Ross 458
 Image of Ross 458 with the legacy surveys. The companion is the red object marked with an crosshair in the lower right. | |
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Virgo |
| Right ascension | 13h 00m 46.557s[1] |
| Declination | +12° 22′ 32.677″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 9.79[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | Main sequence |
| Spectral type | M0.5 + M7.0[3] |
| U−B color index | 1.12[2] |
| B−V color index | 1.44[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −12.33±0.32[1] km/s |
| Proper motion ( | RA: −628.7±0.184 mas/yr[1] Dec.: −33.5±0.133 mas/yr[1] |
| Parallax ( | 86.9010 ± 0.1170 mas[1] |
| Distance | 37.53 ± 0.05 ly (11.51 ± 0.02 pc) |
| Orbit[4] | |
| Period (P) | 13.63±0.03 yr |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 4.93±0.01 |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.245±0.001 |
| Inclination (i) | 130.3±0.3° |
| Longitude of the node ( | 56.25±0.17° |
| Periastron epoch (T) | 2007.67±0.02 |
| Argument of periastron ( (secondary) | 157.5±0.6° |
| Details | |
| Primary (A) | |
| Mass | 0.553±0.007[4] M☉ |
| Radius | 0.473±0.021 R☉[5] 0.368±0.031[6] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 0.044+0.016 −0.012[6] L☉ |
| Temperature | 3,484±50[5] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | 0.09±0.10[6] dex |
| Rotation | 2.89 d[7] |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 9.6±0.9[8] km/s |
| Age | 400–800[3] Myr |
| Secondary (B) | |
| Mass | 88.918+1.836 −2.844[9] MJup |
| C | |
| Mass | 11.7+3.6 −3[10] MJup |
| Radius | 1.1±0.05[10] RJup |
| Luminosity | 2.51×10−6[10] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.38+0.16 −0.17[10] cgs |
| Temperature | 682+16 −17[10] K |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
| ARICNS | data |
Ross 458, also referred to as DT Virginis, is a binary star system in the constellation of Virgo. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 9.79[2] and is located at a distance of 37.6 light-years from the Sun. Both of the stars are low-mass red dwarfs with at least one of them being a flare star. This binary system has a circumbinary sub-stellar companion.
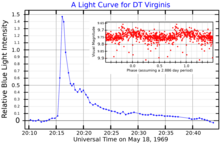
This star was mentioned as a suspected variable by M. Petit in 1957.[14] In 1960, O. J. Eggen classified it as a member of the Hyades moving group based on the system's space motion;[15] it is now considered a likely member of the Carina Near Moving Group.[5] Two flares were reported from this star in 1969 by N. I. Shakhovskaya, confirming it as a flare star.[12] It was identified as an astrometric binary in 1994 by W. D. Heintz, who found a period of 14.5 years.[4] The pair were resolved using adaptive optics in 1999.[4] Early mass estimates placed the companion near the substellar limit, and it was initially proposed as a brown dwarf[16] but is now considered late-type red dwarf.[3]
The primary member, component A, is an M-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of M0.5.[3] It is young, magnetically very active star with a high rate of rotation[16] and strong H
Planetary system
[edit]A distant sub-stellar companion to the binary star system was discovered in 2010 as part of a deep infrared sky survey. This is most likely a T8 spectral type brown dwarf with an estimated rotation period of 6.75±1.58 h. The object varies slightly in brightness, which may be due to patchy clouds.[3] The companion lacks a detectable oxygen in the atmosphere, implying its formation from sequestrated source or peculiar atmospheric chemistry.[17]
| Companion (in order from star) |
Mass | Semimajor axis ( |
Orbital period (years) |
Eccentricity | Inclination | Radius |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 11.7 MJ | 1,110 | — | — | — | 1.1 RJ |
See also
[edit]- CM Draconis
- GU Piscium b
- HD 106906 b
- Kepler-16
- Lists of exoplanets
- NN Serpentis
- QS Virginis
- WD 0806-661
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e Vallenari, A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (2023). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 674: A1. arXiv:2208.00211. Bibcode:2023A&A...674A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940. S2CID 244398875. Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ^ a b c d e Alekseev, I. Y.; Bondar, N. I. (1997). "Spottedness of the emission-line dwarf stars BF CVn, DT Vir, EQ Vir, and V1396 Cyg from photoelectric and photographic observations". Astronomy Letters. 23 (2): 257–262. Bibcode:1997AstL...23..257A. Retrieved 2021-11-30.
