Quoll
| Quoll | |
|---|---|

| |
| Tiger quoll (Dasyurus maculatus) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Infraclass: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Subfamily: | |
| Tribe: | |
| Genus: | Dasyurus É. Geoffroy, 1796
|
| Type species | |
| Dasyurus viverrinus Anon., 1791
(Didelphis viverrina Shaw, 1800) | |
| Species | |
The quoll, or native cat, (genus Dasyurus) is a carnivorous marsupial native to mainland Australia, New Guinea and Tasmania. It is primarily nocturnal and spends most of the day in its den. There are six species of quoll; four are found in Australia and two in New Guinea. Another two species are known from fossil remains in Pliocene and Pleistocene deposits in Queensland. Genetic evidence indicates that the quoll evolved around 15 million years ago in the Miocene, and that the ancestors of the six species had all diverged by around 4 million years ago. The quoll species vary in weight and size, from 300 grams (11 oz) to 7 kilograms (15 lb). They have brown or black fur and pink noses. They are largely solitary, but come together for a few social interactions such as mating, which occurs during the winter season. A female gives birth to up to 18 pups, of which only 6 survive to suckle on her teats.
The quoll eats small mammals such as rabbits, small birds, lizards and insects. Its natural lifespan is between two and five years. All species have drastically declined in numbers since Australasia was colonised by Europeans, with one species — the Eastern quoll — becoming extinct on the Australian mainland and is now found only in Tasmania. Major threats to their survival include the cane toad, predators, urban development and poison baiting. Conservation efforts include breeding programs in captivity.
Taxonomy
The name Dasyurus means "hairy-tail",[1] and was coined by Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire in 1796.
In 1770, Captain Cook collected quolls on his exploration of the east coast of Australia, adopting the Aboriginal name for the animals.[2] Although the origin of Cook's specimens are unclear, the word and its variants je-quoll, jaquol or taquol are derived from the language of the Guugu Yimithirr people of far north Queensland. There is no evidence the local indigenous people used the word in the Sydney area.[3] They were likened in appearance to a polecat or marten in the earliest reports, the tiger quoll being called "spotted marten" and eastern quoll "spotted opossum", but by 1804, the names "native cat" and "tiger cat" had been adopted by early settlers. In the 1960s, noted naturalist David Fleay pushed for the revival of the term "quoll" as he felt the then current vernacular names were misleading.[4]

Four species have been recovered from Pleistocene cave deposits from Mount Etna Caves National Park near Rockhampton in central Queensland. Remains of the tiger quoll and the northern quoll, and a species either identical or very similar to the eastern quoll, as well as a prehistoric species as yet undescribed, all lived in what was a rainforest climate. The northern quoll is still found in the region.[5] The fossil species D. dunmalli, described by Bartholomai in 1971, is the oldest species recovered to date. Its remains were found in Pliocene deposits near Chinchilla in southeastern Queensland. Known only from a lower jaw and some teeth, it was a relative of the tiger quoll.[6]
The first species described, the tiger quoll, was originally placed in the American opossum genus Didelphis. The tribe Dasyurini, to which quolls belong, also includes the Tasmanian devil, the antechinus, the Kowari, and the mulgara.[7] Genetic analysis of cytochrome b DNA and 12S rRNA of the mitochondria indicates the quolls evolved and diversified in the late Miocene between 15 and 5 million years ago, a time of great diversification in marsupials. The ancestors of all current species had diverged by the early Pliocene, around 4 million years ago.[8]
The genus Dasyurus consists of six species of quoll: [7]
- The bronze quoll (D. spartacus) is the only mammal that is found in the Trans Fly ecoregion ] but not in northern Australia. It is found in the southern part of New Guinea south of the Fly River.[9] Rising sea levels due to an increase in global temperature caused a land bridge that once connected Australia and New guinea to be covered up with water. A 2007 study conducted by the University of New South Wales suggests that the bronze quoll is closely related to the western quoll, their ancestors diverging with the separation of land masses.[10]
- The western quoll or Chuditch (D. geoffroii) is restricted to the Jarrah Forest and the central and southern Australian Wheatbelt. It is believed that the western quoll once occupied 70 percent of Australia, but because of cane toads, predators, habitat destruction and poison baiting, it is now less abundant.[11]
- The New Guinean quoll (D. albopunctatus) is found throughout most of New Guinea. It tends to live at an elevation of about 1,000 metres (3,300 ft), and is not found in the south-western lowlands, although it can found on Yapen Island.[12]
