A pythonic client for DataStax Astra DB.
This README targets AstraPy version 2.0+. Click here for v1 and here for the v0 API (which you should not really be using by now).
Install with pip install astrapy.
Get the API Endpoint and the Token to your Astra DB instance at astra.datastax.com.
Try the following code after replacing the connection parameters:
import astrapy
ASTRA_DB_APPLICATION_TOKEN = "AstraCS:..."
ASTRA_DB_API_ENDPOINT = "https://01234567-....apps.astra.datastax.com"
my_client = astrapy.DataAPIClient()
my_database = my_client.get_database(
ASTRA_DB_API_ENDPOINT,
token=ASTRA_DB_APPLICATION_TOKEN,
)
my_collection = my_database.create_collection(
"dreams",
dimension=3,
metric=astrapy.constants.VectorMetric.COSINE,
)
my_collection.insert_one({"summary": "I was flying", "$vector": [-0.4, 0.7, 0]})
my_collection.insert_many(
[
{
"_id": astrapy.ids.UUID("018e65c9-e33d-749b-9386-e848739582f0"),
"summary": "A dinner on the Moon",
"$vector": [0.2, -0.3, -0.5],
},
{
"summary": "Riding the waves",
"tags": ["sport"],
"$vector": [0, 0.2, 1],
},
{
"summary": "Friendly aliens in town",
"tags": ["scifi"],
"$vector": [-0.3, 0, 0.8],
},
{
"summary": "Meeting Beethoven at the dentist",
"$vector": [0.2, 0.6, 0],
},
],
)
my_collection.update_one(
{"tags": "sport"},
{"$set": {"summary": "Surfers' paradise"}},
)
cursor = my_collection.find(
{},
sort={"$vector": [0, 0.2, 0.4]},
limit=2,
include_similarity=True,
)
for result in cursor:
print(f"{result['summary']}: {result['$similarity']}")
# This would print:
# Surfers' paradise: 0.98238194
# Friendly aliens in town: 0.91873914Next steps:
- More info and usage patterns are given in the docstrings of classes and methods
- Data API reference
- AstraPy reference
- Package on PyPI
The main difference to target e.g. a Hyper-Converged Database (HCD)
installation is how the client is
initialized. Here is a short example showing just how to get to a Database
(what comes next is unchaged compared to using Astra DB).
from astrapy import DataAPIClient
from astrapy.constants import Environment
from astrapy.authentication import UsernamePasswordTokenProvider
# Build a token
tp = UsernamePasswordTokenProvider("username", "password")
