James Webb Space Telescope
Webb is the premier observatory of the next decade, serving thousands of astronomers worldwide. It studies every phase in the history of our Universe.

Key Facts
Featured Image/Article
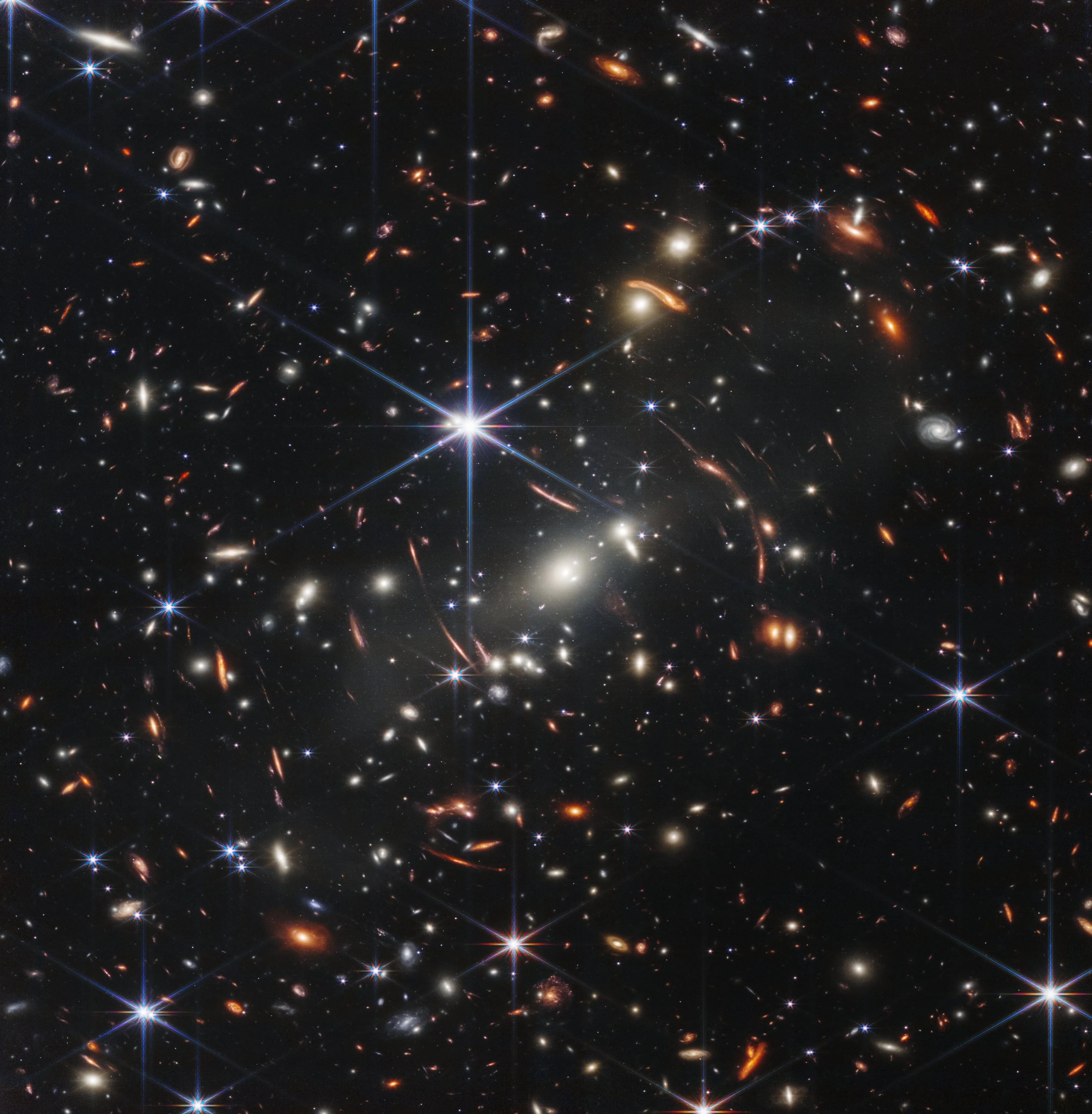
Peering deeply into the cosmos, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope is giving scientists their first detailed glimpse of supernovae from a time when our universe was just a small fraction of its current age. A team using Webb data has identified 10 times more supernovae in the early universe than were previously known. A few of the newfound exploding stars are the most distant examples of their type, including those used to measure the universe's expansion rate.
"Webb is a supernova discovery machine," said Christa DeCoursey, a third-year graduate student at the Steward Observatory and the University of Arizona in Tucson. “The sheer number of detections plus the great distances to these supernovae are the two most exciting outcomes from our survey.”

