Visual art of Singapore: Difference between revisions
fix syntax |
→External links section: fix hdg |
||
| Line 145: | Line 145: | ||
{{reflist}} |
{{reflist}} |
||
== External links |
== External links == |
||
* [http://www.postcolonialweb.org/singapore/arts/painters/channel/contents.html Kwok, Kian Chow (1996). ''Channels & Confluences: A History of Singapore Art.'' Hosted on postcolonialweb.org] |
* [http://www.postcolonialweb.org/singapore/arts/painters/channel/contents.html Kwok, Kian Chow (1996). ''Channels & Confluences: A History of Singapore Art.'' Hosted on postcolonialweb.org] |
||
Revision as of 20:22, 12 April 2023
Certain historical revisions of this page may meet criterion RD1 for revision deletion, as they contain significant copyright violations of Siapa Nama Kamu? Art in Singapore Since the 19th Century. Singapore: National Gallery Singapore. 2015. ISBN 9789811405570. (available here) (Copyvios report) that have been removed in the meantime. A comment was left for the reviewing administrator: See Talk:Visual art of Singapore/GA2 for details. Extensive WP:CLOP from the book "Siapa Nama Kamu? Art in Singapore since the 19th Century", especially in the former history section. Present since very soon after article creation in May 2021..
Note to admins: In case of doubt, remove this template and post a message asking for review at WT:CP. With this script, go to the history with auto-selected revisions. Note to the requestor: Make sure the page has already been reverted to a non-infringing revision or that infringing text has been removed or replaced before submitting this request. This template is reserved for obvious cases only, for other cases refer to Wikipedia:Copyright problems. Note to others: Please do not remove this template until an administrator has reviewed it. |
| Part of a series on the |
| Culture of Singapore |
|---|
 |
| History |
| Topics |
| Research |
| Symbols |
The visual art of Singapore, or Singaporean art, refers to all forms of visual art in or associated with Singapore throughout its history and towards the present-day. The history of Singaporean art includes the indigenous artistic traditions of the Malay Archipelago and the diverse visual practices of itinerant artists and migrants from China, the Indian subcontinent, and Europe.[1]
Singaporean art includes the sculptural, textile, and decorative art traditions of the Malay world; portraiture, landscapes, sculpture, printmaking, and natural history drawings from the country's British colonial period; along with Chinese-influenced Nanyang style paintings, social realist art, abstract art, and photography practices emerging in the post-war period.[1] Today, it includes the contemporary art practices of post-independence Singapore, such as performance art, conceptual art, installation art, video art, sound art, and new media art.[2] The emergence of modern Singaporean art, or more specifically, "the emergence of self-aware artistic expression"[1] is often tied to the rise of art associations, art schools, and exhibitions in the 20th century, though this has since been expanded to include earlier forms of visual representation, such as from Singapore's historical periods.[3][4]
Presently, the contemporary art of Singapore also circulates internationally through art biennales and other major international exhibitions. Contemporary art in Singapore tends to examine themes of "hyper-modernity and the built environment; alienation and changing social mores; post-colonial identities and multiculturalism."[5] Across these tendencies, "the exploration of performance and the performative body" is a common running thread.[5] Singapore carries a notable history of performance art, with the government historically having enacted a no-funding rule for that specific art form from 1994 to 2003, following a controversial performance artwork at the 5th Passage art space.[6][7]
Ancient Singapore
Artefacts and artistic traditions of the Malay world
Situated in the Malay Archipelago, Singapore is connected to the broader sculptural, textile, and decorative art traditions of the Malay world.[8]

A 14th-century golden armlet bearing a repoussé plaque of the Javanese Kala was excavated from Bukit Larangan (Fort Canning Hill) in 1926, demonstrating a link between Singapore and classical Malay sultanates.[9] The kala motif draws from Hindu mythology, and traditionally adorns the top of main entrances of temples and is found in many parts of Indonesia.[9] Demonstrating the use of metalworking techniques, the armlet dates back to the 14th century, around the time a possible Kingdom of Singapura would have been thriving on the island, complementing indigenous Malay writings about the presence of a state in Singapore headed by a Malay elite.[9] The armlet also demonstrates the influence of the Hindu cosmology for Malays in their pre-Islamic past.[9]

