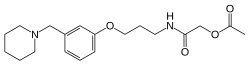
Roxatidine acetate
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 80–90% |
| Protein binding | 5–7% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic deacetylation Minor involvement of CYP2D6 and CYP2A6 |
| Elimination half-life | 5–7 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H28N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 348.443 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Roxatidine acetate is a specific and competitive histamine H2 receptor antagonist drug that is used to treat gastric ulcers, Zollinger–Ellison syndrome, erosive esophagitis, gastro-oesophageal reflux disease, and gastritis.[1][2]
Pharmacodynamic studies showed that 150 mg of roxatidine acetate were optimal in suppressing gastric acid secretion, and that a single bedtime dose of 150 mg was more effective than a dose of 75 mg twice daily in terms of inhibiting nocturnal acid secretion.[1]
It was patented in 1979 and approved for medical use in 1986.[3] It is available in countries including China, Japan, Korea, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Greece and South Africa.[2]
Synthesis

The reductive amination between piperidine [110-89-4] (1) and 3-hydroxybenzaldehyde [100-83-4] (2) gives 3-(1-Piperidinylmethyl)phenol [73279-04-6] (3). William ether synthesis with N-(3-Bromopropyl)phthalimide [5460-29-7] (4) gives PC12898565 (5). W.K. deprotection with hydrazine yielded (3-(1-piperidinylmethyl)phenoxy)propylamine [73278-98-5] (6). Heating with glycolic acid [79-14-1] (7) gave the amide (8). Acetylation with acetic anhydride completed the synthesis of (9).
References
- ^ a b Murdoch D, McTavish D (August 1991). "Roxatidine acetate. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and its therapeutic potential in peptic ulcer disease and related disorders". Drugs. 42 (2): 240–260. doi:10.2165/00003495-199142020-00006. PMID 1717223. S2CID 46973503.
- ^ a b BioSpectrum Bureau 1 November 2012 Sinhuan's generic heart drug gets production approval
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 444. ISBN 9783527607495.
- ^ Castaer, J.; Serradell, MN; TZU-0460. Drugs Fut 1985, 10, 12, 995.
- ^ Kenyu Shibata, 7 More », EP0024510 (1983 to Teikoku Hormone Mfg. Co., Ltd.).
- ^ Zhang Yang, et al. WO2019075976 (to Beijing Xuansheng Pharmaceutical Co Ltd).
- ^ Guo Rongyao & Wang Xiaofeng, CN107698538 (2018 to Inner Mongolia Jingdong Pharmaceutical Co Ltd).
- ^ 刘占滨, et al. CN102993121 (2013 to HARBIN PHARMACEUTICAL GROUP SANJING PHARMACEUTICAL CO Ltd).
- ^ He Minrong, CN101717363 (2012 to Jiangsu Baosheng Longcheng Pharmaceutical Co Ltd).