# Initialize the client and get a "Database" object
client = DataAPIClient(token=tp, environment=Environment.HCD)
database = client.get_database("http://localhost:8181", token=tp)For more on this case, please consult the dedicated reference.
AstraPy's abstractions for working at the data and admin layers are structured as depicted by this diagram:
Here's a small admin-oriented example:
import astrapy
# this must have "Database Administrator" permissions:
ASTRA_DB_APPLICATION_TOKEN = "AstraCS:..."
my_client = astrapy.DataAPIClient(ASTRA_DB_APPLICATION_TOKEN)
my_astra_admin = my_client.get_admin()
database_list = list(my_astra_admin.list_databases())
db_info = database_list[0].info
print(db_info.name, db_info.id, db_info.region)
my_database_admin = my_astra_admin.get_database_admin(db_info.id)
my_database_admin.list_keyspaces()
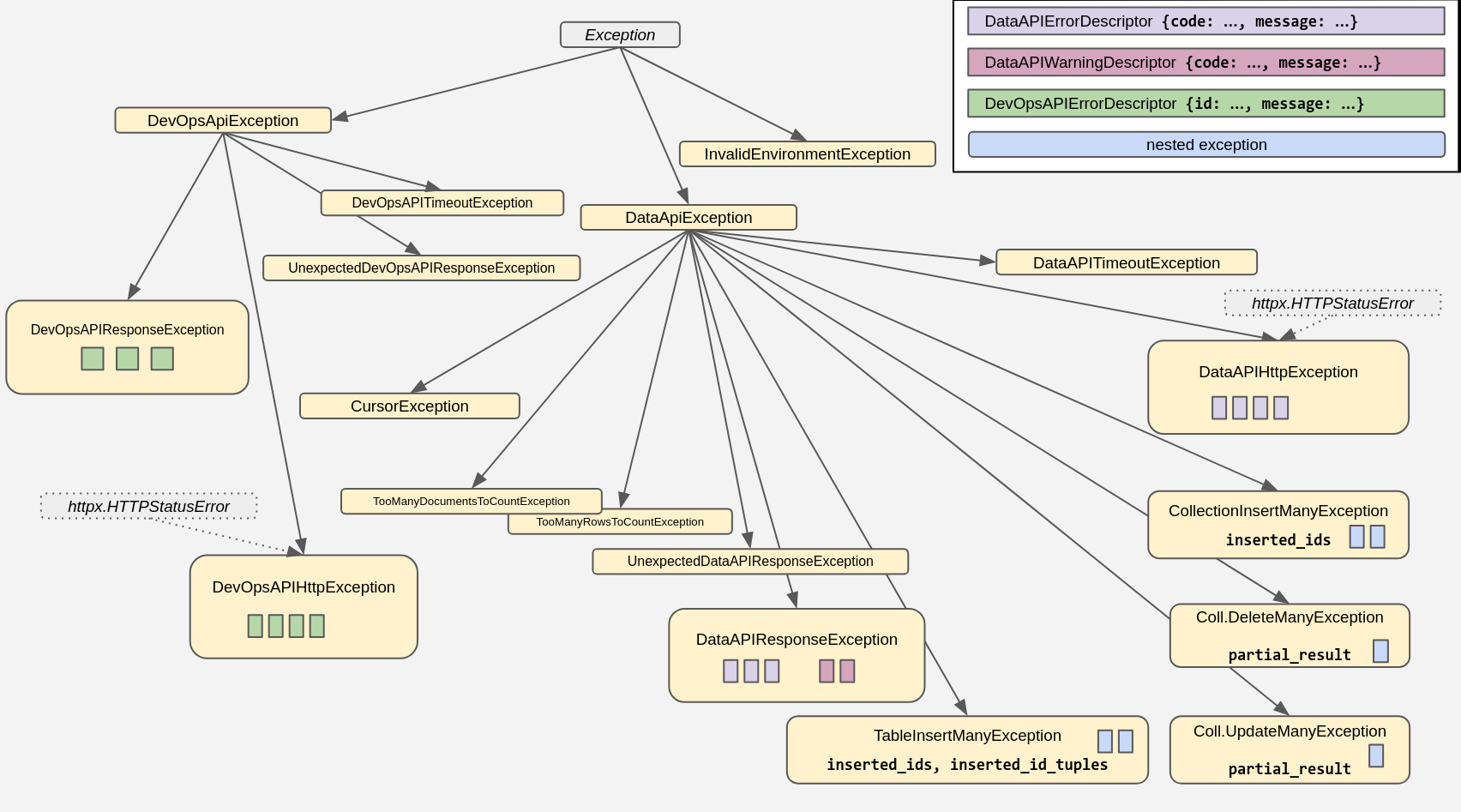
my_database_admin.create_keyspace("my_dreamspace")The package comes with its own set of exceptions, arranged in this hierarchy:
For more information, and code examples, check out the docstrings and consult the API reference linked above.
Date and datetime objects, i.e. instances of the standard library
datetime.datetime and datetime.date classes, can be used anywhere in documents:
import datetime
import astrapy
ASTRA_DB_APPLICATION_TOKEN = "AstraCS:..."
ASTRA_DB_API_ENDPOINT = "https://01234567-....apps.astra.datastax.com"
my_client = astrapy.DataAPIClient()
my_database = my_client.get_database(
ASTRA_DB_API_ENDPOINT,
token=ASTRA_DB_APPLICATION_TOKEN,
)
my_collection = my_database.dreams
my_collection.insert_one({"when": datetime.datetime.now()})
my_collection.insert_one({"date_of_birth": datetime.date(2000, 1, 1)})
my_collection.update_one(
{"registered_at": datetime.date(1999, 11, 14)},
{"$set": {"message": "happy Sunday!"}},
)
print(
my_collection.find_one(
{"date_of_birth": {"$lt": datetime.date(2001, 1, 1)}},
projection={"_id": False},
)
)
# This would print:
# {'date_of_birth': datetime.datetime(2000, 1, 1, 0, 0)}Note: reads from a collection will always
return the datetime class regardless of wheter a date or a datetime was provided
in the insertion.
