Laryngeal cancer: Difference between revisions
Citation bot (talk | contribs) Add: s2cid. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Headbomb | Linked from Wikipedia:WikiProject_Academic_Journals/Journals_cited_by_Wikipedia/Sandbox | #UCB_webform_linked 201/403 |
m task, removed: : Official Journal of the European Society for Medical Oncology |
||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
==Risk factors== |
==Risk factors== |
||
The most important risk factor for laryngeal cancer is smoking. Death from laryngeal cancer is 20 times more likely for the heaviest smokers than for their non-smoking peers.<ref>{{cite book | vauthors = Ridge JA, Glisson BS, Lango MN, Feigenberg S, Horwitz EM | chapter = Head and neck tumors. | veditors = Pazdur R, Wagman LD, Camphausen KA, Hoskins W | title = Cancer management: a multidisciplinary approach. | date = 2008 | volume = 11 | issue = 3 | pages = 369 | url = http://thymic.org/uploads/reference_sub/04headneck.pdf }}</ref> Heavy chronic consumption of [[alcohol (drug)|alcohol]], particularly alcoholic spirits, is also a significant risk factor. When present in combination, the usages of alcohol and tobacco appear to have a synergistic effect. Other reported risk factors include being of low socioeconomic status, male sex, or age greater than 55 years.{{ |
The most important risk factor for laryngeal cancer is smoking. Death from laryngeal cancer is 20 times more likely for the heaviest smokers than for their non-smoking peers.<ref>{{cite book | vauthors = Ridge JA, Glisson BS, Lango MN, Feigenberg S, Horwitz EM | chapter = Head and neck tumors. | veditors = Pazdur R, Wagman LD, Camphausen KA, Hoskins W | title = Cancer management: a multidisciplinary approach. | date = 2008 | volume = 11 | issue = 3 | pages = 369 | url = http://thymic.org/uploads/reference_sub/04headneck.pdf }}</ref> Heavy chronic consumption of [[alcohol (drug)|alcohol]], particularly alcoholic spirits, is also a significant risk factor. When present in combination, the usages of alcohol and tobacco appear to have a synergistic effect. Other reported risk factors include being of low socioeconomic status, male sex, or age greater than 55 years.{{citation needed|date=November 2020}} |
||
Occupational exposure to environmental factors such as wood dust, paint fumes, and certain chemicals used in the metalworking, petroleum, plastics, and textile industries<ref name=SG1>{{Cite web|url=https://www.cancersupportcommunity.org/laryngeal-cancer |title= Laryngeal Cancer|access-date= April 7, 2019}}</ref> is also believed to be a risk factor for laryngeal cancers. Infections by some strains of [[Papillomaviridae]] carry some risk of laryngeal carcinoma.<ref name=PAPV1>{{cite journal | vauthors = Torrente MC, Rodrigo JP, Haigentz M, Dikkers FG, Rinaldo A, Takes RP, Olofsson J, Ferlito A | display-authors = 6 | title = Human papillomavirus infections in laryngeal cancer | journal = Head & Neck | volume = 33 | issue = 4 | pages = 581–586 | date = April 2011 | pmid = 20848441 | doi = 10.1002/hed.21421 | publisher = Head Neck | s2cid = 30274997 }}</ref> |
Occupational exposure to environmental factors such as wood dust, paint fumes, and certain chemicals used in the metalworking, petroleum, plastics, and textile industries<ref name=SG1>{{Cite web|url=https://www.cancersupportcommunity.org/laryngeal-cancer |title= Laryngeal Cancer|access-date= April 7, 2019}}</ref> is also believed to be a risk factor for laryngeal cancers. Infections by some strains of [[Papillomaviridae]] carry some risk of laryngeal carcinoma.<ref name=PAPV1>{{cite journal | vauthors = Torrente MC, Rodrigo JP, Haigentz M, Dikkers FG, Rinaldo A, Takes RP, Olofsson J, Ferlito A | display-authors = 6 | title = Human papillomavirus infections in laryngeal cancer | journal = Head & Neck | volume = 33 | issue = 4 | pages = 581–586 | date = April 2011 | pmid = 20848441 | doi = 10.1002/hed.21421 | publisher = Head Neck | s2cid = 30274997 }}</ref> |
||
People with a history of head and [[neck cancer]] are known to be at higher risk (about 25%) of developing a second, separate cancer of the head, neck, or lung. This is likely due to chronic exposure to the [[alcohol and cancer|carcinogenic effects of alcohol]] and [[tobacco]]. In this situation, a [[field change]] effect may occur, where the epithelial tissues start to become diffusely [[dysplastic]] with a reduced threshold for [[Malignancy|malignant]] change. This risk may be reduced by quitting alcohol and tobacco.{{ |
