Konstanta struktur halus
| Teori medan kuantum |
|---|
 |
| Sejarah |
Dalam fisika, konstanta struktur halus, biasanya dilambangkan dengan
Terdapat beberapa interpretasi fisika atas
Definisi
[sunting | sunting sumber]Beberapa definisi
di mana:
- e adalah muatan elementer (:= 1,602176634×10−19 C);
π adalah konstanta matematika pi;- h adalah konstanta Planck (:= 6,62607015×10−34 J⋅s);
- ħ = h2
π adalah konstanta Planck tereduksi (:= 6,62607015×10−34 J⋅s/2π ); - c adalah laju cahaya dalam vakum (= 299.792.458 m/s);
ε 0 adalah konstanta listrik atau permitivitas dalam vakum (atau ruang bebas);- µ0 adalah konstanta magnetik atau permeabilitas dalam vakum (atau ruang bebas);
- ke adalah konstanta Coulomb;
- RK adalah konstanta von Klitzing;
- Z0 adalah impedansi vakum atau impedansi dalam ruang hampa.
Ketika konstanta lainnya (c, h and e) memiliki nilai yang terdefinisi, definisi di atas mencerminkan hubungan antara
Dalam satuan non-SI
[sunting | sunting sumber]Dalam satuan cgs elektrostatik, satuan muatan listrik, statcoulomb, didefinisikan agar konstanta Coulomb, ke, atau faktor permitivitas, 4
Dalam satuan natural, biasanya digunakan dalam fisika berenergi tinggi, di mana
Jadi, konstanta struktur halus merupakan besaran nirdimensi yang menentukan (atau ditentukan oleh) muatan elementer: e = √4
Dalam satuan atom Hartree (e = me = ħ = 1 dan
Pengukuran
[sunting | sunting sumber]Nilai yang disarankan CODATA 2018 utuk
α = e24π ε 0ħc = 0,0072973525693(11).
Nilai ini memiliki ketidakpastian baku relatif 0,15 bagian per miliar.[7]
Nilai
Untuk mempermudah, nilai invers perkalian dari konstanta struktur halus terkadang ditetapkan juga. Nilai yang disarankan CODATA 2018 adalah[1]
α −1 = 137,035999084(21).
Selain bisa diperkirakan nilai
α −1 = 137,035999174(35).
Pengukuran
Sejarah
[sunting | sunting sumber]
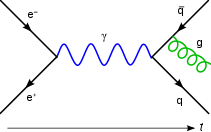
Berdasarkan pengukuran presisi dari spektrun atom hidrogen oleh Michelson dan Morley pada tahun 1887,[11] Arnold Sommerfeld memperluas model Bohr untuk memasukkan orbit eliptis dan kebergantuan relativistik massa pada kecepatan. Dia memperkenalkan sebuah suku untuk konstanta struktur halus pada tahun 1916.[12] Interpretasi fisika pertama dari konstanta struktur halus
Dengan perkembangan elektrodinamika kuantum (QED), pentingnya
Lihat pula
[sunting | sunting sumber]Referensi
[sunting | sunting sumber]- ^ a b Mohr, P. J.; Taylor, B. N.; Newell, D. B. (2019). "Inverse fine structure constant". CODATA Internationally recommended 2018 values of the fundamental physical constants. National Institute of Standards and Technology. Diakses tanggal 2019-05-20.
- ^
α sebanding dengan kuadrat konstanta sambatan bagi sebuah partikel bermuatan ke medan elektromagnetik. Terdapat konstanta serupa yang menjadi parameter bagi kekuatan interaksi gaya nuklir kuat, yang dikenal sebagaiα s (≈1), dan gaya nuklir lemah, yang dikenal sebagaiα w (≈10−6 hingga 10−7). "Coupling Constants for the Fundamental Forces". HyperPhysics. Georgia State University. Diakses tanggal 12 May 2020. - ^ "Convocationde la Conférence générale des poids et mesures (26e réunion)" (PDF). Diarsipkan dari versi asli (PDF) tanggal 2019-09-19. Diakses tanggal 2020-09-10.
- ^ Parker, Richard H.; Yu, Chenghui; Zhong, Weicheng; Estey, Brian; Müller, Holger (2018-04-13). "Measurement of the fine-structure constant as a test of the Standard Model". Science (dalam bahasa Inggris). 360 (6385): 191–195. arXiv:1812.04130
 . Bibcode:2018Sci...360..191P. doi:10.1126/science.aap7706. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 29650669.
