The root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) is calculated, using Kabsch algorithm
(1976) or Quaternion algorithm (1991) for rotation, between two Cartesian
coordinates in either .xyz or .pdb format, resulting in the minimal
RMSD.
For more information please read RMSD and Kabsch algorithm.
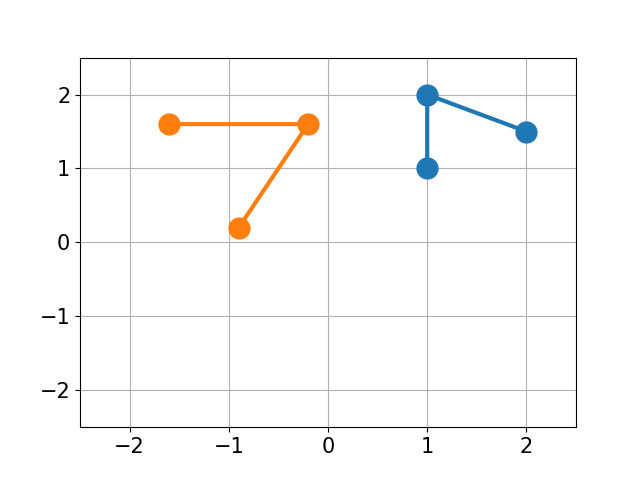
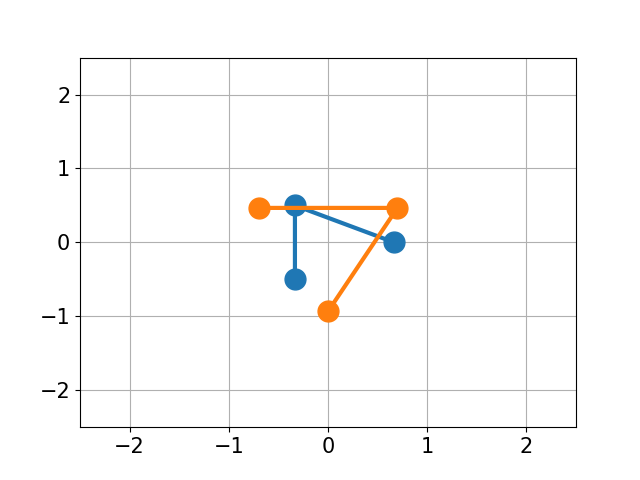
You have molecule A and B and want to calculate the structural difference between those two. If you just calculate the RMSD straight-forward you might get a too big of a value as seen below. You would need to first recenter the two molecules and then rotate them unto each other to get the true minimal RMSD. This is what this script does.
| No Changes | Re-centered | Rotated |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
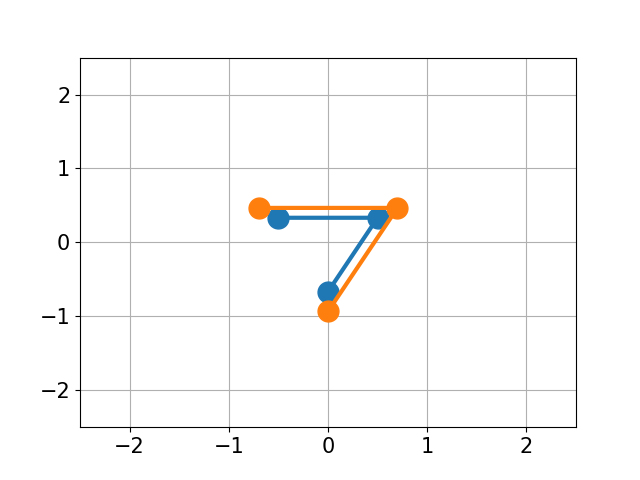 |
| RMSD 2.50 | RMSD 1.07 | RMSD 0.25 |
- Implementation:
- Calculate Root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) of Two Molecules Using Rotation, GitHub, http://github.com/charnley/rmsd, <git commit hash or version number>
- Kabsch algorithm:
- Kabsch W., 1976, A solution for the best rotation to relate two sets of vectors, Acta Crystallographica, A32:922-923, doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1107/S0567739476001873
- Quaternion algorithm:
- Michael W. Walker and Lejun Shao and Richard A. Volz, 1991, Estimating 3-D location parameters using dual number quaternions, CVGIP: Image Understanding, 54:358-367, doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/1049-9660(91)90036-o
Please cite this project when using it for scientific publications.
Easiest is to get the program vis PyPi under the package name rmsd,
pip install rmsdor download the project from GitHub via
git clone https://github.com/charnley/rmsdThere is only one Python file, so you can also download calculate_rmsd.py and put it in your bin folder.
wget -O calculate_rmsd https://raw.githubusercontent.com/charnley/rmsd/master/rmsd/calculate_rmsd.py
chmod +x calculate_rmsdUse calculate_rmsd --help to see all the features. Usage is pretty straight
forward, call calculate_rmsd with two structures in either .xyz or
.pdb. In this example Ethane has the exact same structure, but is
translated in space, so the RMSD should be zero.
calculate_rmsd tests/ethane.xyz tests/ethane_translate.xyzIt is also possible to ignore all hydrogens (useful for larger molecules where hydrogens move around indistinguishable) and print the rotated structure for visual comparison. The output will be in XYZ format.
calculate_rmsd --no-hydrogen --print tests/ethane.xyz tests/ethane_mini.xyzIf the atoms are scrambled and not aligned you can use the --reorder
argument which will align the atoms from structure B unto A. Use
--reorder-method to select what method for reordering. Choose between
Hungarian (default), distance (very approximate) and brute force (slow).
calculate_rmsd --reorder tests/water_16.xyz tests/water_16_idx.xyzIt is also possible to use RMSD as a library in other scripts, see example.py for example usage.
Submit issues or pull requests on GitHub.