People with a history of head and [[neck cancer]] are known to be at higher risk (about 25%) of developing a second, separate cancer of the head, neck, or lung. This is likely due to chronic exposure to the [[alcohol and cancer|carcinogenic effects of alcohol]] and [[tobacco]]. In this situation, a [[field change]] effect may occur, where the epithelial tissues start to become diffusely [[dysplastic]] with a reduced threshold for [[Malignancy|malignant]] change. This risk may be reduced by quitting alcohol and tobacco.{{citation needed|date=November 2020}} |
||
==Diagnosis== |
==Diagnosis== |
||
[[File:Kehlkopf Schema.png|thumb|left|Larynx and nearby structures<br /> Cavitas nasi: [[Nasal cavity]] <br />Cavis orum: [[oral cavity]]<br />Glottis: [[Larynx]]<br />Plica vocalis: [[Vocal cords]]<br />[[Trachea]] <br />Oesophagus: [[Esophagus]] ]] |
[[File:Kehlkopf Schema.png|thumb|left|Larynx and nearby structures<br /> Cavitas nasi: [[Nasal cavity]] <br />Cavis orum: [[oral cavity]]<br />Glottis: [[Larynx]]<br />Plica vocalis: [[Vocal cords]]<br />[[Trachea]] <br />Oesophagus: [[Esophagus]] ]] |
||
Diagnosis is made by the doctor on the basis of a [[medical history]], [[physical examination]], and special investigations which may include a [[chest x-ray]], [[Computed tomography|CT]] or [[MRI]] scans, and tissue biopsy. The examination of the larynx requires some expertise, which may require specialist referral.{{ |
Diagnosis is made by the doctor on the basis of a [[medical history]], [[physical examination]], and special investigations which may include a [[chest x-ray]], [[Computed tomography|CT]] or [[MRI]] scans, and tissue biopsy. The examination of the larynx requires some expertise, which may require specialist referral.{{citation needed|date=November 2020}} |
||
The [[physical exam]] includes a systematic examination of the whole patient to assess general health and to look for signs of associated conditions and metastatic disease. The neck and [[supraclavicular fossa]] are palpated to feel for cervical [[adenopathy]], other masses, and laryngeal crepitus. The [[oral cavity]] and [[oropharynx]] are examined under direct vision. The larynx may be examined by [[indirect laryngoscopy]] using a small angled mirror with a long handle (akin to a dentist's mirror) and a strong light. Indirect laryngoscopy can be highly effective, but requires skill and practice for consistent results. For this reason, many specialist clinics now use fibre-optic nasal endoscopy where a thin and flexible [[endoscope]], inserted through the [[nostril]], is used to clearly visualise the entire [[pharynx]] and larynx. Nasal endoscopy is a quick and easy procedure performed in clinic. [[Local anaesthetic]] spray may be used.{{ |
The [[physical exam]] includes a systematic examination of the whole patient to assess general health and to look for signs of associated conditions and metastatic disease. The neck and [[supraclavicular fossa]] are palpated to feel for cervical [[adenopathy]], other masses, and laryngeal crepitus. The [[oral cavity]] and [[oropharynx]] are examined under direct vision. The larynx may be examined by [[indirect laryngoscopy]] using a small angled mirror with a long handle (akin to a dentist's mirror) and a strong light. Indirect laryngoscopy can be highly effective, but requires skill and practice for consistent results. For this reason, many specialist clinics now use fibre-optic nasal endoscopy where a thin and flexible [[endoscope]], inserted through the [[nostril]], is used to clearly visualise the entire [[pharynx]] and larynx. Nasal endoscopy is a quick and easy procedure performed in clinic. [[Local anaesthetic]] spray may be used.{{citation needed|date=November 2020}} |
||
If there is a suspicion of cancer, [[biopsy]] is performed, usually under [[general anaesthetic]]. This provides [[histological]] proof of cancer type and grade. If the [[lesion]] appears to be small and well localised, the surgeon may undertake excision biopsy, where an attempt is made to completely remove the tumour at the time of first biopsy. In this situation, the [[pathologist]] will not only be able to confirm the diagnosis, but can also comment on the completeness of excision, i.e., whether the tumour has been completely removed. A full endoscopic examination of the larynx, [[Vertebrate trachea|trachea]], and [[esophagus]] is often performed at the time of biopsy.{{ |