Another significant artefact is the Singapore Stone, a surviving fragment of a large sandstone slab inscribed with Indic script that stood at the mouth of the Singapore River, measuring 3 metres in height and width. Believed to date back to at least the 13th century and possibly as early as the 10th or 11th century, the inscription remains undeciphered. More recent theories suggest that the inscription is either in Old Javanese or in Sanskrit, which suggests the possibility that the island was an extension of the Majapahit civilisation in the past. About January 1843,[10] the slab was blown to pieces to widen the passageway at the mouth of the Singapore River to make space for Fort Fullerton and for the quarters of its commander, leaving only fragments of the slab.[11][12]
Early cartographic references
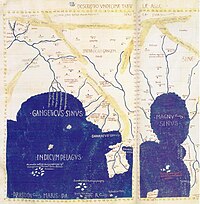
The earliest depictions of ancient Singapore existed predominantly in textual and cartographical forms, with the first possible mention being a 2nd century CE cartographic reference in Greco-Roman astronomer Ptolemy's Geographia. A place called Sabana or Sabara was marked on the 11th Map of Asia at the southern tip of the Golden Khersonese (meaning the Malay Peninsula) where Singapore may lie.[13]

Early Singapore came to be known as "Temasek", a name possibly deriving from "tasik" (Malay for lake or sea) and taken to mean Sea-town in Malay.[14] The landscape of Temasek (
Sometime in its history, the name of Temasek was changed to Singapura. The Sejarah Melayu (Malay Annals) contains a tale of a prince of Srivijaya, Sri Tri Buana (also known as Sang Nila Utama), who landed on Temasek after surviving a storm in the 13th century. According to the tale, the prince saw a strange creature, which he was told was a lion; believing this to be an auspicious sign, he decided to found a settlement called Singapura, which means "Lion City" in Sanskrit. It is unlikely there ever were lions in Singapore, though tigers continued to roam the island until the early 20th century.
Colonial Singapore (1819–1942)

From the 16th to 19th centuries, starting with the arrival of the Portuguese at Malacca in 1509, the Malay Archipelago was gradually taken over by European colonial powers. During the 17th century, the early dominance of the Portuguese was challenged by the Dutch, who came to control most of the ports in the region, while colonial powers such as the British had a relatively minor presence. Sir Stamford Raffles, appointed as the Lieutenant Governor of the British colony at Bencoolen in 1818, arrived in Singapore on 28 January 1819 and soon recognised the island as a choice for a new port. Raffles sought to challenge the Dutch by establishing a new port along the Straits of Malacca, which served as the main ship passageway for India-China trade. A formal treaty was signed on 6 February 1819, ushering in Singapore's colonial period.[18][19]
The visual art of this period includes examples such as Jules Itier’s 1844 daguerreotype of Boat Quay and Singapore River from Government Hill, Heinrich Leutemann's lithograph Unterbrochene Strassenmessung auf Singapore (Road Surveying Interrupted in Singapore) (c. 1865-1885), as well as portraits of colonial figures.
Natural history drawings
William Farquhar commissioned natural history drawings during his time as Resident of Malacca from 1803 to 1818. These were some of the earliest visual practices of the region.[8]
-
Garcinia Mangostana; Booah Mangies; Boorong Merbo (William Farquhar Collection, 1819–1823)
-
Jasminum; Akar Benang; Pokok Akar Banang (William Farquhar Collection, 1819–1823)
-
Onka' Pootie (William Farquhar Collection, 1819–1823)
-
Boorong Antoo; Owl (William Farquhar Collection, 1819–1823)
-
Bentoorong (William Farquhar Collection, 1819–1823)
-
Lava Etam (Malay); Black Pepper; Piper Nigrum (William Farquhar Collection, 1819–1823)
-
Doorean; Durio stercorae; D. zibethina Linn (William Farquhar Collection, 1819–1823)
Early photography

The earliest surviving photographic views of Singapore as a British settlement are Jules Itier's 1844 daguerreotype of Boat Quay and Singapore River from Government Hill.[20]
Art associations, schools, and exhibitions