- The eastern quoll (D. viverrinus) is now considered extinct on mainland Australia: the last sighting there was in the 1960s. But it does inhabit much of nearby Tasmania, where it can be found in rainforests, heathland, alpine areas, and scrubs. It can be found near farms as it eats pasture food. The eastern quoll can also be seen in the Mt. Field National Park.[13]
- The tiger quoll or spotted quoll (D. maculatus), also known as spotted quoll, lives in south-eastern Australia. It tends to prefer rock dens more than dens made out of wood. In a study submitted by Belcher and Darrant in 2006, the habitats of tiger quoll were directly related to the amount of prey found in the area. Gullies and drainage ditches were used quite often by the quolls and ridges with rocky outcrops were used to make the rock dens that the animals enjoy.[14]
- The northern quoll (D. hallucatus) could be found in the northern third of Australia a century ago. Presently, it resides in high rocky areas and areas with heavy rainfall. The northern quoll is abundant on the minor islands surrounding northern Australia. In 2003, northern quolls were translocated to Astell and Pobassoo Islands for conservation reasons.[15] Genetic analysis indicates it is the earliest offshoot from the ancestors of other quolls.[8]
Description

Adults are between 25 and 75 centimetres (10 and 30 in) long, with hairy tails about 20 to 35 centimetres (8 to 10 in) long. Females have six nipples and develop a pouch during the breeding season, which opens toward the tail (with the exception of the tiger quoll, which has a true pouch) when they are rearing young. Their coats are brown or black, with some colour variants in between. They have a bright pink nose and a long snout. Their natural lifespan is between two and five years; the larger species tend to live longer than the smaller.[16] Quolls are largely solitary, nocturnal animals.[17] The average weight differs greatly depending on the species — male western and eastern quolls weigh about 1.3 kilograms (3 lb) and females 0.9 kilograms (2 lb). The tiger quoll is the largest, with the male weighing about 7 kilograms (15 lb) and the female 4 kilograms (9 lb). The northern quoll is the smallest, and the male weighs on average 400–900 grams (14–32 oz), and the female 300–500 grams (11–18 oz).[18]
Distribution and Habitat
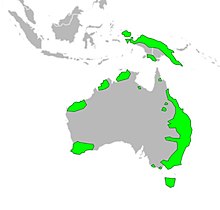
The quoll is indigenous to mainland Australia, New Guinea, and Tasmania. The six species were once widely distributed across the three land masses, but are now restricted in only a few areas. Although primarily ground-dwelling, the genus has developed secondary arboreal characteristics. Each species of quoll lives in distinct geographical areas.[9][12][11] The tiger quoll and eastern quoll are exclusively mesic zone species, that is they inhabit moister habitats. The western quoll also inhabits mesic habitat, but has adapted to arid regions across inland Australia, while the northern quoll inhabits tropical habitat of high rainfall.[19]
Behaviour

The quoll is a carnivorous marsupial. It is primarily nocturnal, sleeping in hollowed out logs or rocky dens and coming out to hunt during the night, though on rare occasions it can be seen looking for prey during the day. It is mostly ground-dwelling, but it is not uncommon to see a quoll climbing a tree. The quoll marks its territory several kilometres away from its den. A male's territory often overlaps many females' territories and male and female quolls only meet for mating.[17] Quolls have communal "bathroom" spots, usually on an outcropping used for marking territory and social functions. These communal latrines may have up to one hundred droppings in them.[20] The quoll is a mostly solitary creature, limiting contact with others to mating or other social activities such as using the latrines.[21]
Diet

The quoll is mostly carnivorous; the smaller quolls primarily eat insects, birds, frogs, lizards and fruit, and the larger species eat birds, reptiles and mammals including echidnas and possums. The tiger quoll's diet is dominated by mammals such as brushtail possums, rabbits and hares. The exact mix is variable according to the availability of prey after bushfires, and can include carrion or bandicoots when food is scarce.[22] The other species of quoll have also been known to eat carrion. The quoll's paws and vibrissae allow it to reach into small burrows to find prey.[20] The quoll hunts by stalking. Depending on the size of its prey, the quoll may leap or pounce on it. It pins small prey down with its front paws while devouring it, and jumps onto larger prey, sinking in its claws and closing its jaws around the neck. The quoll can obtain all the water it needs from its food, making it quite adaptable during droughts or other periods of water shortage.[20]
Reproduction