If there is a suspicion of cancer, [[biopsy]] is performed, usually under [[general anaesthetic]]. This provides [[histological]] proof of cancer type and grade. If the [[lesion]] appears to be small and well localised, the surgeon may undertake excision biopsy, where an attempt is made to completely remove the tumour at the time of first biopsy. In this situation, the [[pathologist]] will not only be able to confirm the diagnosis, but can also comment on the completeness of excision, i.e., whether the tumour has been completely removed. A full endoscopic examination of the larynx, [[Vertebrate trachea|trachea]], and [[esophagus]] is often performed at the time of biopsy.{{citation needed|date=November 2020}} |
||
For small [[glottic]] tumours further imaging may be unnecessary. In most cases, tumour staging is completed by scanning the head and neck region to assess the local extent of the tumour and any pathologically enlarged cervical [[lymph node]]s. |
For small [[glottic]] tumours further imaging may be unnecessary. In most cases, tumour staging is completed by scanning the head and neck region to assess the local extent of the tumour and any pathologically enlarged cervical [[lymph node]]s. |
||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
==Staging== |
==Staging== |
||
Laryngeal tumours are classified according to the guidelines set by academic organisations such as the [[National Comprehensive Cancer Network]] (NCCN) .<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.nccn.org/|title=National Comprehensive Cancer Network - Home|website=NCCN}}</ref> Overall classification, also known as "[[Cancer staging|staging]]", can help predict treatment options for patients.<ref name=":0">{{cite book | vauthors = Amin M, Edge S, Greene F, etal | title = AJCC Cancer Staging Manual | location = New York | publisher = Springer | date = 2017 }}</ref> Staging consists of three separate evaluations. The first is of the tumour/cancer itself ("T").<ref name=":0" /> The second is the extent to which adjacent [[ |
Laryngeal tumours are classified according to the guidelines set by academic organisations such as the [[National Comprehensive Cancer Network]] (NCCN) .<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.nccn.org/|title=National Comprehensive Cancer Network - Home|website=NCCN}}</ref> Overall classification, also known as "[[Cancer staging|staging]]", can help predict treatment options for patients.<ref name=":0">{{cite book | vauthors = Amin M, Edge S, Greene F, etal | title = AJCC Cancer Staging Manual | location = New York | publisher = Springer | date = 2017 }}</ref> Staging consists of three separate evaluations. The first is of the tumour/cancer itself ("T").<ref name=":0" /> The second is the extent to which adjacent [[lymph node]]s are involved in the tumour/cancer's spread ("N").<ref name=":0" /> The third is the presence or absence of any distant [[Metastasis|metastases]] ("M).<ref name=":0" /> The specific “staging” criteria for laryngeal cancer, as utilised in the [[National Comprehensive Cancer Network|NCCN]]’s 2019 Guidelines for Head and Neck Cancers,<ref name="Pfister_2020">{{cite journal | vauthors = Pfister DG, Spencer S, Adelstein D, Adkins D, Anzai Y, Brizel DM, Bruce JY, Busse PM, Caudell JJ, Cmelak AJ, Colevas AD, Eisele DW, Fenton M, Foote RL, Galloway T, Gillison ML, Haddad RI, Hicks WL, Hitchcock YJ, Jimeno A, Leizman D, Maghami E, Mell LK, Mittal BB, Pinto HA, Ridge JA, Rocco JW, Rodriguez CP, Shah JP, Weber RS, Weinstein G, Witek M, Worden F, Yom SS, Zhen W, Burns JL, Darlow SD | display-authors = 6 | title = Head and Neck Cancers, Version 2.2020, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology | journal = Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network | volume = 18 | issue = 7 | pages = 873–898 | date = July 2020 | pmid = 32634781 | doi = 10.6004/jnccn.2020.0031 | s2cid = 220405484 }}</ref> are: |
||
=== <u>T</u> === |
=== <u>T</u> === |
||
| Line 90: | Line 90: | ||
* T1B - Both vocal cords |
* T1B - Both vocal cords |
||
T2: Tumour meets at least one of the following criteria: |
T2: Tumour meets at least one of the following criteria: |
||
* extends to supra- or [[Subglottis|sub-glottis]] |
* extends to supra- or [[Subglottis|sub-glottis]] |
||
* impairs vocal cord mobility |
* impairs vocal cord mobility |
||
T3: Tumour meets at least one of the following criteria: |
T3: Tumour meets at least one of the following criteria: |
||
* causes fixation of the vocal cords |
* causes fixation of the vocal cords |
||
| Line 119: | Line 119: | ||
N0: No involvement of neighbouring lymph nodes |
N0: No involvement of neighbouring lymph nodes |
||
N1: Tumour meets ALL of the following criteria: |
N1: Tumour meets ALL of the following criteria: |
||
