Kymograph
| Kymograph | |
|---|---|
| MeSH | D007734 |
A kymograph (which means 'wave writer') is a device that gives a graphical representation of spatial position over time in which a spatial axis represents time. It basically consists of a revolving drum wrapped with a sheet of paper on which a stylus moves back and forth recording perceived changes of phenomena such as motion or pressure.[1]
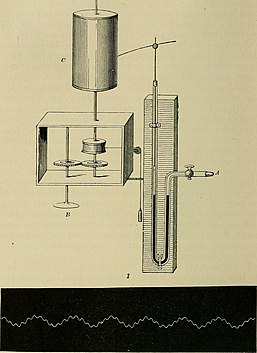
It was invented by German physiologist Carl Ludwig in the 1840s and found its first use as a means to intrusively monitor blood pressure, and has found several applications in the field of medicine.[2] Its primary use was to measure phenomena such as changes in muscular contractions or other physiological processes, including speech sounds. Kymographs were also used to measure atmospheric pressure, tuning fork vibrations, the functioning of steam engines, and the movement of molecules in cells.
See also
- Videokymography
- Depth kymography
- kymograph with Stimulator http://bionicmobin.com/en/
References
