SR-142,948
Izgled
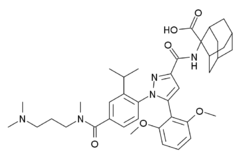
| |||
| (IUPAC) ime | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2-([5-(2,6-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-[4-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl-methylcarbamoyl]-2-propan-2-ylphenyl]pyrazole-3-carbonyl]amino)adamantane-2-carboxylic acid | |||
| Klinički podaci | |||
| Identifikatori | |||
| CAS broj | 184162-64-9 | ||
| ATC kod | ? | ||
| PubChem[1][2] | 5311451 | ||
| ChemSpider[3] | 4470937 | ||
| Hemijski podaci | |||
| Formula | C39H51N5O6 | ||
| Mol. masa | 685.850 g/mol | ||
| SMILES | eMolekuli & PubHem | ||
| |||
| Farmakoinformacioni podaci | |||
| Trudnoća | ? | ||
| Pravni status | |||
SR-142,948 je lek koji se koristi u naučnim istraživanjima. On pripada grupi nepeptidnih antagonista selektivnih za neurotenzinske receptore, mada nije selektivan za specifični tip tog receptora.[4] On je korišten u izučavanju uloge neurotenzina u regulaciji aktivnosti dopaminskog receptora[5][6][7][8] i glutamatne signalizacije u mozgu.[9][10] U životinjskim studies SR-142,948 blokira efekte stimulanata,[11] kao što je MDMA.[12]
- ↑ Li Q, Cheng T, Wang Y, Bryant SH (2010). „PubChem as a public resource for drug discovery.”. Drug Discov Today 15 (23-24): 1052-7. DOI:10.1016/j.drudis.2010.10.003. PMID 20970519.
- ↑ Evan E. Bolton, Yanli Wang, Paul A. Thiessen, Stephen H. Bryant (2008). „Chapter 12 PubChem: Integrated Platform of Small Molecules and Biological Activities”. Annual Reports in Computational Chemistry 4: 217-241. DOI:10.1016/S1574-1400(08)00012-1.
- ↑ Hettne KM, Williams AJ, van Mulligen EM, Kleinjans J, Tkachenko V, Kors JA. (2010). „Automatic vs. manual curation of a multi-source chemical dictionary: the impact on text mining”. J Cheminform 2 (1): 3. DOI:10.1186/1758-2946-2-3. PMID 20331846.
- ↑ Nalivaiko E, Michaud JC, Soubrié P, Le Fur G (October 1998). „Electrophysiological evidence for putative subtypes of neurotensin receptors in guinea-pig mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons”. Neuroscience 86 (3): 799–811. DOI:10.1016/S0306-4522(98)00084-0. PMID 9692718.
- ↑ Alonso R, Gnanadicom H, Fréchin N, Fournier M, Le Fur G, Soubrié P (March 1999). „Blockade of neurotensin receptors suppresses the dopamine D1/D2 synergism on immediate early gene expression in the rat brain”. The European Journal of Neuroscience 11 (3): 967–74. DOI:10.1046/j.1460-9568.1999.00506.x. PMID 10103090.[mrtav link]
- ↑ Matsuyama S, Higashi H, Maeda H, Greengard P, Nishi A (April 2002). „Neurotensin regulates DARPP-32 thr34 phosphorylation in neostriatal neurons by activation of dopamine D1-type receptors”. Journal of Neurochemistry 81 (2): 325–34. DOI:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2002.00822.x. PMID 12064480.[mrtav link]
- ↑ Leonetti M, Brun P, Sotty F, Steinberg R, Soubrié P, Bert L, Renaud B, Suaud-Chagny MF (June 2002). „The neurotensin receptor antagonist SR 142948A blocks the efflux of dopamine evoked in nucleus accumbens by neurotensin ejection into the ventral tegmental area”. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology 365 (6): 427–33. DOI:10.1007/s00210-002-0574-6. PMID 12070755.
- ↑ Panayi F, Colussi-Mas J, Lambás-Señas L, Renaud B, Scarna H, Bérod A (May 2005). „Endogenous neurotensin in the ventral tegmental area contributes to amphetamine behavioral sensitization”. Neuropsychopharmacology : Official Publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology 30 (5): 871–9. DOI:10.1038/sj.npp.1300638. PMID 15637639.
- ↑ Matsuyama S, Fukui R, Higashi H, Nishi A (September 2003). „Regulation of DARPP-32 Thr75 phosphorylation by neurotensin in neostriatal neurons: involvement of glutamate signalling”. The European Journal of Neuroscience 18 (5): 1247–53. DOI:10.1046/j.1460-9568.2003.02859.x. PMID 12956723.[mrtav link]
- ↑ Yin HH, Adermark L, Lovinger DM (January 2008). „Neurotensin reduces glutamatergic transmission in the dorsolateral striatum via retrograde endocannabinoid signaling”. Neuropharmacology 54 (1): 79–86. DOI:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.06.004. PMC 2697967. PMID 17675102.
- ↑ Reynolds SM, Geisler S, Bérod A, Zahm DS (July 2006). „Neurotensin antagonist acutely and robustly attenuates locomotion that accompanies stimulation of a neurotensin-containing pathway from rostrobasal forebrain to the ventral tegmental area”. The European Journal of Neuroscience 24 (1): 188–96. DOI:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.04791.x. PMID 16882016.
- ↑ Marie-Claire C, Palminteri S, Romualdi P, Noble F (June 2008). „Effects of the selective neurotensin antagonist SR 142948A on 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine-induced behaviours in mice”. Neuropharmacology 54 (7): 1107–11. DOI:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.03.001. PMID 18410947.