* involves single lymph node |
* involves single lymph node |
||
* involved lymph node on the same side of the body as tumour |
* involved lymph node on the same side of the body as tumour |
||
* involved lymph node less than 3 |
* involved lymph node less than 3 cm in “greatest dimension” |
||
* lacks extension beyond the lymph node |
* lacks extension beyond the lymph node |
||
N2: Tumour meets ANY of the following criteria |
N2: Tumour meets ANY of the following criteria |
||
* N2A – Same as N1, except size can be between |
* N2A – Same as N1, except size can be between 3–6 cm |
||
* N2B – Same as N2A, except lymph nodes can be multiple, and there is no minimum size |
* N2B – Same as N2A, except lymph nodes can be multiple, and there is no minimum size |
||
* N2C – Same as N2B, except lymph nodes can be on any side of the body |
* N2C – Same as N2B, except lymph nodes can be on any side of the body |
||
| Line 134: | Line 134: | ||
N3: Tumour meets ANY of the following criteria: |
N3: Tumour meets ANY of the following criteria: |
||
* N3A – Same as N1, except size is greater than 6 |
* N3A – Same as N1, except size is greater than 6 cm |
||
* N3B – Tumour obviously extends beyond the lymph node border (regardless of number, size, or location of lymph nodes) |
* N3B – Tumour obviously extends beyond the lymph node border (regardless of number, size, or location of lymph nodes) |
||
| Line 163: | Line 163: | ||
== Treatment == |
== Treatment == |
||
[[File:Kehlkopf.png|thumb|Larynx, removed<br />At right: Fingertip,<br />At the bottom: Holder]] |
[[File:Kehlkopf.png|thumb|Larynx, removed<br />At right: Fingertip,<br />At the bottom: Holder]] |
||
Specific treatment depends on the location, type, and stage of the tumour.<ref name=":2">National Comprehensive Cancer Network, "Evidence Blocks for Head and Neck Cancers," 2019. |
Specific treatment depends on the location, type, and stage of the tumour.<ref name=":2">National Comprehensive Cancer Network, "Evidence Blocks for Head and Neck Cancers," 2019.</ref> Treatment may involve [[surgery]], [[radiotherapy]], or [[chemotherapy]], alone or in combination.<ref name=":2" /> |
||
'''Surgical Treatment''' |
'''Surgical Treatment''' |
||
Surgical treatment may involve partial or full removal of the tumour.<ref name="pmid28325607">{{cite journal | vauthors = Nibu KI, Hayashi R, Asakage T, Ojiri H, Kimata Y, Kodaira T, Nagao T, Nakashima T, Fujii T, Fujii H, Homma A, Matsuura K, Monden N, Beppu T, Hanai N, Kirita T, Kamei Y, Otsuki N, Kiyota N, Zenda S, Omura K, Omori K, Akimoto T, Kawabata K, Kishimoto S, Kitano H, Tohnai I, Nakatsuka T | display-authors = 6 | title = Japanese Clinical Practice Guideline for Head and Neck Cancer | journal = Auris, Nasus, Larynx | volume = 44 | issue = 4 | pages = 375–380 | date = August 2017 | pmid = 28325607 | doi = 10.1016/j.anl.2017.02.004 }}</ref> Neighbouring tissues and structures may or may not be removed, depending on their involvement in the tumour’s structure and spread.<ref name="Grégoire_2010">{{cite journal | vauthors = Grégoire V, Lefebvre JL, Licitra L, Felip E | title = Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: EHNS-ESMO-ESTRO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up | journal = Annals of |
Surgical treatment may involve partial or full removal of the tumour.<ref name="pmid28325607">{{cite journal | vauthors = Nibu KI, Hayashi R, Asakage T, Ojiri H, Kimata Y, Kodaira T, Nagao T, Nakashima T, Fujii T, Fujii H, Homma A, Matsuura K, Monden N, Beppu T, Hanai N, Kirita T, Kamei Y, Otsuki N, Kiyota N, Zenda S, Omura K, Omori K, Akimoto T, Kawabata K, Kishimoto S, Kitano H, Tohnai I, Nakatsuka T | display-authors = 6 | title = Japanese Clinical Practice Guideline for Head and Neck Cancer | journal = Auris, Nasus, Larynx | volume = 44 | issue = 4 | pages = 375–380 | date = August 2017 | pmid = 28325607 | doi = 10.1016/j.anl.2017.02.004 }}</ref> Neighbouring tissues and structures may or may not be removed, depending on their involvement in the tumour’s structure and spread.<ref name="Grégoire_2010">{{cite journal | vauthors = Grégoire V, Lefebvre JL, Licitra L, Felip E | title = Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: EHNS-ESMO-ESTRO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up | journal = Annals of Oncology | volume = 21 | issue = Suppl 5 | pages = v184–6 | date = May 2010 | pmid = 20555077 | doi = 10.1093/annonc/mdq185 }}</ref> [[Total laryngectomy|Full removal of the larynx]] may be necessary in some cases. |
||
'''Adjunct Treatment''' |
'''Adjunct Treatment''' |
