Double-clad fiber: Difference between revisions
m Fix links to disambiguation page Mode |
Remove figure numbers, which have become out of sync with the references to them in the text. Shift images to align with text. Rephrase. |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:Dispersion-dc.png|thumb|right| |
[[Image:Dispersion-dc.png|thumb|right|Refractive index profile of dispersion compensating double-clad fiber. c:core, i:inner cladding, o:outer cladding.]] |
||
[[Image:High-power-dc.png|thumb|right| |
[[Image:High-power-dc.png|thumb|right|Refractive index profile of double-clad fiber for high power fiber lasers and amplifiers. c:core, i:inner cladding, o:outer cladding.]] |
||
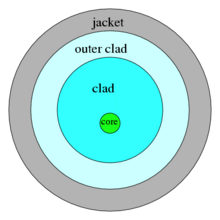
'''Double-clad fiber''' (DCF) is a class of [[optical fiber]], with a structure consisting of three layers of optical material instead of the usual two. The inner-most layer is called the ''[[Fiber optics#Principle of operation|core]]''. It is surrounded by the ''inner [[Cladding (fiber optics)|cladding]]'', which is surrounded by the ''outer cladding''. The three layers are made of materials with different [[refractive index|refractive indices]]. |
'''Double-clad fiber''' (DCF) is a class of [[optical fiber]], with a structure consisting of three layers of optical material instead of the usual two. The inner-most layer is called the ''[[Fiber optics#Principle of operation|core]]''. It is surrounded by the ''inner [[Cladding (fiber optics)|cladding]]'', which is surrounded by the ''outer cladding''. The three layers are made of materials with different [[refractive index|refractive indices]]. |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
== Fiber for amplifiers and fiber lasers== |
== Fiber for amplifiers and fiber lasers== |
||
[[Image:Fl.png|thumb|center|900px| |
[[Image:Fl.png|thumb|center|900px|Schematic diagram of cladding pumped double-clad fiber laser.]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Image: |
[[Image:RectaDFC.png|thumb|right|Cross-section of DCF with rectangular inner cladding |
||
| ⚫ | |||
<ref name="Kouznetsov">{{cite journal|title=Highly efficient, high-gain, short-length, and power-scalable incoherent diode slab-pumped fiber amplifier/laser| author= Kouznetsov, D.| coauthors=Moloney, J.V.| journal=[[IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics]]| url=http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/freeabs_all.jsp?tp=&arnumber=1242365&isnumber=27838|volume=39 | year=2003 | issue=11 | pages=1452–1461 | doi=10.1109/JQE.2003.818311}}</ref> ]] |
<ref name="Kouznetsov">{{cite journal|title=Highly efficient, high-gain, short-length, and power-scalable incoherent diode slab-pumped fiber amplifier/laser| author= Kouznetsov, D.| coauthors=Moloney, J.V.| journal=[[IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics]]| url=http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/freeabs_all.jsp?tp=&arnumber=1242365&isnumber=27838|volume=39 | year=2003 | issue=11 | pages=1452–1461 | doi=10.1109/JQE.2003.818311}}</ref> ]] |
||
In modern double-clad fibers for high power fiber amplifiers and lasers, the inner cladding has a higher refractive index than the outer cladding. This enables the inner cladding to guide light by [[total internal reflection]] in the same way the core does, but for a different range of wavelengths. This allows [[diode laser]]s, which have high power but low [[Radiance|brightness]], to be used as the optical pump source. The pump light can be easily coupled into the large inner cladding, and propagates through the inner cladding while the signal propagates in the smaller core. The doped core gradually absorbs the cladding light as it propagates, driving the amplification process. This pumping scheme is often called ''cladding pumping'', which is an alternative to the conventional ''core pumping'', in which the pump light is coupled into the small core. The invention of the cladding pumping by a Polaroid fiber research team (H. Po, ''et al.'') revolutionized the power scaling method of fiber amplifiers and lasers.<ref name="Po">{{cite conference |title= Doubly clad high brightness Nd fiber laser pumped by GaAlAs phased array|author= H. Po|coauthors= E. Snitzer, L. Tumminelli, F. Hakimi, N.M. Chu, and T. Haw|conference = Optical Fiber Communication Conference|year= 1989|id= PD7}}</ref> Using this method, modern fiber lasers can produce continuous power up to several kilowatts, while the signal light in the core maintains near [[Diffraction-limited system|diffraction-limited beam quality]].<ref name=jeong>{{cite journal |author= Y. Jeong, J. Sahu, D. Payne, and J. Nilsson|year= 2004|title= Ytterbium-doped large-core fiber laser with 1.36 kW continuous-wave output power|journal= Optics Express|volume= 12|issue= 25|pages= 6088–6092|url= http://www.opticsinfobase.org/abstract.cfm?id=81942 |doi= 10.1364/OPEX.12.006088 |pmid= 19488250}}</ref> |