The emergence of modern Singaporean art is often tied to the rise of art associations, art schools, and exhibitions in the 20th century.[21] In 1909, the Amateur Drawing Association was founded. the Amateur Drawing Association, led by its first president Tan Kok Tiong, had a club house in Amoy Street and a membership of about 50 in its first year. The association's activities included "drawing, literary pursuits and physical culture," but as there were few "drawing members" in spite of an exhibition of members' drawings held in February 1913. The Amateur Drawing Association suggests a social network of art enthusiasts who were associated with the Straits Chinese and British elite.[22]
Low Kway Song's Lynx (1921) and Thai Temple (1923) are art historically notable as some of the few oil paintings from Singapore that can be traced to this moment of artistic production in the early 20th century.[22]
Japanese Occupation (1942–1945)

Artistic activity slowed down after World War II arrived in Singapore, with works reflecting artist's varied experiences of the war.[1] Richard Walker's Epiphany (1942) was likely painted as a makeshift altarpiece in Changi Prison during the artist's internment there during the war.[22] It is an oil painting that depicts the Virgin Mary as an Asian woman, suggesting the universality of Christian religious values.[22]
In 1946, just after the war had ended, Liu Kang published Chop Suey, a multi-volume series of sketches that depicted Japanese brutality during wartime Malaya.[23]
Post-war period (1945–1955)
Society of Malay Artists Malaya (Late 1940s–50s)
On 1 May 1949 at the Kota Raja Club in Singapore's Kampung Glam,[24] artists Mahat bin Chadang (C. Mahat) and Mohammed Salehuddin founded the Persatuan Pelukis Melayu Malaya (PPMM, Society of Malay Artists Malaya).[24][25][26][27] The founding of the society is seen as an early instance of collective artistic organisation for Malay artists in Singapore.[26]
Nanyang Style (Late 1940s–50s)

While the visual art of Singapore is influenced by a multitude of cultures from neighbouring regions, the most dominantly historicised aesthetics from the modern period lies with the local and migrant Chinese artists whose art practices depicted local Southeast Asian subject matter while drawing upon Western watercolor and oil painting, as well as Chinese ink traditions.[28][29] The most well-known are the migrant Chinese artists who painted in the Nanyang style in the 1950s, which includes figures such as Georgette Chen.[30] The name of the movement draws from "Nanyang" (Chinese:
Pictorialism and salon photography (1950s–60s)
Pictorialism by photographers in Singapore is defined as "an assertion of individual expression that manifested as a distinct pluralism of styles and subject matter", with an emphasis on "expression and beauty" in their photographs.[33] This is different from earlier pictorial photographers in Europe and North America, who were working towards getting photography recognised as fine art.[33] Singaporean photographers, who had art exhibitions featuring photographs with paintings from 1951, did not face the same tensions between photography and painting, and were thus more open to a variety of photographic styles.[33]
Self-government (1955–1963)
Social Realism and the Equator Art Society (mid-1950s–70s)
The Equator Art Society was an artists' group founded in 1956 in Singapore, known for promoting social realist art.[34][35] The Equator Art Society sought to represent the realities and struggles of the masses, depicting Singapore's working classes and the poor often through the use of portraiture painting, woodcut prints, and sculpture.[34]
Internationalism and abstract art
Artists such as Anthony Poon, Thomas Yeo, Goh Beng Kwan, and Kim Lim were influenced by their time overseas, with their work reminiscent of the visual language of Abstract Expressionism, Op Art, and Minimalism.[36] For example, Singaporean-British artist Kim Lim's stainless steel sculpture, Column (1971–72), has been seen as an instance of Minimalist art in Britain.[37]
Association of Artists of Various Resources (APAD)
In April 1961, the art section of Lembaga Tetap Kongres Bahasa dan Kebudayaan Melayu (LTK, Permanent Board of Congress of Malay Language and Culture) staged a major exhibition at the Victoria Memorial Hall. The exhibition featured the works of 34 Malay artists, both established and emerging.[38] The exhibition publication documented works in the show from established artists such as C. Mahat, Sulaiman Haji Suhaimi, M. Salehuddin, M. Sawoot, Aman Ahmad, and younger artists like Abdul Ghani Hamid, S. Mohdir, S. Mahdar and Rohani Ismail.[38] Calls for an art society for Malay artists led to the formation of the Angkatan Pelukis Aneka Daya (APAD, Association of Artists of Various Resources) in July 1962.[38] APAD was led by Abdul Ghani Hamid, Muhammad Ali Sabran, S. Mohdir, Ahmin Haji Noh, Hamidah M. F. Suhaimi and Mustafa Yassin.[38] Other members that came to contribute to APAD include Rohani Ismail, Maisara (Sara) Dariat, Rosma Mahyuddin Guha, and Hamidah Jalil.[39]