||
[[Adjunct treatment]], most commonly the administration of [[chemotherapy]] or [[Radiation therapy|radiotherapy]], may be necessary.<ref name="Grégoire_2010" /> Chemotherapy or radiotherapy may be necessary singly, in combination with each other, or in combination with surgery.<ref name="Pfister_2020" /> Adjunct treatment may be necessary [[Neoadjuvant therapy|prior to surgical treatment]], alongside surgical treatment, or [[Adjuvant therapy|after surgical treatment]]. Clinical decision-making can be difficult in circumstances where the patient is unable to access necessary adjunct treatment. |
[[Adjunct treatment]], most commonly the administration of [[chemotherapy]] or [[Radiation therapy|radiotherapy]], may be necessary.<ref name="Grégoire_2010" /> Chemotherapy or radiotherapy may be necessary singly, in combination with each other, or in combination with surgery.<ref name="Pfister_2020" /> Adjunct treatment may be necessary [[Neoadjuvant therapy|prior to surgical treatment]], alongside surgical treatment, or [[Adjuvant therapy|after surgical treatment]]. Clinical decision-making can be difficult in circumstances where the patient is unable to access necessary adjunct treatment. |
||
'''Multi-Disciplinary Treatment''' |
'''Multi-Disciplinary Treatment''' |
||
Often, successful treatment of and recovery from laryngeal cancer will involve expertise outside of the realms of [[surgery]] or [[oncology]]. [[Physical therapy|Physical therapists]], [[ |
Often, successful treatment of and recovery from laryngeal cancer will involve expertise outside of the realms of [[surgery]] or [[oncology]]. [[Physical therapy|Physical therapists]], [[occupational therapist]]s, [[Speech–language pathology|speech therapists]], [[psychiatrist]]s, [[psychologist]]s, [[Oral and maxillofacial surgery|oral/maxillofacial surgeons]], [[dentist]]s, [[Neurology|neurologists]], [[Neurosurgery|neurosurgeons]], and [[Endocrinology|endocrinologists]] may all become involved in the care of patients with laryngeal cancer. |
||
==Epidemiology== |
==Epidemiology== |
||
Incidence is five in 100,000 (12,500 new cases per year) in the US.<ref name="AMN">{{cite web | vauthors = Beenken SW | title =Laryngeal Cancer (Cancer of the larynx)| url=http://www.health.am/cr/laryngeal-cancer/ | publisher=Armenian Health Network, Health.am | access-date=2007-03-22}}</ref> The [[American Cancer Society]] estimated that 9,510 men and women (7,700 men and 1,810 women) would be diagnosed with and 3,740 men and women would die of laryngeal cancer in 2006.{{ |
Incidence is five in 100,000 (12,500 new cases per year) in the US.<ref name="AMN">{{cite web | vauthors = Beenken SW | title =Laryngeal Cancer (Cancer of the larynx)| url=http://www.health.am/cr/laryngeal-cancer/ | publisher=Armenian Health Network, Health.am | access-date=2007-03-22}}</ref> The [[American Cancer Society]] estimated that 9,510 men and women (7,700 men and 1,810 women) would be diagnosed with and 3,740 men and women would die of laryngeal cancer in 2006.{{citation needed|date=November 2020}} |
||
According to the [[GLOBOCAN]] 2018 estimates of cancer incidence and mortality produced by the [[International Agency for Research on Cancer]], there were 177,422 new cases of laryngeal cancer worldwide in 2018 (1.0% of the global total.) Among worldwide cancer deaths, 94,771 (1.0%) were due to laryngeal cancer. |
According to the [[GLOBOCAN]] 2018 estimates of cancer incidence and mortality produced by the [[International Agency for Research on Cancer]], there were 177,422 new cases of laryngeal cancer worldwide in 2018 (1.0% of the global total.) Among worldwide cancer deaths, 94,771 (1.0%) were due to laryngeal cancer. |
||
Revision as of 23:42, 29 November 2021
| Laryngeal cancer | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Cancer of the larynx, laryngeal carcinoma |
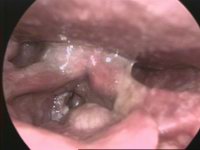 | |
| Larynx cancer - endoscopic view | |
| Specialty | Oncology |
| Deaths | 94,800 (2018) [1] |
Laryngeal cancers are mostly squamous-cell carcinomas, reflecting their origin from the epithelium of the larynx.
Cancer can develop in any part of the larynx. The prognosis is affected by the location of the tumour. For the purposes of staging, the larynx is divided into three anatomical regions: the glottis (true vocal cords, anterior and posterior commissures); the supraglottis (epiglottis, arytenoids and aryepiglottic folds, and false cords); and the subglottis.
Most laryngeal cancers originate in the glottis, with supraglottic and subglottic tumours being less frequent.
