What is the difference between weather and climate?
‘Weather’ describes the combination of wind, rain, temperature and other natural atmospheric conditions we experience at a particular time and place. ‘Climate’ is the pattern of weather of an area averaged over many years.
If we have extremes in weather conditions, such as a long summer drought or a very cold winter, it doesn’t necessarily mean that the climate is changing. We can only show whether climate change has occurred after decades of careful measurements and analysis.
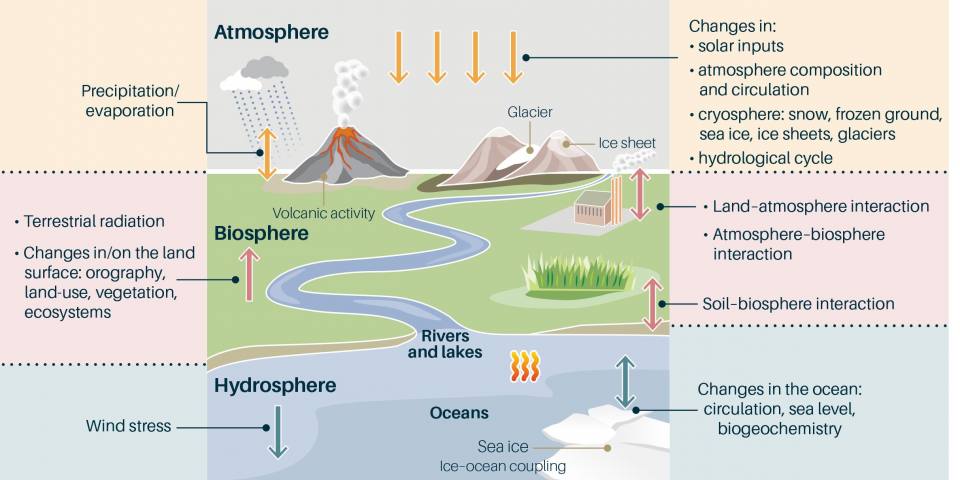
The climate system
We can see from the diagram that the climate system has many components that interact with each other; a change in one component may alter the operation of another. The effects of changes are often dependent on the operation of feedback mechanisms. A feedback that enhances an initial change in climate is positive, but those that decrease the size of the change are negative.
For example, if the amount of solar energy absorbed on the Earth’s surface were to increase, then the surface temperature would increase. This would lead to a decrease in the amount of snow cover. Snow reflects more solar energy than land, vegetation or water, so a decrease in the amount of land covered by snow would allow more solar radiation to be absorbed and so a positive feedback is initiated.

The carbon story
The carbon cycle describes the process in which carbon atoms continually travel from the atmosphere into the Earth, then released back into the atmosphere.

What causes the Earth’s climate to change?
Geological records demonstrate that there have been a number of large variations in Earth’s climate in the past.

Impacts of climate change
Temperature rises can affect agriculture, sea levels and the frequency of extreme weather incidents. We can study past climate change by looking at the evidence in rocks, fossils and changes in the landscape.

The greenhouse effect
Gases in the Earth’s atmosphere act as an insulating blanket around the planet, trapping more of the Sun’s heat.
What are we doing about climate change?
BGS is committed to research aimed at slowing down the effects of a changing climate, whilst helping society to become resilient to climate change.

Understanding carbon capture and storage
Carbon capture and storage involves capturing carbon dioxide at emission sources, such as power stations, then transporting and storing it underground.
You may also be interested in

Rocks and minerals
Find out more about the differences between rocks and minerals and how they are formed.

Geological processes
Planet Earth is dynamic with a surface that is always changing. Find out about the processes that cause these changes.