The association continues to organise solo and group exhibitions, also collaborating with other cultural groups, art societies, and institutions, locally and regionally.[38]
Merger with Malaysia (1963–1965)
On 16 September 1963, the merger between Malaya, Singapore, North Borneo (renamed Sabah), and Sarawak took place, marking the official formation of Malaysia.[40]
The Modern Art exhibition (1963) and the Modern Art Society
The Modern Art Society (MAS) organised the Modern Art exhibition, held at the National Library from 12 October to 27 October 1963.[41]
Republic of Singapore (1965–present)
Contemporary art in Singapore tends to examine themes of "hyper-modernity and the built environment; alienation and changing social mores; post-colonial identities and multiculturalism."[42] Across these tendencies, "the exploration of performance and the performative body" is a common running thread.[42]
The Artists Village, 5th Passage, and performance art
Singapore carries a notable history of performance art, with the state having enacted a de facto ban on the art form for a decade from 1994 to 2004, following a controversial performance artwork at the 5th Passage art space in Singapore.[43][44]
2000s onwards
In 2001, Singapore participated in the Venice Biennale with its own national pavilion for the first time, with artists Henri Chen KeZhan, Matthew Ngui, Salleh Japar, and Suzann Victor exhibiting work.[45] Singapore continued its participation in the Venice Biennale with the exception of 2013, when the National Arts Council reassessed its participation in future biennales and resumed in 2015 after signing a 20-year lease on a national pavilion at the Arsenale in Venice.[46] Documenta11 in 2002 would see the participation of Charles Lim and Woon Tien Wei as the internet art collective tsunamii.net, presenting the work alpha 3.4 (2002).[47] After several years of hosting large-scale exhibitions such as the Singapore Art Show, the Nokia Singapore Art series, and SENI Singapore in 2004, Singapore launched the inaugural Singapore Biennale in 2006.[48]

In 2003, the "Art in Transit" (AIT) initiative was established by the Land Transport Authority (LTA) in tandem with the completion of the North East Line on the country's Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) system.[49] The initiative gave MRT stations specially commissioned permanent artworks by Singaporean artists in a wide variety of art styles and mediums, including sculptures, murals and mosaics often integrated into the stations' interior architecture.[49][50] With over 300 art pieces across 80 stations, it is Singapore's largest public art programme.[49][51]
In 2009, Ming Wong was the first Singaporean to receive an award at the Venice Biennale, receiving the Special Mention (Expanding Worlds) during the Biennale's Opening Ceremony for his work Life of Imitation.[52] The NTU Centre for Contemporary Art Singapore opened in 2013 with Ute Meta Bauer as founding director, and the National Gallery Singapore opened in 2015. Singaporean art continues in its circulation, with artists such as Ho Tzu Nyen and Shubigi Rao making appearances on the on the 2019 edition of the ArtReview Power 100 list, which charts the most influential individuals working in contemporary art.[53][54]
Further reading
- Abdul Ghani Hamid (1960). Sa-kilas pandang seni lukis dan perkembangannya (A Glimpse of the Arts and its Development). Singapore.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Hsü, Marco (1999). A Brief History of Malayan Art (马来亚艺术简
史 ). Translated by Lai, Chee Kien. Singapore: Millenium Books. ISBN 9810416393. - Nadarajan, Gunalan; Storer, Russell; Eugene, Tan (2007). Contemporary Art in Singapore. Singapore: Institute of Contemporary Arts Singapore. ISBN 978-981-05-6461-2.
- Low, Sze Wee (2015). Siapa Nama Kamu? Art in Singapore Since the 19th Century. Singapore: National Gallery Singapore. ISBN 9789811405570.
- Nadarajan, Gunalan; Storer, Russell; Eugene, Tan (2007). Contemporary Art in Singapore. Singapore: Institute of Contemporary Arts Singapore. ISBN 978-981-05-6461-2.
- Sabapathy, T.K. (2010). Road to Nowhere: The Quick Rise and the Long Fall of Art History in Singapore. Singapore: The Art Gallery, National Institute of Education. ISBN 978-9810852641.
