Tell Afis: Difference between revisions
Ploversegg (talk | contribs) |
Ploversegg (talk | contribs) →Further reading: add 1 |
||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
==Further reading== |
==Further reading== |
||
*Ciafardoni, Paola, "Tell Afis: Un Insediamento Del Ferro Nella Regione Di Idlib", Egitto e Vicino Oriente, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 5–23, 1987 |
*Ciafardoni, Paola, "Tell Afis: Un Insediamento Del Ferro Nella Regione Di Idlib", Egitto e Vicino Oriente, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 5–23, 1987 |
||
*Giannessi, Deborah, "Tell Afis: the Late Chalcolithic Painted Ware", Levant 34.1, pp. 83-97, 2002 |
|||
*Amadasi Guzzo, Maria Giulia, "Un Fragment de Stèle Araméenne de Tell Afis", Orientalia, vol. 78, no. 3, pp. 336–47, 2009 |
*Amadasi Guzzo, Maria Giulia, "Un Fragment de Stèle Araméenne de Tell Afis", Orientalia, vol. 78, no. 3, pp. 336–47, 2009 |
||
*Mazzoni, Stefania, "The Italian Excavations of Tell Afis (Syria): from Chiefdom to an Aramaean State", Pise, 1998 |
*Mazzoni, Stefania, "The Italian Excavations of Tell Afis (Syria): from Chiefdom to an Aramaean State", Pise, 1998 |
||
Revision as of 15:45, 21 September 2023
تل آفس | |
| Alternative name | Hazrek |
|---|---|
| Location | Idlib Governorate, Syria |
| Coordinates | 35°54′18″N 36°47′55″E / 35.905°N 36.798611°E |
| Type | settlement |
| Site notes | |
| Excavation dates | 1986–2010 |
| Archaeologists | Stefania Mazzoni and Serena Maria Cecchini |
| Condition | ruins |
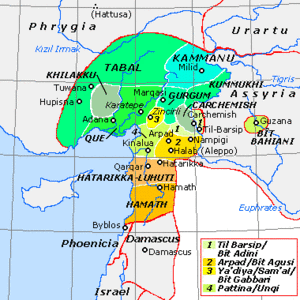
Tell Afis is an archaeological site in the Idlib Governorate of northern Syria, and lies about fifty kilometers southeast of Aleppo and 11 kilometers north of the ancient site of Ebla.[1] The site is thought to be that of ancient Hazrek (or Hazrach; Hatarikka for the Assyrians) capital of the Kingdom of Hamath and Luhuti.[2] The Stele of Zakkur (KAI 202), dated c, 785 BC, which contains a dedication in Aramaic to the gods Iluwer and Baalshamin, was discovered at the top of the acropolis in 1903 by the French Consul Henri Pognon. It is now in the Louvre Museum.[3]
History
Occupation of the site extends from the Late Chalcolithic, Ubaid period, Early Bronze I period, Middle Bronze II, until the Iron Age.[4] In the Late Chalcolithic it was surrounded by a strong stone wall with an economy based on the herding of mostly sheep but also pigs. The find of elderly bovines indicated that agriculture was being practices.[5]
Bronze Age
In the lower town Middle Bronze Age II occupation is attested (excavation Area D) but in a much smaller area than the later Iron Age II-III Aramaean town, as well as on the acropolis.
In the Late Bronze Age, around 1350 BC, the Hittite ruler Suppiluliuma I gained control over the northern parts of Syria. This region was then called Nuhasse. Levels VII to V have been firmly dated to the time of control by 13th century BC Hittite ruler Hattusili III by seals, pottery, and nine cuneiform tablets and fragments (in Building F). Two of the tablets, and a fragment, were in Hittite while the others, badly damaged, were administrative documents in local clay.[6][7][8]
Iron Age

In Iron Age I the site was a small settlement. In Iron Age II Tell Afis grew to substantial size and was part of the Kingdom of Hamath. [2] On the western side of the Acropolis a multiperiod temple was found. The two lowest levels (A3.2 followed by A3.1) date from Iron Age I, both of mudbrick with the same plan and a 2.5 meter wide gate to the south. In A3.1 a plastered central podium was found with pit of ashes which included animal bones and fragments of a painted keros jar. A cylinder seal depicting a storm god was also found. The earlier temples were leveled when the Iron Age II-III temples, A2 followed by A1, were constructed. They were of a tripartite longroom design 38 meters by 32 meters with a vestibule, a long hall, a rear room, and rooms along the sides and constructed of stone.Temple A1 was dismantled and the materials re-used.[9] A sizable Iron Age II cultic area was discovered to the east of Temple A2, on the eastern acropolis. In Building G, 25 meters to the east of the sacred area, a pottery shard marked "LWR" was found. It was speculated that they were three letters of the god of Hazrek El-we.[10] Three additional Aramaic fragments were later found.[11] Late in Iron Age III the site was occupied c. 738 BC by the Neo-Assyrian empire under Tiglath-Pileser III. In 720 BC Sargon II defeated the Kingdom of Hamath.[2]
Archaeology