- ^ a b c d e f Manjavacas, Elena; et al. (April 2019). "Cloud Atlas: Rotational Spectral Modulations and Potential Sulfide Clouds in the Planetary-mass, Late T-type Companion Ross 458C". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 875 (2): 7. arXiv:1903.10702. Bibcode:2019ApJ...875L..15M. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ab13b9. S2CID 85518395. L15.
- ^ a b c d Laugier, R.; et al. (March 2019). "Recovering saturated images for high dynamic kernel-phase analysis. Application to the determination of dynamical masses for the system Gl 494AB". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 623: 8. arXiv:1901.02824. Bibcode:2019A&A...623A.164L. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201834387. S2CID 119495214. A164.
- ^ a b c d Houdebine, E. R. (September 2010). "Observation and modelling of main-sequence star chromospheres - XIV. Rotation of dM1 stars". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 407 (3): 1657–1673. Bibcode:2010MNRAS.407.1657H. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.16827.x.
- ^ a b c d Khata, Dhrimadri; et al. (April 2020). "Understanding the physical properties of young M dwarfs: NIR spectroscopic studies". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 493 (3): 4533–4550. arXiv:2002.05762. Bibcode:2020MNRAS.493.4533K. doi:10.1093/mnras/staa427.
- ^ Küker, M.; et al. (2019). "Cycle period, differential rotation and meridional flow for early M dwarf stars". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 622: A40. arXiv:1804.02925. Bibcode:2019A&A...622A..40K. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833173. S2CID 118842388.
- ^ Fouqué, Pascal; et al. (April 2018). "SPIRou Input Catalogue: global properties of 440 M dwarfs observed with ESPaDOnS at CFHT". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 475 (2): 1960–1986. arXiv:1712.04490. Bibcode:2018MNRAS.475.1960F. doi:10.1093/mnras/stx3246.
- ^ Feng, Fabo; Butler, R. Paul; et al. (August 2022). "3D Selection of 167 Substellar Companions to Nearby Stars". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series. 262 (21): 21. arXiv:2208.12720. Bibcode:2022ApJS..262...21F. doi:10.3847/1538-4365/ac7e57. S2CID 251864022.
- ^ a b c d e f Zhang, Zhoujian; Liu, Michael C.; Marley, Mark S.; Line, Michael R.; Best, William M. J. (2021-07-01). "Uniform Forward-Modeling Analysis of Ultracool Dwarfs. I. Methodology and Benchmarking". The Astrophysical Journal. 916 (1): 53. arXiv:2011.12294. Bibcode:2021ApJ...916...53Z. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/abf8b2. ISSN 0004-637X.
- ^ "DT Virginis". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2019-09-07.
- ^ a b Shakhovskaya, N. I. (July 1969). "Flares of BD +13 2618". Information Bulletin on Variable Stars. 361: 1. Bibcode:1969IBVS..361....1S.
- ^ Kiraga, M. (March 2012). "ASAS Photometry of ROSAT Sources. I. Periodic Variable Stars Coincident with Bright Sources from the ROSAT All Sky Survey". Acta Astronomica. 62 (1): 67–95. arXiv:1204.3825. Bibcode:2012AcA....62...67K. Retrieved 2 May 2022.
- ^ Petit, M. (October 1957). "On the International Cooperation for the Study of Flare Variable Stars". Soviet Astronomy. 1: 783. Bibcode:1957SvA.....1..783P.
- ^ Eggen, Olin J. (1960). "Stellar Groups, VII. The Structure of the Hyades Group". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 120 (6): 540–62. Bibcode:1960MNRAS.120..540E. doi:10.1093/mnras/120.6.540.
- ^ a b Beuzit, J. -L.; et al. (October 2004). "New neighbours. III. 21 new companions to nearby dwarfs, discovered with adaptive optics". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 425: 997–1008. arXiv:astro-ph/0106277. Bibcode:2004A&A...425..997B. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20048006. S2CID 15398860.
- ^ Gaarn, Josefine; Burningham, Ben; Faherty, Jacqueline K.; Visscher, Channon; Marley, Mark S.; Gonzales, Eileen C.; Calamari, Emily; Bardalez Gagliuffi, Daniella; Lupu, Roxana; Freedman, Richard (2023), "The puzzle of the formation of T8 dwarf Ross 458c", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 521 (4): 5761–5775, arXiv:2303.16863, doi:10.1093/mnras/stad753
- ^ "Ross 458 Overview". NASA Exoplanet Archive.