- Sabapathy, T.K. (2018). Ahmad, Mashadi; Lingham, Susie; Schoppert, Peter; Toh, Joyce (eds.). Writing the Modern: Selected Texts on Art & Art History in Singapore & Southeast Asia 1973–2015. Singapore: Singapore Art Museum. ISBN 9789811157639.
Reference section
- ^ a b c d Susanto, Melinda (2015). "Tropical Tapestry". Siapa Nama Kamu? Art in Singapore Since the 19th Century. Singapore: National Gallery Singapore. pp. 30–41. ISBN 9789811405570.
- ^ Toh, Charmaine (2015). "Shifting Grounds". In Low, Sze Wee (ed.). Siapa Nama Kamu? Art in Singapore Since the 19th Century. National Gallery Singapore. p. 92. ISBN 9789810973841.
- ^ Low, Sze Wee, ed. (2015). "Some Introductory Remarks". Siapa Nama Kamu? Art in Singapore since the 19th Century. Singapore: National Gallery Singapore. pp. 8–29. ISBN 9789810973520.
- ^ "T.K. Sabapathy". Esplanade Offstage. 12 October 2016. Archived from the original on 27 February 2021. Retrieved 27 February 2021.
- ^ a b Teh, David (2017). "Insular Visions: notes on video art in Singapore". The Japan Foundation Asia Center Art Studies. 3. Archived from the original on 8 January 2023. Retrieved 17 May 2021 – via Academia.org.
- ^ Lee, Weng Choy (1996). "Chronology of a Controversy". In Krishnan, S.K. Sanjay; Lee, Weng Choy; Perera, Leon; Yap, Jimmy (eds.). Looking at Culture. Singapore: Artres Design & Communications. ISBN 9810067143. Archived from the original on 8 June 2020.
- ^ Lingham, Susie (November 2011). "Art and Censorship in Singapore: Catch 22?". ArtAsiaPacific (76). Archived from the original on 15 September 2014. Retrieved 8 June 2020.
- ^ a b Susanto, Melinda (2015). "Tropical Tapestry". Siapa Nama Kamu? Art in Singapore Since the 19th Century. Singapore: National Gallery Singapore. pp. 30–41. ISBN 9789811405570.
- ^ a b c d Joraimi, Faris (9 September 2017). "A History of Malay Singaporeans in Ten Objects". New Naratif. Archived from the original on 28 April 2021. Retrieved 19 May 2021.
- ^ Abdullah bin Abdul Kadir, Hikayat Abdullah, above, at 166 n. 18.
- ^ Cornelius-Takahama, Vernon (30 March 2000). "The Singapore Stone". Singapore Infopedia, National Library, Singapore. Archived from the original on 29 November 2020. Retrieved 16 October 2016.
- ^ Miksic, John N. (1985). Archaeological Research on the 'Forbidden Hill' of Singapore : Excavations at Fort Canning, 1984. Singapore: National Museum. pp. 13, 40, 41. ISBN 9971-917-16-5. The information is referred to in Lee, Jack Tsen-Ta (September 2004). "Treaties, Time Limits and Treasure Trove: The Legal Protection of Cultural Objects in Singapore". Art, Antiquity & Law. 9 (3): 237 at 239–240. SSRN 631781..
- ^ Paul Wheatley (1961). The Golden Khersonese: Studies in the Historical Geography of the Malay Peninsula before A.D. 1500. Kuala Lumpur: University of Malaya Press. pp. 151–152. OCLC 504030596.
- ^ Singapore Street Names: A Study of Toponymics. Marshall Cavendish. 15 June 2013. p. 381. ISBN 9789814484749. Archived from the original on 12 April 2023. Retrieved 18 May 2021.
{{cite book}}: Cite uses deprecated parameter|authors=(help) - ^ Sally Church (2008). by Helaine Selin (ed.). Encyclopaedia of the History of Science, Technology, and Medicine in Non-Western Cultures (2nd ed.). Springer. pp. 2354–2355. ISBN 978-1402045592.
- ^ a b "
島 夷 誌 略 ". Archived from the original on 1 December 2020. Retrieved 18 May 2021. - ^ a b Paul Wheatley (1961). The Golden Khersonese: Studies in the Historical Geography of the Malay Peninsula before A.D. 1500. Kuala Lumpur: University of Malaya Press. pp. 82–83. OCLC 504030596.