. Bibcode:2018Sci...360..191P. doi:10.1126/science.aap7706. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 29650669.
- ^ Davis, Richard S. (2017). "Determining the value of the fine-structure constant from a current balance: Getting acquainted with some upcoming changes to the SI". American Journal of Physics (dalam bahasa Inggris). 85 (5): 364–368. arXiv:1610.02910
 . Bibcode:2017AmJPh..85..364D. doi:10.1119/1.4976701. ISSN 0002-9505.
. Bibcode:2017AmJPh..85..364D. doi:10.1119/1.4976701. ISSN 0002-9505.
- ^ Peskin, M.; Schroeder, D. (1995). An Introduction to Quantum Field Theory. Westview Press. hlm. 125. ISBN 978-0-201-50397-5.
- ^ a b Mohr, P. J.; Taylor, B. N.; Newell, D. B. (2019). "Fine structure constant". CODATA Internationally recommended 2018 values of the fundamental physical constants. National Institute of Standards and Technology.
- ^ a b Yu, C.; Zhong, W.; Estey, B.; Kwan, J.; Parker, R. H.; Müller, H. (2019). "Atom‐Interferometry Measurement of the Fine Structure Constant". Annalen der Physik. 531: 1800346. doi:10.1002/andp.201800346
 .
.
- ^
Aoyama, T.; Hayakawa, M.; Kinoshita, T.; Nio, M. (2012). "Tenth-order QED contribution to the electron g−2 and an improved value of the fine structure constant". Physical Review Letters. 109 (11): 111807. arXiv:1205.5368
 . Bibcode:2012PhRvL.109k1807A. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.109.111807. PMID 23005618.
. Bibcode:2012PhRvL.109k1807A. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.109.111807. PMID 23005618.
- ^
Bouchendira, Rym; Cladé, Pierre; Guellati-Khélifa, Saïda; Nez, François; Biraben, François (2011). "New determination of the fine-structure constant and test of the quantum electrodynamics" (PDF). Physical Review Letters (Submitted manuscript). 106 (8): 080801. arXiv:1012.3627
 . Bibcode:2011PhRvL.106h0801B. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.106.080801. PMID 21405559.
. Bibcode:2011PhRvL.106h0801B. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.106.080801. PMID 21405559.
- ^ Michelson, Albert A.; Morley, Edward W. (1887). "Method of making the wave-length of sodium light the actual and practical standard of length". The American Journal of Science. 3rd series. 34 (204): 427–430.
- Reprinted in: Michelson, Albert A.; Morley, Edward W. (1887). "Method of making the wave-length of sodium light the actual and practical standard of length". The Philosophical Magazine. 5th series. 24 (151): 463–466.
- ^ Sommerfeld, A. (1916). "Zur Quantentheorie der Spektrallinien" [On the quantum theory of spectral lines]. Annalen der Physik. 4th series (dalam bahasa German). 51 (17): 1–94. From p.91: "Wir fügen den Bohrschen Gleichungen (46) und (47) die charakteristische Konstante unserer Feinstrukturen (49)
α = 2π e2/ch hinzu, die zugleich mit der Kenntnis des Wasserstoffdubletts oder des Heliumtripletts in §10 oder irgend einer analogen Struktur bekannt ist." (We add the characteristic constant of our fine structures (49)α = 2π e2/ch to Bohr's equations (46) and (47), which is recognized at the same time from knowledge of the hydrogen doublet or the helium triplet in §10 or any analogous structure.) - ^ "Introduction to the Constants for Nonexperts – Current Advances: The Fine-Structure Constant and Quantum Hall Effect". The NIST Reference on Constants, Units, and Uncertainty. NIST. Diakses tanggal 11 April 2009.
- ^ Kesalahan pengutipan: Tag
<ref>tidak sah; tidak ditemukan teks untuk ref bernamaKragh03
Pranala luar
[sunting | sunting sumber]- Stephen L. Adler, "Theories of the Fine Structure Constant
α " FERMILAB-PUB-72/059-T - "Introduction to the constants for nonexperts", diadaptasi dari Encyclopædia Britannica, edisi ke-15. Disebarkan oleh halaman web NIST.
- Nilai yang direkomendasikan CODATA untuk
α , sejak tahun 2018. - Kutipan-kutipan mengenai konstanta struktur halus