Laryngeal cancer may spread by: direct extension to adjacent structures, metastasis to regional cervical lymph nodes, or via the blood stream. The most common site of distant metastases is the lung. Laryngeal cancer occurred in 177,000 people in 2018, and resulted in 94,800 deaths (an increase from 76,000 deaths in 1990).[1][2] Five-year survival rates in the United States are 60.3%.[3]
Signs and symptoms
The symptoms of laryngeal cancer depend on the size and location of the tumour. Symptoms may include the following:[4][5]
- Hoarseness or other voice changes
- A lump in the neck
- A sore throat or feeling that something is stuck in the throat
- Persistent cough
- Stridor - a high-pitched wheezing sound indicative of a narrowed or obstructed airway
- Bad breath
- Earache (due to referred pain)
- Difficulty swallowing
Adverse effects of treatment can include changes in appearance, difficulty eating, dry mouth, or loss of voice that may require learning alternate methods of speaking.[6]
Risk factors
The most important risk factor for laryngeal cancer is smoking. Death from laryngeal cancer is 20 times more likely for the heaviest smokers than for their non-smoking peers.[7] Heavy chronic consumption of alcohol, particularly alcoholic spirits, is also a significant risk factor. When present in combination, the usages of alcohol and tobacco appear to have a synergistic effect. Other reported risk factors include being of low socioeconomic status, male sex, or age greater than 55 years.[citation needed]
Occupational exposure to environmental factors such as wood dust, paint fumes, and certain chemicals used in the metalworking, petroleum, plastics, and textile industries[8] is also believed to be a risk factor for laryngeal cancers. Infections by some strains of Papillomaviridae carry some risk of laryngeal carcinoma.[9]
People with a history of head and neck cancer are known to be at higher risk (about 25%) of developing a second, separate cancer of the head, neck, or lung. This is likely due to chronic exposure to the carcinogenic effects of alcohol and tobacco. In this situation, a field change effect may occur, where the epithelial tissues start to become diffusely dysplastic with a reduced threshold for malignant change. This risk may be reduced by quitting alcohol and tobacco.[citation needed]
Diagnosis
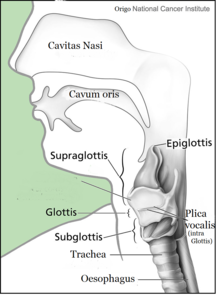
Cavitas nasi: Nasal cavity
Cavis orum: oral cavity
Glottis: Larynx
Plica vocalis: Vocal cords
Trachea
Oesophagus: Esophagus
Diagnosis is made by the doctor on the basis of a medical history, physical examination, and special investigations which may include a chest x-ray, CT or MRI scans, and tissue biopsy. The examination of the larynx requires some expertise, which may require specialist referral.[citation needed]
The physical exam includes a systematic examination of the whole patient to assess general health and to look for signs of associated conditions and metastatic disease. The neck and supraclavicular fossa are palpated to feel for cervical adenopathy, other masses, and laryngeal crepitus. The oral cavity and oropharynx are examined under direct vision. The larynx may be examined by indirect laryngoscopy using a small angled mirror with a long handle (akin to a dentist's mirror) and a strong light. Indirect laryngoscopy can be highly effective, but requires skill and practice for consistent results. For this reason, many specialist clinics now use fibre-optic nasal endoscopy where a thin and flexible endoscope, inserted through the nostril, is used to clearly visualise the entire pharynx and larynx. Nasal endoscopy is a quick and easy procedure performed in clinic. Local anaesthetic spray may be used.[citation needed]
If there is a suspicion of cancer, biopsy is performed, usually under general anaesthetic. This provides histological proof of cancer type and grade. If the lesion appears to be small and well localised, the surgeon may undertake excision biopsy, where an attempt is made to completely remove the tumour at the time of first biopsy. In this situation, the pathologist will not only be able to confirm the diagnosis, but can also comment on the completeness of excision, i.e., whether the tumour has been completely removed. A full endoscopic examination of the larynx, trachea, and esophagus is often performed at the time of biopsy.[citation needed]
For small glottic tumours further imaging may be unnecessary. In most cases, tumour staging is completed by scanning the head and neck region to assess the local extent of the tumour and any pathologically enlarged cervical lymph nodes.
The final management plan will depend on the site, stage (tumour size, nodal spread, distant metastasis), and histological type. The overall health and wishes of the patient must also be taken into account. A prognostic multigene classifier has been shown to be potentially useful for the distinction of laryngeal cancer of low or high risk of recurrence and might influence the treatment choice in future.[10]
Staging
Laryngeal tumours are classified according to the guidelines set by academic organisations such as the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) .[11] Overall classification, also known as "staging", can help predict treatment options for patients.[12] Staging consists of three separate evaluations. The first is of the tumour/cancer itself ("T").[12] The second is the extent to which adjacent lymph nodes are involved in the tumour/cancer's spread ("N").[12] The third is the presence or absence of any distant metastases ("M).[12] The specific “staging” criteria for laryngeal cancer, as utilised in the NCCN’s 2019 Guidelines for Head and Neck Cancers,[13] are:
T
TX: Unable to assess
Tis: Carcinoma in situ
Supraglottis
T1: Tumour present in only one subsite of the supraglottis. Vocal cords have normal mobility.