- ^ Jenny Ng (7 February 1997). "1819 – The February Documents". Ministry of Defence (Singapore). Archived from the original on 17 July 2017. Retrieved 18 July 2006.
- ^ "Milestones in Singapore's Legal History". Supreme Court, Singapore. Retrieved 18 July 2006.[dead link]
- ^ Liu, Gretchen (1999). Singapore: A Pictorial History, 1819–2000. Singapore: Archipelago Press in association with the National Heritage Board. pp. 18–89. ISBN 981301881X.
- ^ Low, Sze Wee, ed. (2015). "Some Introductory Remarks". Siapa Nama Kamu? Art in Singapore since the 19th Century. Singapore: National Gallery Singapore. pp. 8–29. ISBN 9789810973520.
- ^ a b c d Kwok, Kian Chow (1996). Channels & Confluences: A History of Singapore Art. Singapore: Singapore Art Museum. ISBN 9789810074883.
- ^ Tan, Bonny (2016). "Liu Kang". NLB Infopedia. Archived from the original on 5 May 2021. Retrieved 19 May 2021.
- ^ a b Soon, Simon (2015). "Moving Suara for Sovereignty: Reading the shifts in 1950's Modern Art Discourses in Malay through Kamus Politik". Dato' Hoessein Enas: From His Personal Collection. Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia: IB Tower Gallery Sdn Bhd. pp. 116–137. ISBN 9789671350904. Archived from the original on 12 April 2023. Retrieved 20 January 2022.
- ^ Ong, Zhen Min (2015). Nanyang Reverie. Siapa Nama Kamu? Art in Singapore Since the 19th Century: National Gallery Singapore. pp. 42–53. ISBN 9789811405570.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ a b Apad: Tradition, Innovation & Continuity. Singapore: Singapore Art Museum & Angkatan Pelukis Aneka Daya. 2008. ISBN 978-9810820923. Archived from the original on 16 January 2022. Retrieved 16 January 2022.
- ^ Ramli, Nadia (2019). "Creative Collectives: Abdul Ghani Hamid and His Contemporaries". BiblioAsia. (Jan-Mar 2019) 14 (4): 56–59. Archived from the original on 16 January 2022. Retrieved 16 January 2022.
- ^ "T.K. Sabapathy". Esplanade Offstage. 12 October 2016. Archived from the original on 27 February 2021. Retrieved 27 February 2021.
- ^ Sabapathy, T.K. (2010). Road to Nowhere: The Quick Rise and the Long Fall of Art History in Singapore. Singapore: The Art Gallery, National Institute of Education. ISBN 9810852649.
- ^ a b Balagopal, Roberta; Yeo, Alicia (31 August 2009). "The Nanyang Style". National Library Board. Archived from the original (article) on 10 March 2011. Retrieved 6 August 2010.
- ^ Ting Szu Kiong (2005). "Nanyang Art". Central Singapore Community Development Council. Archived from the original (article) on 27 December 2009. Retrieved 6 August 2010.
- ^ Yeo, Alicia (April 2006). "Singapore Art, Nanyang Style" (PDF). biblioasia. Singapore: National Library Board. pp. 4–11. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 February 2012. Retrieved 6 August 2010.
- ^ a b c Toh, Charmaine (October 2018). "Pictorialism and Modernity in Singapore, 1950–60". Southeast of Now: Directions in Contemporary and Modern Art in Asia. 2 (2): 9–31. doi:10.1353/sen.2018.0013. S2CID 192678258. Archived from the original on 7 July 2022. Retrieved 23 May 2021 – via Project MUSE.
- ^ a b Yeo, Alicia Kay Ling (2016). "Equator Art Society". NLB Infopedia. Archived from the original on 5 May 2021. Retrieved 26 August 2021.
- ^ Kwok, Kian Chow (1996). Channels & Confluences: A History of Singapore Art. Singapore: Singapore Art Museum. p. 71. ISBN 9810074883. Archived from the original on 17 May 2021. Retrieved 17 May 2021.
- ^ Seng, Yu Jin; Cai, Heng (2015). "The Real Against the New: Social Realism and Abstraction". Siapa Nama Kamu?. Singapore: National Gallery Singapore. pp. 54–67. ISBN 9789811405570.