Astrapy repackages the ObjectId from bson and the UUID class and utilities
from the uuid package and its uuidv6 extension. You can also use them directly.
Even when setting a default ID type for a collection, you still retain the freedom to use any ID type for any document:
import astrapy
import bson
ASTRA_DB_APPLICATION_TOKEN = "AstraCS:..."
ASTRA_DB_API_ENDPOINT = "https://01234567-....apps.astra.datastax.com"
my_client = astrapy.DataAPIClient()
my_database = my_client.get_database(
ASTRA_DB_API_ENDPOINT,
token=ASTRA_DB_APPLICATION_TOKEN,
)
my_collection = my_database.create_collection(
"ecommerce",
default_id_type=astrapy.constants.DefaultIdType.UUIDV6,
)
my_collection.insert_one({"_id": astrapy.ids.ObjectId("65fd9b52d7fabba03349d013")})
my_collection.find({
"_id": astrapy.ids.UUID("018e65c9-e33d-749b-9386-e848739582f0"),
})
my_collection.update_one(
{"tag": "in_stock"},
{"$set": {"inventory_id": bson.objectid.ObjectId()}},
upsert=True,
)
my_collection.insert_one({"_id": astrapy.ids.uuid8()})First install poetry with pip install poetry and then the project dependencies with poetry install --with dev.
Linter, style and typecheck should all pass for a PR:
make formatWith make format-fix the style and imports are autofixed (by ruff)
Features must be thoroughly covered in tests (see tests/idiomatic/* for
naming convention and module structure).
Tests are grouped in three blocks (in as many subdirs of tests/):
- idiomatic: all 1.0+ classes and APIs, except...
- vectorize: ... everything making use of
$vectorize(within the idiomatic classes)
Actually, for convenience, sub-blocks of tests are considered:
- idiomatic regular: everything except the admin parts
- idiomatic admin Astra: the Astra-specific admin operations
- idiomatic admin nonAstra: the nonAstra-specific admin operations
- vectorize in-depth: many Data API interactions for a single choice of provider/model. This is mostly test the client
- vectorize all-providers: a slightly more shallow test repeated for all providers, models, auth methods etc. This is mostly testing the API
Tests can be run on three types of Data API targets (with slight differences in what is applicable):
- DockerCompose: HCD started by the test initialization with
docker-compose. Note that in this case you will have to manually destroy the created containers. - nonAstra: a ready-to-use (user-supplied) local Data API
- Astra: an Astra DB target account (or two, as some tests are specific to dev environment)
Depending on the (sub-block, target) combination, some environment variables may be needed.
Templates for the environment variables are to be found in tests/env_templates.
The general expectation is that idiomatic non-Admin tests, and vectorize in-depth tests, are part of the main CI flow; conversely, admin and vectorize all-providers are kept as a manual task to run (locally in most cases) when circumstances require it (use your judgement).
Below is a detail of the reference template files needed for the various types of testing:
- DockerCompose: generally no variables needed, except:
- vectorize in-depth: provide as in
env.vectorize-minimal.template - vectorize all-providers: provide as in
env.vectorize.template - (also note that idiomatic admin Astra amounts to nothing in this case)
- vectorize in-depth: provide as in
- nonAstra: all tests require as in
env.local.template, plus:- vectorize in-depth: also provide as in
env.vectorize-minimal.template - vectorize all-providers: also provide as in
env.vectorize.template - (also note that idiomatic admin Astra amounts to nothing in this case)
- vectorize in-depth: also provide as in
- Astra: all tests require as in
env.astra.template, plus:- idiomatic admin Astra: also provide as in
env.astra.admin.template - vectorize in-depth: also provide as in
env.vectorize-minimal.template - vectorize all-providers: also provide as in
env.vectorize.template - (also note that idiomatic admin nonAstra amounts to nothing in this case)
- idiomatic admin Astra: also provide as in
For the DockerCompose case, prepend all of the following with DOCKER_COMPOSE_LOCAL_DATA_API="yes" .
All the usual pytest ways of restricting the test selection hold in addition
(e.g. poetry run pytest tests/idiomatic/unit or [...] -k <test_name_selector>).
