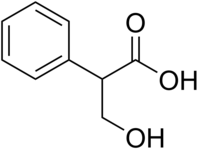
Tropic acid
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-Hydroxy-2-phenylpropanoic acid
| |
| Other names
2-Phenylhydracrylic acid; Tropate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.201 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | C011377 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H10O3 | |
| Molar mass | 166.176 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Tropic acid is a chemical with IUPAC name 3-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanoic acid and condensed structural formula HOCH2CHPhCOOH. It is a laboratory reagent used in the chemical synthesis of atropine and hyoscyamine. Tropic acid is a chiral substance, existing as either a racemic mixture or as a single enantiomer.
Synthesis
| Tropic acid synthesis 1:[1] | Tropic acid synthesis 2:[1] |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Pharmaceutical Uses
- Tropic acid is reacted with tropine (product of tropinone) to produce atropine (cf. Homatropine).
- Scopine is reacted with tropic acid in a Fischer esterification to produce scopolamine also.
- Other examples: tropicamide, Anisodamine.
- Quats: Hyoscine butylbromide, Butropium bromide (Coliopan®), Fentonium, Methylatropine, methscopolamine.
References
- ^ a b Template:Cite PMID
- ^ Sletzinger, Paulsen, U.S. patent 2,390,278 (1945 to Merck & Co.).
- ^ Blicke, U.S. patent 2,716,650 (1955 to University of Michigan).
- ^ DE 923426 (1955 to Sterling Drug).