T2: Tumour invades mucosa. There is no fixation of the larynx.
T3: Tumour causes fixation of the vocal cords, with or without invasion of neighbouring areas.
T4:
- T4A - Tumour invades at least one of the following: the outer cortex of the thyroid cartilage, extra-laryngeal tissue
- T4B - Tumour invades at least one of the following: the pre-vertebral space, any structures of the mediastinum, the carotid sheath, or the structures within the carotid sheath.
Glottis
T1: Tumour only involves the vocal cords. Vocal cords have normal mobility.
- T1A - One vocal cord
- T1B - Both vocal cords
T2: Tumour meets at least one of the following criteria:
- extends to supra- or sub-glottis
- impairs vocal cord mobility
T3: Tumour meets at least one of the following criteria:
- causes fixation of the vocal cords
- invades the paraglottic space
- involves the thyroid cartilage’s inner cortex
T4: Same as “Supraglottis”
Subglottis
T1: Tumour is only in the subglottis
T2: Tumour involves both subglottis and vocal cords (regardless of cord mobility)
T3: Same as “Glottis”
T4: Same as “Supraglottis”
N
If Using Clinical (Non-Pathological) Diagnosis
NX: Unable to assess
N0: No involvement of neighbouring lymph nodes
N1: Tumour meets ALL of the following criteria:
- involves single lymph node
- involved lymph node on the same side of the body as tumour
- involved lymph node less than 3 cm in “greatest dimension”
- lacks extension beyond the lymph node
N2: Tumour meets ANY of the following criteria
- N2A – Same as N1, except size can be between 3–6 cm
- N2B – Same as N2A, except lymph nodes can be multiple, and there is no minimum size
- N2C – Same as N2B, except lymph nodes can be on any side of the body
N3: Tumour meets ANY of the following criteria:
- N3A – Same as N1, except size is greater than 6 cm
- N3B – Tumour obviously extends beyond the lymph node border (regardless of number, size, or location of lymph nodes)
If Using Pathological Diagnosis
NX: Same as “Clinical Diagnosis – NX”
N0: Same as “Clinical Diagnosis – N0”
N1: Same as “Clinical Diagnosis – N1”
N2: Tumour meets ANY of the following criteria
- N2A – Same as “Clinical Diagnosis – N2A”, except tumour can extend beyond the involved lymph node
- N2B – Same as “Clinical Diagnosis – N2B”
- N2C – Same as “Clinical Diagnosis – N2C”
N3: Tumour meets ANY of the following criteria:
- N3A – Same as “Clinical Diagnosis – N3A”
- N3B – Any provable presence of tumour extension beyond the lymph node
M
M0: No evidence of distant metastasis
M1: Evidence of distant metastasis
Treatment

At right: Fingertip,
At the bottom: Holder
Specific treatment depends on the location, type, and stage of the tumour.[14] Treatment may involve surgery, radiotherapy, or chemotherapy, alone or in combination.[14]
Surgical Treatment
Surgical treatment may involve partial or full removal of the tumour.[15] Neighbouring tissues and structures may or may not be removed, depending on their involvement in the tumour’s structure and spread.[16] Full removal of the larynx may be necessary in some cases.
Adjunct Treatment
Adjunct treatment, most commonly the administration of chemotherapy or radiotherapy, may be necessary.[16] Chemotherapy or radiotherapy may be necessary singly, in combination with each other, or in combination with surgery.[13] Adjunct treatment may be necessary prior to surgical treatment, alongside surgical treatment, or after surgical treatment. Clinical decision-making can be difficult in circumstances where the patient is unable to access necessary adjunct treatment.
Multi-Disciplinary Treatment
Often, successful treatment of and recovery from laryngeal cancer will involve expertise outside of the realms of surgery or oncology. Physical therapists, occupational therapists, speech therapists, psychiatrists, psychologists, oral/maxillofacial surgeons, dentists, neurologists, neurosurgeons, and endocrinologists may all become involved in the care of patients with laryngeal cancer.