In modern double-clad fibers for high power fiber amplifiers and lasers, the inner cladding has a higher refractive index than the outer cladding. This enables the inner cladding to guide light by [[total internal reflection]] in the same way the core does, but for a different range of wavelengths. This allows [[diode laser]]s, which have high power but low [[Radiance|brightness]], to be used as the optical pump source. The pump light can be easily coupled into the large inner cladding, and propagates through the inner cladding while the signal propagates in the smaller core. The doped core gradually absorbs the cladding light as it propagates, driving the amplification process. This pumping scheme is often called ''cladding pumping'', which is an alternative to the conventional ''core pumping'', in which the pump light is coupled into the small core. The invention of the cladding pumping by a Polaroid fiber research team (H. Po, ''et al.'') revolutionized the power scaling method of fiber amplifiers and lasers.<ref name="Po">{{cite conference |title= Doubly clad high brightness Nd fiber laser pumped by GaAlAs phased array|author= H. Po|coauthors= E. Snitzer, L. Tumminelli, F. Hakimi, N.M. Chu, and T. Haw|conference = Optical Fiber Communication Conference|year= 1989|id= PD7}}</ref> Using this method, modern fiber lasers can produce continuous power up to several kilowatts, while the signal light in the core maintains near [[Diffraction-limited system|diffraction-limited beam quality]].<ref name=jeong>{{cite journal |author= Y. Jeong, J. Sahu, D. Payne, and J. Nilsson|year= 2004|title= Ytterbium-doped large-core fiber laser with 1.36 kW continuous-wave output power|journal= Optics Express|volume= 12|issue= 25|pages= 6088–6092|url= http://www.opticsinfobase.org/abstract.cfm?id=81942 |doi= 10.1364/OPEX.12.006088 |pmid= 19488250}}</ref> |
||
| Line 59: | Line 56: | ||
=== Chaotic fibers === |
=== Chaotic fibers === |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
In general, modes of a waveguide have "scars", which correspond to the classical trajectories. The scars may avoid the core, then |
In general, modes of a waveguide have "scars", which correspond to the classical trajectories. The scars may avoid the core, then |
||
the mode is not coupled, and it is vain to excite such a mode in the double-clad fiber amplifier. The scars can be distributed more or less uniformly in |
the mode is not coupled, and it is vain to excite such a mode in the double-clad fiber amplifier. The scars can be distributed more or less uniformly in |
||
| Line 76: | Line 68: | ||
====Spiral shape==== |
====Spiral shape==== |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
An almost-circular shape with small spiral deformation seems to be the most efficient for [[chaotic fiber]]s. In such a fiber, the [[angular momentum]] of a ray increases at each reflection from the smooth wall, until the ray hits the "chunk", at which the spiral curve is broken (see figure at right). The core, placed in vicinity of this chunk, is intercepted more regularly by all the rays compared to other chaotic fibers. This behavior of rays has an analogy in wave optics. In the language of [[Normal mode|modes]], all the modes have non-zero derivative in vicinity of the chunk, and cannot avoid the core if it is placed there. One example of modes is shown in the figure below and to the right. Although some of modes are show wide voids, none of these voids cover the core. |
|||
The property of DCFs with spiral-shaped cladding can be interpreted as conservation of angular momentum. The square of the derivative of a mode at the boundary can be interpreted as pressure. Modes (as well as rays), touching the spiral-shaped boundary transfer it some angular momentum. This transfer of angular momentum should be compensated with pressure at the chunk. Therefore, no one mode can avoid the chunk. Modes can show strong scarring along the classical trajectories (rays) and wide voids, but at least one of scars should approach the chunk to compensate the angular momentum transferredby the spiral part. |
|||
An almost-circular shape with small spiral deformation seems to be the most efficient for [[chaotic fiber]]s. |
|||
In such a fiber, the [[angular momentum]] of a ray increases at each reflection from the smooth wall, until the |
|||
