This repository contains a python implementation of an automatic parallel parking system in a virtual environment that includes path planning, path tracking, and parallel parking. The agent navigates its route through the environment and is directed to the assigned park location by the MPC controller. You can find the article on Towards Data Science.
The first step to develop an auto park system is to design and develop an environment capable of giving visual render using OpenCV library.
The environment is implemented in environment.py as a class and receives obstacles at the beginning env = Environment(obs).
The agent can be placed using env.render(x,y,angle).
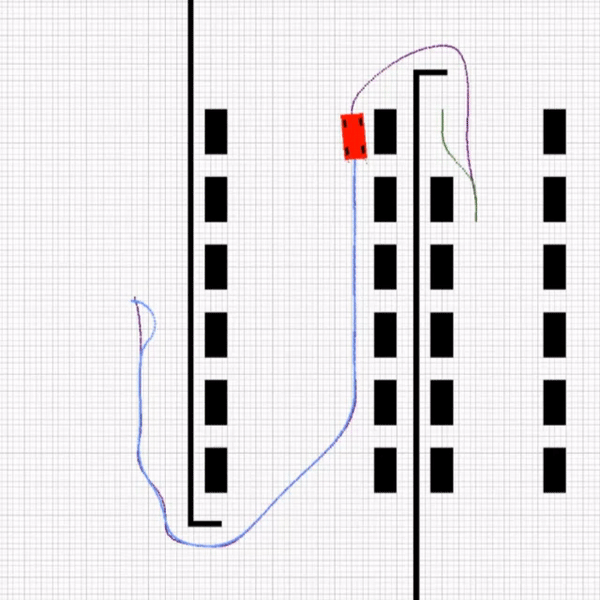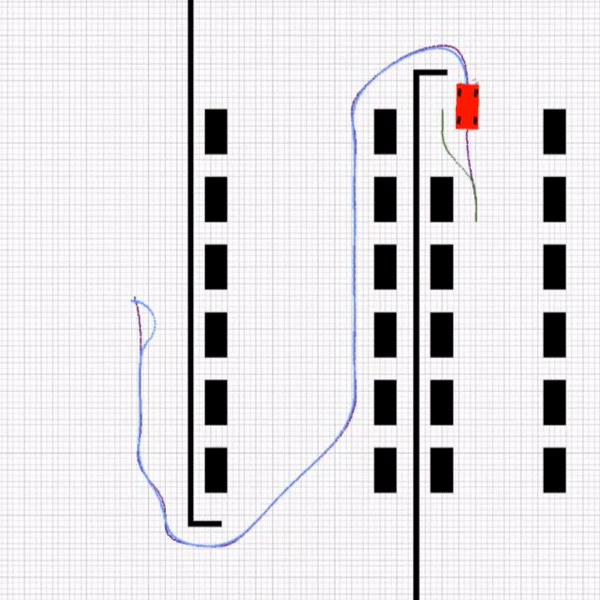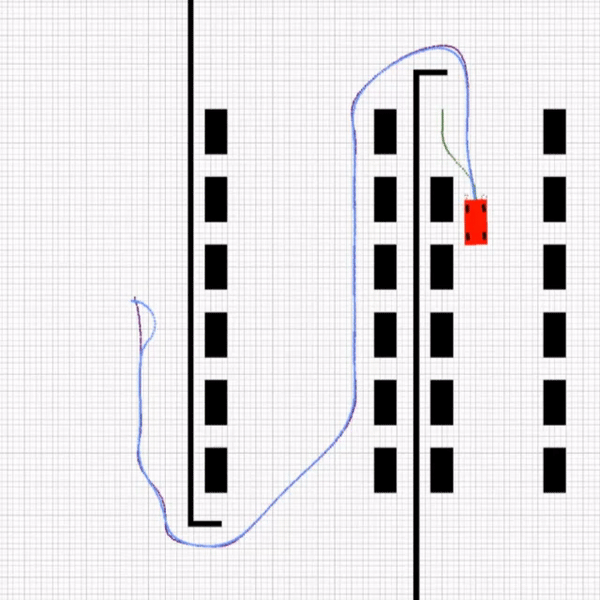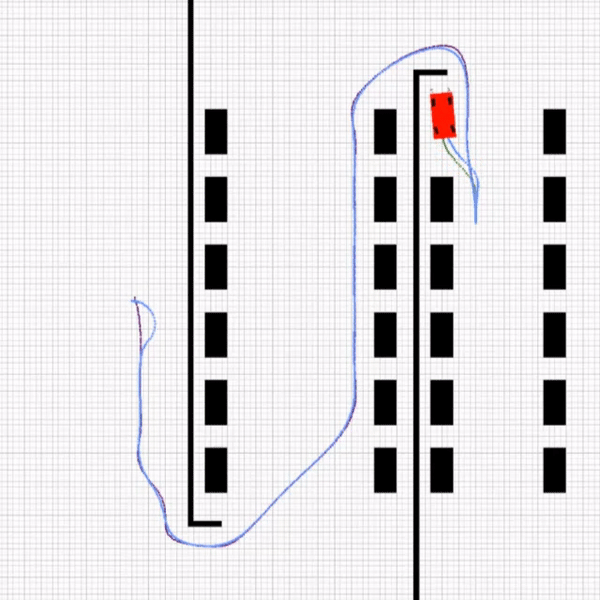
A sample of the environment is displayed below. You can choose the parking spot from 1 to 24.
The agent will find a path from start to its goal using A*. This implementation of A* from PythonRobotics considers parameters like obstacles and robot radius.
After finding a path in a discrete 100*100 space, the path is smoothed and scaled to 1000*1000 space of environment using b-spline. The result is a set of points to guide our agent!
The kinematic model of the car is:
a: acceleration,
The state vector is:
x: x-position, y: y-position, v: velocity,
The input vector is:
a: acceleration,
The MPC controller controls vehicle speed and steering based on the model and the car is directed through the path. There is an option for using the linearized model for MPC. In this case MPC linearizes the kinematic model around the operating point and then does the optimization.
This part consists of 4 rules that the agent must choose according to parking position. At first, the agent will find a path to park position then it will compute the arriving angle. Based on the arriving angle, the agent chooses a coordinate as ensure1. After that, the parking path is planned from ensure1 to ensure2 using 2 circle equations as mentioned below. MPC controls the agent and car parks in ensure2 coordinate.
Run the code using this command:
$ python main_autopark.py --x_start 0 --y_start 90 --psi_start 0 --parking 7
We as Team Pandas won 1st place in the National Rahneshan competition 2020-2021 for autonomous vehicles. This contest has been one of the most competitive and challenging contests in the Rahneshan tournaments with more than 15 teams competing from top universities in Iran.
Feel free to contact us via email or connect with us on linkedin.