Epidemiology
Incidence is five in 100,000 (12,500 new cases per year) in the US.[17] The American Cancer Society estimated that 9,510 men and women (7,700 men and 1,810 women) would be diagnosed with and 3,740 men and women would die of laryngeal cancer in 2006.[citation needed]
According to the GLOBOCAN 2018 estimates of cancer incidence and mortality produced by the International Agency for Research on Cancer, there were 177,422 new cases of laryngeal cancer worldwide in 2018 (1.0% of the global total.) Among worldwide cancer deaths, 94,771 (1.0%) were due to laryngeal cancer. [18]
In 2019, it is estimated that there will be 12,410 new laryngeal cancer cases in the United States, (3.0 per 100,000).[19] The number of new cases decreases every year at a rate of 2.4%,[19] and this is believed to be related to decreased cigarette smoking in the general population.[20]
Laryngeal cancer is listed as a "rare disease" by the Office of Rare Diseases (ORD) of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). This means that laryngeal cancer affects fewer than 200,000 people in the US.[21]
See also
References
- ^ a b "Larynx Cancer Factsheet" (PDF). Global Cancer Observatory. Retrieved 8 November 2019.
- ^ Naghavi M, Wang H, Lozano R, Davis A, Liang X, Zhou M, et al. (GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators) (January 2015). "Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013". Lancet. 385 (9963): 117–171. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2. PMC 4340604. PMID 25530442.
- ^ "SEER Stat Fact Sheets: Larynx Cancer". NCI. Retrieved 22 January 2020.
- ^ Laryngeal cancer at Mount Sinai Hospital
- ^ DeVita VT, Lawrence TS, Rosenberg SA (2011). Devita, Hellman, and Rosenberg's cancer : principles & practice of oncology (10th ed.). Philadelphia. ISBN 978-1-4511-9294-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ "Cancer of the Larynx - Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Diagnosis - MedBroadcast.com". Retrieved 2018-01-25.
- ^ Ridge JA, Glisson BS, Lango MN, Feigenberg S, Horwitz EM (2008). "Head and neck tumors.". In Pazdur R, Wagman LD, Camphausen KA, Hoskins W (eds.). Cancer management: a multidisciplinary approach (PDF). Vol. 11. p. 369.
- ^ "Laryngeal Cancer". Retrieved April 7, 2019.
- ^ Torrente MC, Rodrigo JP, Haigentz M, Dikkers FG, Rinaldo A, Takes RP, et al. (April 2011). "Human papillomavirus infections in laryngeal cancer". Head & Neck. 33 (4). Head Neck: 581–586. doi:10.1002/hed.21421. PMID 20848441. S2CID 30274997.
- ^ Mirisola V, Mora R, Esposito AI, Guastini L, Tabacchiera F, Paleari L, et al. (August 2011). "A prognostic multigene classifier for squamous cell carcinomas of the larynx". Cancer Letters. 307 (1): 37–46. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2011.03.013. PMID 21481529.
- ^ "National Comprehensive Cancer Network - Home". NCCN.
- ^ a b c d Amin M, Edge S, Greene F, et al. (2017). AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. New York: Springer.
- ^ a b Pfister DG, Spencer S, Adelstein D, Adkins D, Anzai Y, Brizel DM, et al. (July 2020). "Head and Neck Cancers, Version 2.2020, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology". Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network. 18 (7): 873–898. doi:10.6004/jnccn.2020.0031. PMID 32634781. S2CID 220405484.
- ^ a b National Comprehensive Cancer Network, "Evidence Blocks for Head and Neck Cancers," 2019.
- ^ Nibu KI, Hayashi R, Asakage T, Ojiri H, Kimata Y, Kodaira T, et al. (August 2017). "Japanese Clinical Practice Guideline for Head and Neck Cancer". Auris, Nasus, Larynx. 44 (4): 375–380. doi:10.1016/j.anl.2017.02.004. PMID 28325607.
- ^ a b Grégoire V, Lefebvre JL, Licitra L, Felip E (May 2010). "Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: EHNS-ESMO-ESTRO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up". Annals of Oncology. 21 (Suppl 5): v184–6. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdq185. PMID 20555077.
- ^ Beenken SW. "Laryngeal Cancer (Cancer of the larynx)". Armenian Health Network, Health.am. Retrieved 2007-03-22.
- ^ Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (November 2018). "Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries". Ca. 68 (6). Wiley: 394–424. doi:10.3322/caac.21492. PMID 30207593. S2CID 52188256.
- ^ a b "Cancer Stat Facts: Larynx Cancer". Retrieved 2019-08-09.
- ^ "Throat Cancer Statistics | Cases of Throat Cancer Per Year". www.cancer.org.
- ^ "Annual Report on the Rare Diseases and Conditions Research". National Institutes of Health. Retrieved 2007-03-22.
External links
- Staging cancer of the larynx
- Cancer Management Handbook: Head and Neck Cancers
- Clinically reviewed laryngeal cancer information for patients, from Cancer Research UK
- UK laryngeal cancer statistics from Cancer Research UK