ray hits the chunk [fig.3] of the spiral curve. The core placed in vicinity of this chunk is visited by all the rays more regularly, than in other chaotic fibers. |
|||
This behavior of rays has analogy in the wave optics. On the language of [[Normal mode|modes]], all the modes have non-zero |
|||
derivative in vicinity of the chunk, and cannot avoid the core placed there. |
|||
One example of modes is shown in fig.4. Although some of modes are scared and show wide voids, none of these voids cover the core. |
|||
The property of the DCF with spiral-shaped cladding can be interpreted as conservation of angular momentum. |
|||
The square of the derivative of a mode at the boundary can be interpreted as pressure. Modes (as well as rays), touching the spiral-shaped boundary transfer it some angular momentum. |
|||
This transfer of angular momentum should be compensated with pressure at the chunk. Therefore, no one mode can avoid the chunk. |
|||
Modes can show strong scarring along the classical trajectories (rays) and wide voids, but at least one of scars should approach the chunk to compensate the angular momentum transferredby the spiral part. |
|||
The interpretation with angular momentum indicates the reasonable size of the chunk. There is no reason to make this chunk larger than the core; a large chunk would not localize the scars sufficiently to provide coupling with the core. There is no reason to locaize the scars within an angle smaller than the core: the small derivative to the radius makes the manufacturing less robust; the larger is <math>R'(\phi)</math>, the larger fluctuations |
The interpretation with angular momentum indicates the reasonable size of the chunk. There is no reason to make this chunk larger than the core; a large chunk would not localize the scars sufficiently to provide coupling with the core. There is no reason to locaize the scars within an angle smaller than the core: the small derivative to the radius makes the manufacturing less robust; the larger is <math>R'(\phi)</math>, the larger fluctuations |
||
| Line 115: | Line 100: | ||
=== Filling factor === |
=== Filling factor === |
||
[[Image:FillingFactor.png|thumb|400px| |
[[Image:FillingFactor.png|thumb|400px|Estimates of the pump efficiency in a double-clad fiber with <math>F=0.8 |
||
</math> (blue) and <math> F=0.9</math> (red) , discussed in<ref name="Kouznetsov"/> |
</math> (blue) and <math> F=0.9</math> (red) , discussed in<ref name="Kouznetsov"/> |
||
compared to the results of the ray tracing simulations<ref name="Liu" />(black curves).]] |
compared to the results of the ray tracing simulations<ref name="Liu" />(black curves).]] |
||
| Line 131: | Line 116: | ||
The exponential behavior of the efficiency of absorption of pump in the core is not obvious. We could expect, that some modes of the cladding |
The exponential behavior of the efficiency of absorption of pump in the core is not obvious. We could expect, that some modes of the cladding |
||
(or some rays) are better coupled to the core than others; therefore, the "true" dependence could be combination of several exponentials; and the |
(or some rays) are better coupled to the core than others; therefore, the "true" dependence could be combination of several exponentials; and only comparison with simulations justifies this approximation, as shown in the figure above and to the right. In particular, this approximation does not work for circular fibers, see the initial work by Bedo et all, cited below. |
||
only comparison with simulations (Fig.5) justifies this approximation. In particular, this approximation does not work for circular fibers, see the initial work by Bedo et all, cited below. |
|||
For chaotic fibers, <math>~F~</math> approaches unity. The value of <math>~F~</math> can be estimated by [[numerical analysis]] with propagation of waves, expansion by modes or by geometrical optics ray tracing, |
For chaotic fibers, <math>~F~</math> approaches unity. The value of <math>~F~</math> can be estimated by [[numerical analysis]] with propagation of waves, expansion by modes or by geometrical optics ray tracing, |
||
and values 0.8 and 0.9 are only empiric adjusitng parameters, which provide good agreement of the |
and values 0.8 and 0.9 are only empiric adjusitng parameters, which provide good agreement of the |
||
Revision as of 03:26, 14 June 2011


Double-clad fiber (DCF) is a class of optical fiber, with a structure consisting of three layers of optical material instead of the usual two. The inner-most layer is called the core. It is surrounded by the inner cladding, which is surrounded by the outer cladding. The three layers are made of materials with different refractive indices.