The tell is 28 hectares in area (570 meters by 500 meters) with an extensive lower city and an acropolis on the northern edge. The site had been subject to quarrying by the local populace for building materials. The lower town was protected by a Late Iron Age 5.2 meter wide wall. The wall was build without foundation or facing which the excavators took to indicate it was built rapidly.[12] In 1932 William F. Albright collected Iron Age pottery in a surface collection.[13] In 1970, 1972, and 1978 excavations were conducted by Paolo Matthiae with the Italian Archaeological Mission in Syria.[14] The site was excavated from 1986 until 2010 by a joint project from the universities of Rome, Pisa and Bologna, under the direction of Stefania Mazzoni and Serena Maria Cecchini. Two areas (B and D) were excavated in the northern part of the lower town. On the acropolis, areas A, G, and, E (on the western slope) were excavated.[15][1][4][16]
The site was reportedly damaged by encampments during the Syrian civil war.[17]
See also
References
- ^ a b Venturi, F., "La Siria nell’Età delle Trasformazioni: Nuovi Contributi dallo Scavo di Tell Afis", Cooperativa Libraria Universitaria Editirice Bologna, 2007
- ^ a b c Soldi, Sebastiano, "Aramaeans and Assyrians in North-Western Syria: Material Evidence from Tell Afis", Syria, vol. 86, pp. 97–118, 2009
- ^ J. C. L. Gibson, Textbook of Syrian Semitic Inscriptions: II. Aramaic Inscriptions, Oxford University Press, 1975 ISBN 9780198131861
- ^ a b Stefania Mazzoni, "Tell Afis: History and Excavations", Near Eastern Archaeology, vol. 76(4), pp. 204-212, December 2013
- ^ [1]Wilkens, Barbara, "Archaeozoology. Westwards: the Fauna of Tell Afis (Syria)", Topoi. Orient-Occident 2.1, pp. 5-14, 2000
- ^ Alfonso Archi, and Fabrizio Venturi, "Tell Afis in the Thirteenth Century BC: Under the Rule of the Hittites", Near Eastern Archaeology, vol. 76, no. 4, pp. 214–22, 2013
- ^ Archi, Alfonso, and Fabrizio Venturi, "Hittites at Tell Afis (Syria)", Orientalia, vol. 81, no. 1, pp. 1–55, 2012
- ^ Archi, A., "Hittites at Tell Afis II. The Cuneiform Tablets", Orientalia, pp. 81, pp. 32–55, 2012
- ^ Stefania Mazzoni, "Tell Afis in the Iron Age: The Temple on the Acropolis", Near Eastern Archaeology, vol. 77, no. 1, pp. 44–52, 2014
- ^ Serena Maria Cecchini, "Tell Afis in the Iron Age: The Official Buildings on the Eastern Acropolis", Near Eastern Archaeology, vol. 77, no. 1, pp. 58–63, 2014
- ^ Maria Giulia Amadasi Guzzo, "Tell Afis in the Iron Age: The Aramaic Inscriptions", Near Eastern Archaeology, vol. 77, no. 1, pp. 54–57, 2014
- ^ Michele, Angelo Di, "Tell Afis Area N. Excavations Seasons 2001-2007. Phases XI-I. Middle Bronze Age - Iron Age I. Stratigraphy, pottery and small finds", Le Lettere (Studi di Archeologia Siriana 7), 2022 ISBN 9788893663014
- ^ W. F.Albright, "Archaeological and Topographical Explorations in Palestine and Syria", Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research, vol. 49, pp. 23–31, 1933
- ^ P. Matthiae, "Sondages à Tell Afis (Syrie), 1978", Akkadica, vol. 14, pp. 2–5, 1978
- ^ Venturi, Fabrizio, Tell Afis. The Excavations of Areas E2-E4. Phases V-I. The End of the Late Bronze/ Iron Age I Sequence. Stratigraphy, Pottery and Small Finds. (Firenze, Studi di Archeologia Siriana 4, Le Lettere, 2020) ISBN 978-88-9366-127-0
- ^ S.M. Cecchini, S. Mazzoni (Eds), "Teli Afis (Siria). Scavi sull'acropoli 1988-1992, The 1988-1992 Excavations on the Acropolis", Pise, 1998
- ^ Cunliffe, Emma., Damage to the Soul: Syria's cultural heritage in conflict, Durham University and the Global Heritage Fund, 1 May 2012
Further reading
- Ciafardoni, Paola, "Tell Afis: Un Insediamento Del Ferro Nella Regione Di Idlib", Egitto e Vicino Oriente, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 5–23, 1987
- Giannessi, Deborah, "Tell Afis: the Late Chalcolithic Painted Ware", Levant 34.1, pp. 83-97, 2002
- Amadasi Guzzo, Maria Giulia, "Un Fragment de Stèle Araméenne de Tell Afis", Orientalia, vol. 78, no. 3, pp. 336–47, 2009
- Mazzoni, Stefania, "The Italian Excavations of Tell Afis (Syria): from Chiefdom to an Aramaean State", Pise, 1998
- Mazzoni, Stefania, et al., "Tell Afis (Siria) 1994 – Rapporto Preliminare", Egitto e Vicino Oriente, vol. 18, pp. 243–306, 1995
- Mazzoni, Stefania, et al., "Tell Afis (Siria) 1999", Egitto e Vicino Oriente, vol. 22/23, pp. 5–103, 1999
- Mazzoni, Stefania, et al., "Tell Afis (Siria) 2000-2001", Egitto e Vicino Oriente, vol. 25, pp. 5–108, 2002
- Mazzoni, Stefania, et al., "Tell Afis (Siria) 2002-2004", Egitto e Vicino Oriente, vol. 28, pp. 4–210, 2005
- Merluzzi, Emanuela, "Un tripode in basalto da Tell Afis. Origine ed evoluzione dei recipienti litici a tre piedi cerimoniali e/o rituali", Egitto e Vicino Oriente, vol. 25, pp. 231–67, 2002
- Venturi, Fabrizio, "Un vase zoomorphe du Fer I à Tell Afis (Syrie)", Syria, vol. 88, pp. 251–63, 2011