Geography of Liechtenstein: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
No edit summary |
To indicate the municipality of location; remove Easternmost coordinates as obviously inaccurate |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
*Extreme points: |
*Extreme points: |
||
** North - River [[Rhine]] {{coord|47|16|15|N|9|31|51|E|type:landmark_region:LI|name=Rhine (North)}} |
** North - River [[Rhine]], [[Ruggell]] {{coord|47|16|15|N|9|31|51|E|type:landmark_region:LI|name=Rhine (North)}} This point is also the westernmost point in Austria. |
||
** South - summit of [[Mazorakopf]]/Falknishorn (2452 m) {{coord|47|2|55|N|9|33|26|E|type:mountain_region:LI|name=Mazerakopf (South)}} |
** South - summit of [[Mazorakopf]]/Falknishorn (2452 m), [[Triesen]] {{coord|47|2|55|N|9|33|26|E|type:mountain_region:LI|name=Mazerakopf (South)}} |
||
** East - border post 28, above [[Nenzinger Himmel]] {{coord|47| |
** East - border post 28, above [[Nenzinger Himmel]] |
||
** West - River Rhine, [[Balzers]] {{coord|47|3|46|N|9|28|18|E|region:LI_type:landmark|name=Rhine (West)}} |
|||
** |
** highest - [[Vorder Grauspitz]] (2599 m), [[Triesen]] {{coord|47|3|10|N|9|34|54|E|region:LI_type:mountain|name=Vorder Grauspitz (highest)}} |
||
** |
** lowest - [[Bangserfeld]] (429 m), [[Ruggell]] {{coord|47|15|57|N|9|32|14|E|region:LI_type:landmark|name=Bangserfeld (lowest)}} |
||
** lowest - [[Bangserfeld]] (429 m) {{coord|47|15|57|N|9|32|14|E|region:LI_type:landmark|name=Bangserfeld (lowest)}} |
|||
{{Geography of Europe}} |
{{Geography of Europe}} |
||
Revision as of 07:30, 19 June 2014
This article was imported from the CIA's World Factbook. |
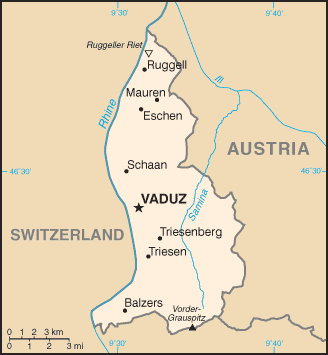

The principality of Liechtenstein encompasses most of the right (eastern) half of the Rhine Valley, wedged between Austria and Switzerland.
Along with Uzbekistan, Liechtenstein is one of only two doubly landlocked countries in the world; it contains a great variety of microclimates based on elevation.
Data from the CIA Factbook:
47°10′N 9°32′E / 47.167°N 9.533°E
- Area: 160 km² (land, 0 km² water)
- Land boundaries: total: 76 km; border countries: Austria 35 km, Switzerland 41 km
- Coastline: 0 km (landlocked)
- Maritime claims: none (landlocked)
- Climate: continental; cold, cloudy winters with frequent snow or rain; cool to moderately warm, cloudy, humid summers, great variety of microclimates based on elevation
- Terrain: mostly mountainous (Alps) with Rhine Valley in western third
- Natural resources: hydroelectric potential, arable land
- Lake: The only lake in Liechtenstein is the Gampriner Seele.
- Land use: arable land: 21.88%, permanent crops: 0%, other: 78.12% (2011)
- Natural hazards: NA
- Environment - international agreements:
- party to:
Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Sulphur 85, Air Pollution-Sulphur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands,
- signed, but not ratified:
- Extreme points:
- North - River Rhine, Ruggell 47°16′15″N 9°31′51″E / 47.27083°N 9.53083°E This point is also the westernmost point in Austria.
- South - summit of Mazorakopf/Falknishorn (2452 m), Triesen 47°2′55″N 9°33′26″E / 47.04861°N 9.55722°E
- East - border post 28, above Nenzinger Himmel
- West - River Rhine, Balzers 47°3′46″N 9°28′18″E / 47.06278°N 9.47167°E
- highest - Vorder Grauspitz (2599 m), Triesen 47°3′10″N 9°34′54″E / 47.05278°N 9.58167°E
- lowest - Bangserfeld (429 m), Ruggell 47°15′57″N 9°32′14″E / 47.26583°N 9.53722°E