There are two different kinds of double-clad fibers. The first was developed early in optical fiber history with the purpose of engineering the dispersion of optical fibers. In these fibers, the core carries the majority of the light, and the inner and outer cladding alter the waveguide dispersion of the core-guided signal. The second kind of fiber was developed in the late 1980s for use with high power fiber amplifiers and fiber lasers. In these fibers, the core is doped with active dopant material; it both guides and amplifies the signal light. The inner cladding and core together guide the pump light, which provides the energy needed to allow amplification in the core. In these fibers, the core has the highest refractive index and the outer cladding has the lowest. In most cases the outer cladding is made of a polymer material rather than glass.
Dispersion-compensating fiber
In double-clad fiber for dispersion compensation, the inner cladding layer has lower refractive index than the outer layer. This type of fiber is also called depressed-inner-cladding fiber and W-profile fiber (from the fact that a symmetrical plot of its refractive index profile superficially resembles the letter W).[1]
This type of double-clad fiber has the advantage of very low microbending losses. It also has two zero-dispersion points, and low dispersion over a much wider wavelength range than standard singly clad fiber. Since the dispersion of such double-clad fibers can be engineered to a great extent, these fibers can be used for the compensation of chromatic dispersion in optical communications and other applications.
Fiber for amplifiers and fiber lasers


In modern double-clad fibers for high power fiber amplifiers and lasers, the inner cladding has a higher refractive index than the outer cladding. This enables the inner cladding to guide light by total internal reflection in the same way the core does, but for a different range of wavelengths. This allows diode lasers, which have high power but low brightness, to be used as the optical pump source. The pump light can be easily coupled into the large inner cladding, and propagates through the inner cladding while the signal propagates in the smaller core. The doped core gradually absorbs the cladding light as it propagates, driving the amplification process. This pumping scheme is often called cladding pumping, which is an alternative to the conventional core pumping, in which the pump light is coupled into the small core. The invention of the cladding pumping by a Polaroid fiber research team (H. Po, et al.) revolutionized the power scaling method of fiber amplifiers and lasers.[3] Using this method, modern fiber lasers can produce continuous power up to several kilowatts, while the signal light in the core maintains near diffraction-limited beam quality.[4]
The shape of the cladding is very important at narrow core and wide cladding. Circular symmetry in a double-clad fiber seems to be the worst solution for a fiber laser; in this case, many modes of the light in the cladding miss the core and hence cannot be used to pump it.[5] In the language of geometrical optics, most of the rays of the pump light do not pass through the core, and hence cannot pump it. Ray tracing,[6] simulations of the paraxial propagation[7] and mode analysis[8] give similar results.
Chaotic fibers
In general, modes of a waveguide have "scars", which correspond to the classical trajectories. The scars may avoid the core, then the mode is not coupled, and it is vain to excite such a mode in the double-clad fiber amplifier. The scars can be distributed more or less uniformly in so-called chaotic fibers[9] have more complicated cross-sectional shape and provide more uniform distribution of intensity in the inner cladding, allowing efficient use of the pump light. However, the scaring takes place even in chaotic fibers.