Warning: this will also trigger the very long-running idiomatic admin Astra if the vars as in env.astra.admin.template are also detected. Likewise, the idiomatic admin nonAstra may start (if DO_IDIOMATIC_ADMIN_TESTS is set), which however takes few seconds.
poetry run pytest tests/idiomatic
poetry run pytest tests/idiomatic/integration/test_admin.py
DO_IDIOMATIC_ADMIN_TESTS="1" poetry run pytest tests/idiomatic/integration/test_nonastra_admin.py
poetry run pytest tests/vectorize_idiomatic/integration/test_vectorize_methods*.py
or just:
poetry run pytest tests/vectorize_idiomatic/integration/test_vectorize_methods_sync.py
This generates all possible test cases and runs them:
poetry run pytest tests/vectorize_idiomatic
For a spot test, you may restrict to one case, e.g.
EMBEDDING_MODEL_TAGS="openai/text-embedding-3-large/HEADER/0" poetry run pytest tests/vectorize_idiomatic/integration/test_vectorize_providers.py -k test_vectorize_usage_auth_type_header_sync
Remove logging noise with:
poetry run pytest [...] -o log_cli=0
Increase logging level to DEBUG (i.e. level 10):
poetry run pytest [...] -o log_cli=1 --log-cli-level=10
Client, data and admin abstractions:
from astrapy import (
AstraDBAdmin,
AstraDBDatabaseAdmin,
AsyncCollection,
AsyncDatabase,
Collection,
DataAPIClient,
DataAPIDatabaseAdmin,
Database,
)Constants for data-related use:
from astrapy.constants import (
DefaultIdType,
Environment,
ReturnDocument,
SortDocuments,
VectorMetric,
)ObjectIds and UUIDs:
from astrapy.ids import (
UUID,
ObjectId,
uuid1,
uuid3,
uuid4,
uuid5,
uuid6,
uuid7,
uuid8,
)API Options:
from astrapy.api_options import (
APIOptions,
DataAPIURLOptions,
DevOpsAPIURLOptions,
PayloadTransformOptions,
TimeoutOptions,
)Result classes:
from astrapy.results import (
OperationResult,
DeleteResult,
InsertOneResult,
InsertManyResult,
UpdateResult,
)Exceptions:
from astrapy.exceptions import (
CollectionAlreadyExistsException,
CollectionNotFoundException,
CumulativeOperationException,
CursorIsStartedException,
DataAPIDetailedErrorDescriptor,
DataAPIErrorDescriptor,
DataAPIException,
DataAPIFaultyResponseException,
DataAPIHttpException,
DataAPIResponseException,
DataAPITimeoutException,
DeleteManyException,
DevOpsAPIErrorDescriptor,
DevOpsAPIException,
DevOpsAPIFaultyResponseException,
DevOpsAPIHttpException,
DevOpsAPIResponseException,
DevOpsAPITimeoutException,
InsertManyException,
TooManyDocumentsToCountException,
UpdateManyException,
)Info/metadata classes:
from astrapy.info import (
AdminDatabaseInfo,
CollectionDefaultIDOptions,
CollectionDescriptor,
CollectionInfo,
CollectionOptions,
CollectionVectorOptions,
CollectionVectorServiceOptions,
DatabaseInfo,
EmbeddingProvider,
EmbeddingProviderAuthentication,
EmbeddingProviderModel,
EmbeddingProviderParameter,
EmbeddingProviderToken,
FindEmbeddingProvidersResult,
)Admin-related classes, functions and constants:
from astrapy.admin import (
DatabaseAdmin,
ParsedAPIEndpoint,
fetch_database_info,
parse_api_endpoint,
)Cursors:
from astrapy.cursors import (
AsyncCommandCursor,
AsyncCursor,
CommandCursor,
Cursor,
CursorState,
)If your code still uses the pre-1.0.0 astrapy (i.e. from astrapy.db import AstraDB, AstraDBCollection and so on)
you are strongly advised to migrate to the current API. All of the astrapy pre-1.0 API (later dubbed "core")
works throughout astrapy v1, albeit with a deprecation warning on astrapy v. 1.5.
Version 2 drops "core" support entirely. In order to use astrapy version 2.0+, you need to migrate your application. Check the links at the beginning of this README for the updated documentation and API reference.
Check out previous versions of this README for more on "core": 1.5.2 and pre-1.0.