- ^ Kee, Joan (2018). "Minimalism by All Means". Minimalism: Space. Light. Object. Singapore: National Gallery Singapore. pp. 64–72. ISBN 9789811166808.
- ^ a b c d e Ramli, Nadia (2019). "Creative Collectives: Abdul Ghani Hamid and His Contemporaries". BiblioAsia. (Jan-Mar 2019) 14 (4): 56–59. Archived from the original on 16 January 2022. Retrieved 16 January 2022.
- ^ Rahmat, Nurdiana (2021). "Terms and Conditions: Re-examining Singapore Art History Through the Art Making Experiences of Early Malay Women Artists". Currents Journal. Archived from the original on 16 January 2022. Retrieved 16 January 2022.
- ^ "Singapore – Road to Independence". U.S. Library of Congress. Archived from the original on 4 July 2014. Retrieved 27 June 2006.
- ^ Seng, Yu Jin (2017). "Claiming the Modern: The Modern Art Society's Inaugural Exhibition in 1963 within a Timeline of Singapore Art". In Seng, Yu Jin; Tan, Ping Chiang (eds.). Transcend: 50 Years of Singapore Modern Art. Singapore: Iola Liu. pp. 14–21. ISBN 978-981-11-3759-4.
- ^ a b Teh, David (2017). "Insular Visions: notes on video art in Singapore". The Japan Foundation Asia Center Art Studies. 3. Archived from the original on 17 May 2021. Retrieved 17 May 2021 – via Academia.org.
- ^ Lee, Weng Choy (1996). "Chronology of a Controversy". In Krishnan, S.K. Sanjay; Lee, Weng Choy; Perera, Leon; Yap, Jimmy (eds.). Looking at Culture. Singapore: Artres Design & Communications. ISBN 9810067143. Archived from the original on 8 June 2020.
- ^ Lingham, Susie (November 2011). "Art and Censorship in Singapore: Catch 22?". ArtAsiaPacific (76). Archived from the original on 15 September 2014. Retrieved 8 June 2020.
- ^ Toh, Charmaine (2015). "Shifting Grounds". In Low, Sze Wee (ed.). Siapa Nama Kamu? Art in Singapore Since the 19th Century. National Gallery Singapore. p. 92. ISBN 9789810973841.
- ^ Nanda, Akshita (6 May 2015). "Singapore signs 20-year lease on Venice Biennale pavilion". The Straits Times. Archived from the original on 24 November 2015. Retrieved 22 May 2021.
- ^ "alpha 3.4". Rhizome Net Art Anthology. 27 October 2016. Archived from the original on 1 February 2021. Retrieved 22 May 2021.
- ^ Lim, Siew Kim; Goh, Lee Kim (2017). "Singapore Biennale". NLB Infopedia. Archived from the original on 21 October 2020. Retrieved 21 October 2020.
{{cite web}}:|archive-date=/|archive-url=timestamp mismatch; 15 July 2020 suggested (help) - ^ a b c "Getting Around - Public Transport - A Better Public Transport Experience - Art in Transit". LTA. 7 April 2020. Archived from the original on 21 April 2020. Retrieved 23 June 2022.
- ^ "Art in Transit brochure" (PDF). Land Transport Authority. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 August 2005. Retrieved 23 June 2022.
- ^ Lim, Melanie (19 November 2019). "LTA looking for artists to spruce up Punggol Coast MRT station, applications close Dec. 19, 2019". Mothership. Bridgewater Holdings Pte Ltd. Archived from the original on 27 March 2022. Retrieved 23 June 2022.
- ^ Toh, Charmaine (2015). "Shifting Grounds". In Low, Sze Wee (ed.). Siapa Nama Kamu? Art in Singapore Since the 19th Century. National Gallery Singapore. p. 92. ISBN 9789810973841.
- ^ "Power 100: Most influential people in 2019 in the contemporary artworld: Ho Tzu Nyen". ArtReview. 2019. Archived from the original on 11 August 2020. Retrieved 11 August 2020.
- ^ "Power 100: Most influential people in 2019 in the contemporary artworld: Bose Krishnamachari & Shubigi Rao". ArtReview. 2019. Archived from the original on 26 July 2020. Retrieved 26 July 2020.