Spiral shape


An almost-circular shape with small spiral deformation seems to be the most efficient for chaotic fibers. In such a fiber, the angular momentum of a ray increases at each reflection from the smooth wall, until the ray hits the "chunk", at which the spiral curve is broken (see figure at right). The core, placed in vicinity of this chunk, is intercepted more regularly by all the rays compared to other chaotic fibers. This behavior of rays has an analogy in wave optics. In the language of modes, all the modes have non-zero derivative in vicinity of the chunk, and cannot avoid the core if it is placed there. One example of modes is shown in the figure below and to the right. Although some of modes are show wide voids, none of these voids cover the core.
The property of DCFs with spiral-shaped cladding can be interpreted as conservation of angular momentum. The square of the derivative of a mode at the boundary can be interpreted as pressure. Modes (as well as rays), touching the spiral-shaped boundary transfer it some angular momentum. This transfer of angular momentum should be compensated with pressure at the chunk. Therefore, no one mode can avoid the chunk. Modes can show strong scarring along the classical trajectories (rays) and wide voids, but at least one of scars should approach the chunk to compensate the angular momentum transferredby the spiral part.
The interpretation with angular momentum indicates the reasonable size of the chunk. There is no reason to make this chunk larger than the core; a large chunk would not localize the scars sufficiently to provide coupling with the core. There is no reason to locaize the scars within an angle smaller than the core: the small derivative to the radius makes the manufacturing less robust; the larger is , the larger fluctuations of shape are allowed without breaking the condition . Therefore, the size of the chunk should be of order of size of the core.
More rigorously, the property of the spiral-shaped domain follows from the theorem about boundary behavior of modes of the Dirichlet Laplacian.[10] Although this theorem is formulated for the core-less domain, it prohibits the modes avoiding the core. A mode avoiding the core, then, should be similar to that of the core-less domain.
The stochastic optimization of the shape of cladding confirm that almost circular spiral realizes the best coupling of pump into the core.[11]
Filling factor

The efficiency of absorption of pumping energy in the fiber is an important parameter of a double-clad fiber laser. In many cases this efficiency can be approximated with[2]
where
- is the cross-sectional area of the cladding
- is the radius of the core (which is taken to be circular)
- is the absorption coefficient of pump light in the core
- is the length of the double-clad fiber, and
- is a dimensionless adjusting parameter, which is sometimes called the "filling factor"; .
The filling factor may depend on the initial distribution of the pump light, the shape of the cladding, and the position of the core within it.
The exponential behavior of the efficiency of absorption of pump in the core is not obvious. We could expect, that some modes of the cladding (or some rays) are better coupled to the core than others; therefore, the "true" dependence could be combination of several exponentials; and only comparison with simulations justifies this approximation, as shown in the figure above and to the right. In particular, this approximation does not work for circular fibers, see the initial work by Bedo et all, cited below. For chaotic fibers, approaches unity. The value of can be estimated by numerical analysis with propagation of waves, expansion by modes or by geometrical optics ray tracing, and values 0.8 and 0.9 are only empiric adjusitng parameters, which provide good agreement of the simple estimate with numerical simulations for two specific classes of double-clad fibers, circular ofset and rectangular. Obviously, the simple estimate above fails, as the ofset parameter becomes small compared to the size of cladding.
The filling factor approaches unity especially quickly in the spiral-shaped cladding, due to the special boundary behavior of the modes of the Dirichlet Laplacian.[10] Designers of double-clad fiber look for a reasonable compromise between the optimized shape (for the efficient couplung of pump into the core) and the simplicity of the manufacturing of the preform used to draw the fibers.