Mating occurs during the winter months. Once a female quoll has been impregnated, the folds on her stomach convert into a pouch that opens at the back. The gestation period is 21 days. A baby quoll, or pup, is the size of a grain of rice. Up to 18 quolls are born in each litter, but only six survive the first two weeks. The survivors stay in their mother's pouch for eight weeks, suckling on one of the mother's six teats for milk. During the ninth week the pups venture out of the pouch and onto the mother's back, where they remain for six weeks.[23] The quoll reaches maturity when it is one year old, and has a natural lifespan of between two and five years.[24] A 2008 study of the pouches of tiger quolls reported that the pouches' appearance' were reliable indicators of the quolls' reproductive status: during the follicular phase, pouches were found to be red and have many secretions. Post-ovulation, pouches became deep and wet. Researchers and scientists can use this information to determine where a female quoll is in her ovarian cycle, which is anticipated to be helpful in breeding management.[25]
Threats

Cane toads were introduced into Queensland in 1935, since when their numbers have grown exponentially. These poisonous toads pose a significant threat to the northern quoll, which may die after consuming one. Cane toads can also shoot their venom, which can easily blind an animal. The Department of Sustainability, Environment, Water, Population and Communities has stated that cane toads are highly invasive and are major threats to the quoll's survival.[15] Predators such as foxes and cats prey on quolls and compete with them for food. For example, both quolls and foxes catch and consume rabbits. Since the introduction of foxes, the rabbit population has dropped dramatically. Foxes have been eradicated from many of the islands off the coast of Australia in an effort to protect the quoll.[15]
The quoll is suffering badly from urbanization, housing development, mining development, and expansion of agricultural lands. Habitats are also being destroyed by large herbivores trampling the grass and overgrowth, making camouflage impossible. Forest fires and weeds also contribute to habitat destruction.[15]
The poison sodium monofluoroacetate is commonly used in Australia to control pests such as European rabbits, foxes, feral predators, and wild dogs such as dingoes. It is cooked into meat which is put into the wild for the animals to ingest. The poison is extremely toxic to wild dogs and other pests, but considerably less so to quolls. Size is a main factor in how the poison will affect a quoll; larger quolls will suffer no ill effects from eating one piece of prepared meat containing sodium monofluroacetate, but will suffer if they eat more than one within a short period of time. One piece of meat may be lethal to female and juvenile quolls. Since the quoll is a carnivore and will readily consume any meat left out, it is at high risk from the poison. The meat is supposed to be buried at least 8 centimetres (3 in) underground, but has been found under minimal dirt that a quoll can dig around to get to it. Poisoning is currently being investigated, as many believe that the number of quolls protected from predators by the bait is much more than those who ingest the poison and die.[15][26]
Conservation efforts
Since 1770, all Australian quoll species have declined in number owing to habitat loss caused by urbanization. The northern quoll is threatened by toxic cane toads, but a University of Sydney project revealed in 2010 is teaching them to avoid eating the invasive amphibians.[27] In 2008 the Northern Territory Wildlife Park in Australia recorded their first litter of quoll pups in the park. The quolls bred well in captivity, with over fifteen litters in the 2008 breeding season alone.[28]
In late October 2011, a litter of five tiger quoll pups was born at Wild Life Sydney in Darling Harbour, Australia. The pups were born to inexperienced parents, both just one year old. The reason for the young parents was the fact that older male quolls can become violent and kill the female if they do not want to mate. By breeding one year old quolls, there was no threat of violence. Four of the quoll pups will be sent to other zoos or wildlife parks across Australia but one-whom the researchers named Nelson, will stay at the centre to become an "ambassador for all quolls".[29]
Fox control programs have benefited the western quoll. The Department of Environment and Conservation (Western Australia) monitors western quoll populations in the Jarrah Forest as part of its faunal management programs, as well as ongoing research into fox control, timber harvesting, and prescribed burning. The Perth Zoo has been monitoring a successful captive breeding program since 1989. They have successfully bred more than sixty western quolls; most being transferred to Julimar Conservation Park, with proposals to translocate to Wheatbelt reserves and Shark Bay.[11]
The bronze quoll is kept in Wasur National Park and Tonda Wildlife Management Area. More research on distribution and threats is needed for further conservation.[9]
References
- ^ Strahan 2008, pp. 62–64
- ^ "Australian Threatened Species, Tiger Quoll, Spotted-tailed Quoll or Spot-tailed Quoll, Dasyurus maculatus" (PDF).
