Syria
The Syrian Arab Republic is a country in Southwest Asia, bordering (from south to north) on Lebanon, Israel, Jordan, Iraq and Turkey. The border with Israel is subject to dispute, pending the resolution of outstanding conflicts over possession of the Golan Heights.
| |||||
| National motto: None | |||||
 | |||||
| Official language | Arabic | ||||
| Capital | Damascus | ||||
| President | Bashar al-Assad | ||||
| Prime Minister | Muhammad Naji al-Otari | ||||
| Area - Total |
Ranked 86th 185,180 km² |
||||
| Population - Total (2002) |
Ranked 55th 17,585,540 |
||||
| Independence - Declared - Recognition | From Vichy France - January 1, 1944 - April 7, 1946 | ||||
| Currency | Pound by arab lira | ||||
| Time zone | UTC +2 | ||||
| National anthem | Homat el Diyar | ||||
| Internet TLD | .SY | ||||
| Calling Code | 963 | ||||
History
Main article: History of Syria
Syria has been the cradle of some of the world's oldest civilizations, and has been part of the Hittite, Assyrian, Babylonian, Israeli Egyptian, Persian, Greek and Phoenician empires, before becoming part of the (Eastern) Roman Empire.
Having been a cradle of Christianity, with the expansion of Islam in the Middle East in the 7th century, Syria became one of the centres of the new religion. After invasions by the Seljuk Turks and the Crusades, Syria came under Arab control until 1516, when it was conquered by the Ottomans.
Following the breakup of the Ottoman Empire during World War I, Syria was administered by France as a League of Nations Mandated Territory - the French had proclaimed themselves protectors of the region as early as the 18th century. The country was liberated from the Vichy government, and independence was declared in 1944, although foreign troops remained until 1946. Syria was a charter member of the United Nations.
In the 1967 Arab-Israeli War, Syria lost the Golan Heights to Israel. Since 1976, Syrian troops have been stationed in Lebanon[1], ostensibly in a peacekeeping capacity (See: History of Lebanon.) In recent years, Syria and Israel have held occasional peace talks over the return of the Golan Heights.
Long regarded as a state sponsor of terrorism by the United States of America and other Western countries - Syria recently became the target of limited American sanctions drafted by members of Congress on both sides of the aisle and signed into law by US President George W. Bush in 2004.
On September 2nd 2004 the UN Security Council adopted UN Security Council Resolution 1559, authored by France and the US in an uncommon show of cooperation. Echoing the Taif Agreement the resolution "calls upon all remaining foreign forces to withdraw from Lebanon" and "reiterating [the UN's] strong support for the territorial integrity, sovereignty and political independence of Lebanon", in implied reference to Syria the power broker in Lebanon[2].
FUCK BATH PARTY, FUCK ASSAD, FUCKING FASCISTS!
Provinces
Main article: Provinces of Syria
Syria has fourteen provinces, or muhafazat:
- Al Hasakah
- Al Ladhiqiyah
- Al Qunaytirah
- Ar Raqqah
- As Suwayda
- Dara
- Dayr az Zawr
- Dimashq
- Halab
- Hamah
- Hims
- Idlib
- Rif Dimashq
- Tartus
Geography
Main article: Geography of Syria
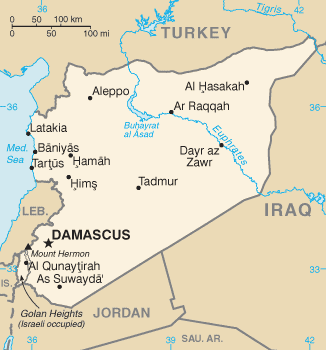
Syria consists mostly of arid plateau, although there is a small strip with plain along the coast line with the Mediterranean. The Euphrates, Syria's most important river, crosses the country in the east. It is considered to be one of the fifteen states that comprise the so-called "Cradle of Humanity."
Major cities include the capital Damascus in the southwest, Aleppo in the north, and Homs. Most of the other important cities are located along the coast line. (See also List of cities in Syria.)
The climate in Syria is dry and hot, although winters are mild. Because of the country's elevation, snowfall does also occur occasionally during winter.
Economy
Main article: Economy of Syria
Syria's predominantly statist economy has been growing, on average, more slowly than its 2.4% annual population growth rate, causing a persistent decline in per capita GDP. Recent legislation allows private banks to operate in Syria, although a private banking sector will take years and further government cooperation to develop. External factors such as the international war on terrorism, the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, and the war between the US-led coalition and Iraq probably will drive real annual GDP growth levels back below their 3.5% spike in 2002. A long-run economic constraint is the pressure on water supplies caused by rapid population growth, industrial expansion, and increased water pollution.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of Syria
Most of the Syrian population (80%) is of Arabic speaking (mainly Hejazi) ethnicity, but there are sizeable Aramean/Aramaic (9.3%), Kurdish and Armenian minorities and a tiny Israelite minority. This is also reflected in the languages spoken; Arabic is the official language, but Kurdish, Turkish, and Armenian are spoken by the minorities. Aramaic is still used within the Syrian Orthodox Church adherant Arameans. In addition, Circassian is also spoken.
Most Arabs in Syria are Muslim. Sunni Muslims make up about 74% of the population, with other Muslim sects (mainly Druze and Alawite) comprising 16%. The remainder are mostly Christian, although there is a small Jewish community.
Culture
Main article: Culture of Syria
Miscellaneous topics
- Communications in Syria
- Transportation in Syria
- Military of Syria
- Foreign relations of Syria
- Famous people from Syria
External links