series of Core-X processors |
| Socket sTRX4/ Socket SP3r3 |
2019 | AMD Ryzen Threadripper (3000 series) | Desktop | LGA | 4094 | ? | Depends on DDR4 speed | compatible with 3rd generation AMD Ryzen Threadripper processors |
| LGA 4189 | 2020 | Intel Cooper Lake Intel Ice Lake-SP |
Desktop Server |
LGA | 4189[16] | 0.99[16] | ||
| LGA 1200 | 2020 | Intel Comet Lake (10th gen) Intel Rocket Lake (11th gen) |
Desktop | LGA | 1200 | |||
| LGA 1700 | 2021 | Intel Alder Lake (12th gen) Intel Raptor Lake (13th gen) Intel Raptor Lake (14th gen) |
Desktop | LGA | 1700 | |||
| Socket sWRX8 | 2022 | AMD Ryzen Threadripper Pro (5000 series) | Desktop | LGA | 4094 | |||
| Socket AM5 | 2022 | AMD Ryzen 7000 series AMD Ryzen 8000 series (APU) |
Desktop | LGA | 1718 | Zen 4 Ryzen CPUs | ||
| Socket SP5 | 2022 | AMD Epyc Genoa | Server | LGA | 6096 | Used for Epyc Genoa and Milan | ||
| LGA 4677 | 2022 | Intel Sapphire Rapids | Server | LGA | 4677 | |||
| Socket SP6 | 2023 | AMD Epyc Siena | Server | LGA | 4844 | |||
| Socket sTR5 | 2023 | AMD Ryzen Threadripper AMD Ryzen Threadripper Pro (7000 series) |
Desktop | LGA | 4844 | |||
| LGA 1851 | 2024 | Intel Meteor Lake-PS (Core Ultra Series 1) Intel Arrow Lake (Core Ultra 200S Series) TBA |
Desktop | LGA | 1851 | |||
| LGA 7529 | 2024 | Intel Sierra Forest | Server | LGA | 7529 | |||
| Socket name |
Year of introduction | CPU families supported | Computer type | Package | Pin count | Pin pitch (mm) |
Bus clock & transfers |
Notes |
| Socket name |
Year of introduction | CPU families supported | Computer type | Package | Pin count | Pin pitch (mm) |
Bus clock & transfers |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daughter Card | 1995 | PowerPC 601+ | Desktop | Slot | 146 | ? | 40-60 |
|
| Socket 288 | ? | PowerPC 603+ | Desktop | PGA | 288 | ? | 40-60 |
|
| Socket 431 | 1995 | Alpha 21064/21064A | Desktop | PGA | 431 | ? | 12.5–66.67 MHz | |
| Socket 499 | 1997 | Alpha 21164/21164A | Desktop | PGA | 499 | ? | 15–100 MHz | |
| Socket 587 | 1998 | Alpha 21264 | Desktop | PGA | 587 | ? | 12.5–133 MHz | |
| Slot B | 1999 | Alpha 21264/21264A | Desktop | Slot | 587 | ? | 100 MHz[17] | |
| PAC418 | 2001 | Intel Itanium | Server | PGA | 418 | ? | 133 MHz | |
| PAC611 | 2002 | Intel Itanium 2 HP PA-8800, PA-8900 |
Server | PGA | 611 | ? | 200 MHz | |
| LGA 1248 | 2010 | Intel Itanium 9300-series and up | Server | LGA | 1248 | ? | 4.8-6.4 GT/s | |
| Socket name |
Year of introduction | CPU families supported | Computer type | Package | Pin count | Pin pitch (mm) |
Bus clock & transfers |
Notes |
Slotkets
[edit]Slotkets are special adapters for using socket processors in bus-compatible slot motherboards.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Intel 815 Chipset Family" (PDF). Intel. Retrieved May 4, 2009.
- ^ "423 Pin Socket (PGA423) Design Guidelines" (PDF). Intel. Archived (PDF) from the original on December 29, 2009. Retrieved May 3, 2009.
- ^ "495-Pin and 615-pin micro-PGA ZIF Socket Design Specification Application Note" (PDF). Intel. Retrieved May 3, 2009.
- ^ a b "mPGA 604 Socket Mechanical Design Guide" (PDF). Intel. Retrieved May 3, 2009.
- ^ "Intel Pentium 4 Processor 478-Pin Socket (mPGA478) Design Guidelines" (PDF). Intel. Retrieved May 3, 2009.
- ^ "AMD Sempron Processor Product Data Sheet" (PDF). AMD. Retrieved May 3, 2009.
- ^ "AMD Opteron Processor Product Data Sheet" (PDF). AMD. Retrieved May 3, 2009.
- ^ CPU only has 478 pins, but the socket has 479.
- ^ a b c d "AMD Opteron Processor Product Data Sheet" (PDF). AMD. Retrieved May 3, 2009.
- ^ "LGA 775 Socket Mechanical Design Guide" (PDF). Intel. Retrieved May 4, 2009.
- ^ "LGA771 Socket Mechanical Design Guide" (PDF). Intel. Retrieved May 3, 2009.
- ^ "Low-Profile Socket S1 Design Specification" (PDF). AMD. Retrieved May 3, 2009.
- ^ "Thermal Design Guide for Socket F (1207) Processors" (PDF). AMD. Retrieved May 6, 2009.
- ^ CPU only has 938 pins, but the socket has 941.
- ^ AMD Documentation "Socket AM3 design Specification" (PDF). AMD. Retrieved January 5, 2012.
- ^ a b "LGA 4189 Socket and Hardware" (PDF).
- ^ Hachman, Mark (February 2, 1999). "Alpha camp moves to "Slot B" connector to push further into workstations". EE Times. Retrieved November 10, 2022.
External links
[edit]- Socket ID Guide up to 2005
- CPU Sockets Chart - A fairly detailed table listing x86 Sockets and associated attributes.
- techPowerUp! CPU Database
- Processor sockets
