A fully managed messaging service that allows for event-driven systems and real-time analytics on Google Cloud Platform. Key features include:
- Scalability: Automatically scales to handle high-throughput workloads.
- Durability: Ensures message delivery with at-least-once delivery guarantees.
- Flexibility: Supports both push and pull delivery models.
- Integration: Easily integrates with other Google Cloud services.
- GO: pubsub, to wrap and simplify pubsub. Example is at go-pubsub-sample
- nodejs: google-pubsub, to wrap and simplify @google-cloud/pubsub. Example is at pubsub-sample
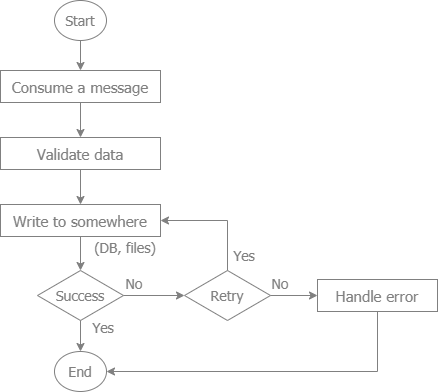
- The libraries to implement this flow are:
- mq for GOLANG. Example is at go-pubsub-sample
- mq-one for nodejs. Example is at pubsub-sample
Common use cases include event-driven architectures, log collection, and streaming analytics.
- Scenario: Building applications where different components communicate via events (e.g., microservices)
- Benefit: Decouples components, allowing independent scaling and development
- Scenario: Aggregating logs from multiple applications and systems.
- Benefit: Centralized logging and monitoring, improving visibility and debugging capabilities.
- Scenario: Collecting and analyzing data streams from various sources like IoT devices, social media, or user activity.
- Benefit: Enables real-time data processing and analytics, providing timely insights and actions.
- Type: Managed real-time messaging service.
- Use Case: Event-driven architectures, real-time analytics.
- Scalability: Automatically scales.
- Delivery Guarantees: At-least-once delivery.
- Integration: Tight with Google Cloud services.
- Delivery Models: Push and pull.
- Type: Managed message queuing service.
- Use Case: Decoupling and scaling microservices, asynchronous tasks.
- Scalability: Automatically scales.
- Delivery Guarantees: At-least-once, FIFO (exactly-once).
- Integration: Deep integration with AWS services.
- Delivery Models: Primarily pull, with long polling.
- Type: Open-source event streaming platform.
- Use Case: High-throughput messaging, event sourcing, log aggregation.
- Scalability: High with partitioned topics.
- Delivery Guarantees: Configurable (at-least-once, exactly-once).
- Integration: Broad ecosystem with various connectors.
- Delivery Models: Pull-based consumer groups.
- Management: Pub/Sub and SQS are managed services, while Kafka is typically self-managed or via managed services like Confluent.
- Use Case Focus: Pub/Sub and Kafka are ideal for real-time processing, whereas SQS is great for decoupling microservices and handling asynchronous tasks.
- Delivery Models: Pub/Sub supports push and pull, SQS supports pull with long polling, and Kafka primarily uses pull with consumer groups.
- Scalability: All three are highly scalable, but Kafka offers the most control over performance tuning.
- Integration: Pub/Sub integrates well with Google Cloud, SQS with AWS, and Kafka has a broad integration ecosystem.
- Google Pub/Sub: If you're using Google Cloud and need a managed, real-time messaging solution.
- Amazon SQS: For reliable, scalable message queuing in AWS environments.
- Apache Kafka: For complex event streaming and log aggregation, with a need for fine-tuned control and a broad integration ecosystem.
Please make sure to initialize a Go module before installing core-go/pubsub:
go get -u github.com/core-go/pubsubImport:
import "github.com/core-go/pubsub"