The power scaling of a fiber laser is limited by the unwanted nonlinear effects, such as stimulated Brillouin scattering and the stimulated Raman scattering. Therefore the powerful fiber laser should be short. However, for the efficient operation, the pump shold be absorbed in the core along the short length; and the estimate (1) provides the optimistic estimate for this case. In particular, the higher step of the index of refraction from the inner cladding to the outher one allows to focus (and confine) the pump in a smaller inner cladding. As a limiting case, the index step can be of order of two, from glass to air .[12] The estimate with filling factor gives an estimate, how shorter can be made an efficient DCF due to reduction of size of the inner cladding.
Alternative structures
For the good choice of the shape of the cladding, the filing factor above approaches unity; the following enhancement is possible at various kinds of tapering of the cladding
- [13] non-conventional shapes of such cladding are suggested
.[14] The planar waveguides with gain medium take an intermediate position between conventional solid-state lasers and the conventional double-clad lasers. The planar waveduide may confine multi-mode pump and high-quality signal, allowing the efficient coupling of pump and the diffraction-limited output[7][15]
Notes and references
- ^ S. Kawakami and S. Nishida (1974). "Characteristics of a doubly clad optical fiber with a low-index inner cladding". IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics. 10 (12): 879–887. doi:10.1109/JQE.1974.1068118.
- ^ a b c Kouznetsov, D. (2003). "Highly efficient, high-gain, short-length, and power-scalable incoherent diode slab-pumped fiber amplifier/laser". IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics. 39 (11): 1452–1461. doi:10.1109/JQE.2003.818311.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ H. Po (1989). Doubly clad high brightness Nd fiber laser pumped by GaAlAs phased array. Optical Fiber Communication Conference. PD7.
{{cite conference}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Y. Jeong, J. Sahu, D. Payne, and J. Nilsson (2004). "Ytterbium-doped large-core fiber laser with 1.36 kW continuous-wave output power". Optics Express. 12 (25): 6088–6092. doi:10.1364/OPEX.12.006088. PMID 19488250.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ S. Bedo (1993). "The effective absorption coefficient in double-clad fibers". Optics Communications. 99 (5–6): 331–335. doi:10.1016/0030-4018(93)90338-6.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b A. Liu (1996). "The absorption characteristics of circular, offset, and rectangular double-clad fibers". Optics Communications. 132 (5–6): 511–518. doi:10.1016/0030-4018(96)00368-9.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Kouznetsov, D. (2003). "Efficiency of pump absorption in double-clad fiber amplifiers. 2: Broken circular symmetry". JOSAB. 39 (6): 1259–1263. doi:10.1364/JOSAB.19.001259.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Kouznetsov, D. (2003). "Efficiency of pump absorption in double-clad fiber amplifiers.3:Calculation of modes". JOSAB. 19 (6): 1304–1309. doi:10.1364/JOSAB.19.001304.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Leproux, P. (2003). "Modeling and optimization of double-clad fiber amplifiers using chaotic propagation of pump". Optical Fiber Technology. 7 (4): 324–339. doi:10.1006/ofte.2001.0361.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b D.Kouznetsov (2004). "Boundary behaviour of modes of a Dirichlet Laplacian". Journal of Modern Optics. 51: 1362–3044.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ I.Dristas (2007). "Stochastic optimization of conventional and holey double-clad fibres". Journal of Optics A. 9 (4): 1362–3044. doi:10.1088/1464-4258/9/4/016.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ N.A.Mortensen (2007). "Air-clad fibers: pump absorption assisted by chaotic wave dynamics?". Optics Express. 15 (14): 8988–8996. doi:10.1364/OE.15.008988.
- ^ V. Filippov (2008). "Double clad tapered fiber for high power applications". Optics Express. 16 (3): 1929–1944. doi:10.1364/OE.16.001929.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ D.Kouznetsov (2004). "Slab delivery of incoherent pump light to double-clad fiber amplifiers: An analytic approach". IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics. 40 (4): 378–383. doi:10.1109/JQE.2004.824695.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ C.L.Bonner (2000). "Double-clad structures and proximity coupling for diode-bar-pumped planar waveguide lasers". IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics. 36 (2): 236–242. doi:10.1109/3.823470.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)