- ^ Mahoney, J.A.; Ride, W.D.L. (1984). "The Identity of Captain Cook's Quoll Mustela quoll Zimmermann 1783 (Marsupialia: Dasyuridae)". Australian Mammalogy. 7 (1–2): 57–62.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Olsen, Penny (2010). Upside Down World: Early European Impressions of Australia's Curious Animals. National Library Australia. pp. 42–47. ISBN 0642277060.
- ^ Cramb, Jonathan; Hucknull, Scott; (Webb, Gregory E. (2009). "High diversity Pleistocene rainforest Dasyurid assemblages with implications for the radiation of the dasyuridae". Austral Ecology. 34 (6): 663–669. doi:10.1111/j.1442-9993.2009.01972.x.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Long, John A.; Archer, Michael (2002). Prehistoric mammals of Australia and New Guinea: one hundred million years of evolution. UNSW Press. p. 53. ISBN 0868404357.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Groves 2005, pp. 24–25
- ^ a b Krajewski, Carey; Wroe, Stephen; Westerman, Michael (2000). "Molecular evidence for phylogenetic relationships and the timing of cladogenesis in dasyurid marsupials". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 130 (3): 375–404. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2000.tb01635.x.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c "Dasyurus spartacus". IUCN. Retrieved 20 October 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "New Guinea's bronze quoll could be a long lost Aussie". UNSW. Retrieved 20 October 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ a b c "Dasyurus geoffroii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Retrieved 20 October 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) Cite error: The named reference "IUCN3" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page). - ^ a b "Dasyurus albopunctatus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Retrieved 20 October 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "Eastern Quoll, Dasyurus viverrinus". Parks and Wildlife Service, Tasmania. Retrieved 20 October 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ Belcher, C.A.; Darrant, J.P. (2006). "Habitat Use by Tiger Quoll (Dasyurus maculatus) (Marsupialia: Dasyuridae)in south-eastern Australia". Journal of Zoology. 269 (2): 183–190. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.2006.00056.x. Retrieved 20 October 2011.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d e Hill, B. M.; Ward, S. J. "National Recovery Plan for the Northern Quoll Dasyurus hallucatus" (PDF). Department of Natural Resources, Environment, The Arts and Sport, Darwin. pp. 1, 3, 6, 7. Retrieved 20 October 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) Cite error: The named reference "Hill" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page). - ^ "Quolls of Australia". Australian Government:Department of Environment and Heritage.
{{cite web}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Missing or empty|url=(help) - ^ a b York Fei Leung. "Dasyurus geoffroi i". University of Michigan Museum of Zoology. Retrieved 31 October 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "Quolls of Australia". Australian Government: Department of the Environment and Heritage. 2003. Retrieved 2 November 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ Cooper, C.E.; Withers, P.C. (2010). "Comparative physiology of Australian quolls (Dasyurus; Marsupialia)". PubMed: 857–68. Retrieved 21November2011.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c Jones, Menna E.; Rose, Robert K.; Burnett, Scott (2001). "Dasyurus maculatus" (PDF). Mammalian Species (676). American Society of Mammalogists: 1–9. Retrieved 25 October 2011.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "Native Plants and Animals". Department of Primary Industries, Parks, Water and Environment. Retrieved 1 November 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|published=ignored (help) - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1071/WR05101, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1071/WR05101instead. - ^ "Parks and Wildlife Service-Spotted-tail Quoll". Parks and Wildlife Service Tasmania. Retrieved 19 October 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "Quolls of Australia". Government of Australia. 3 June 2011. Retrieved 6 October 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=and|date=(help) - ^ Hesterman, H.; Jones, S. M.; Schwarzenberger, F. (2008). "Pouch appearance is a reliable indicator of the reproductive status in the Tasmanian devil and the spotted-tailed quoll". Journal of Zoology. 275 (2). The Zoological Society of London: 130–138. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.2008.00419.x. Retrieved 26 October 2011.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "Draft revised Tiger Quoll Action Statement". Otway Ranges Environment Network. June 2001.
- ^ "Taste training for northern quolls". Australian Geographic. Retrieved 15 April 2010.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "Endangered Quolls breeding well in captivity in Darwin". Wildlife Extra. Retrieved 2 November 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ Liz T. Williams (October 26, 2011). "Baby quolls a boost for breeding program". Australian Geographic. Retrieved 2 November 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help)
Bibliography
- Groves, C.; Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (2005). Mammal Species of the World. John Hopkins University Press. pp. 24–25. ISBN 0-801-88221-4.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Strahan, Ronald; van Dyck, Steve (2008). The Mammals of Australia. New Holland. pp. 62–64. ISBN 9781877069253.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