Featured Image Alternate Versions
Annotated - max rez, 12k pixel wide (135MB png)
JADES Deep Field with transients circled.
Unannotated - max rez, 12k pixel wide (135MB png)
Unnnotated - 4k pixel wide (2.5MB jpg)

Latest News
Webb's latest news releases in reverse chronological order. Search and sort the news feed with the controls immediately below.

Investigating the Origins of the Crab Nebula With NASA’s Webb
New data revises our view of this unusual supernova explosion. A team of scientists used NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope to parse the composition of the Crab Nebula, a supernova remnant located 6,500 light-years away in the constellation Taurus. With…

NASA’s Webb Reveals Long-Studied Star Is Actually Twins
Managed by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory through launch, Webb’s Mid-Infrared Instrument also revealed jets of gas flowing into space from the twin stars. Scientists recently got a big surprise from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope when they turned the observatory…

NASA’s Webb Opens New Window on Supernova Science
Peering deeply into the cosmos, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope is giving scientists their first detailed glimpse of supernovae from a time when our universe was just a small fraction of its current age. A team using Webb data has…

Webb Finds Plethora of Carbon Molecules Around Young Star
An international team of astronomers has used NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope to study the disk of gas and dust around a young, very low-mass star. The results reveal the largest number of carbon-containing molecules seen to date in such…
Webb's Blog
Webb's Blog posts offer an insider's point of view covering a variety of topics that include exciting Webb science images/spectra that are not yet peer reviewed and therefore not released as NASA feature articles ( IE the above official Webb News Feed). Blog posts are often co-authored by scientists and engineers and offer unique insights.
Read Webb's Blog
Latest Webb Blog
Reconnaissance of Potentially Habitable Worlds with NASA’s Webb
Small exoplanets are common in our galaxy, and some even orbit in the so-called habitable zone of their star. NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has been busy observing a few of these small, potentially habitable planets, and astronomers are now hard at work analyzing Webb data. We invite Drs. Knicole Colón and Christopher Stark, two Webb project scientists at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, to tell us more about the challenges in studying these other worlds.
Read More
Latest 2024 Images
The image below is a SLIDESHOW. Hover over the image to see the image title and controls. Click the image to go to a detail page with more info and the ability to download the image at various resolutions (click downward arrow in lower right corner).
More Webb Images
What is Webb Observing?
See current, upcoming and recent past observations scientists are making with the Webb Space Telescope. View details about each observation's science focus areas, the instruments used and more.
View the Tool
The Webb Mission
Webb is the premier observatory of the next decade, serving thousands of astronomers worldwide. It studies every phase in the history of our Universe, ranging from the first luminous glows after the Big Bang, to the formation of solar systems capable of supporting life on planets like Earth, to the evolution of our own Solar System.
Learn More
Webb's Science Goals
The James Webb Space Telescope is a giant leap forward in our quest to understand the Universe and our origins. Webb is examining every phase of cosmic history: from the first luminous glows after the Big Bang to the formation of galaxies, stars, and planets to the evolution of our own solar system. Learn about the 4 main science themes for Webb.
Learn More
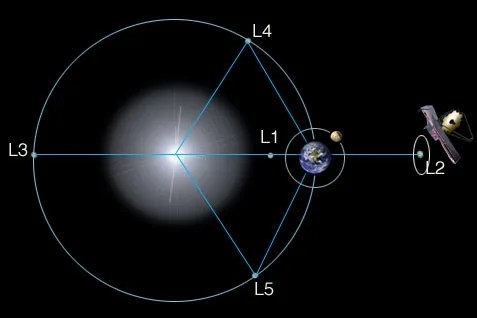
The Spacecraft
The Webb Space Telescope is the largest, most powerful and most complex telescope ever launched into space . It's design and development history stretches back before the Hubble Space Telescope was launched. Learn about the design, the major components and subsystems of Webb and see Webb in 3d in a 3d Solar System.
Learn More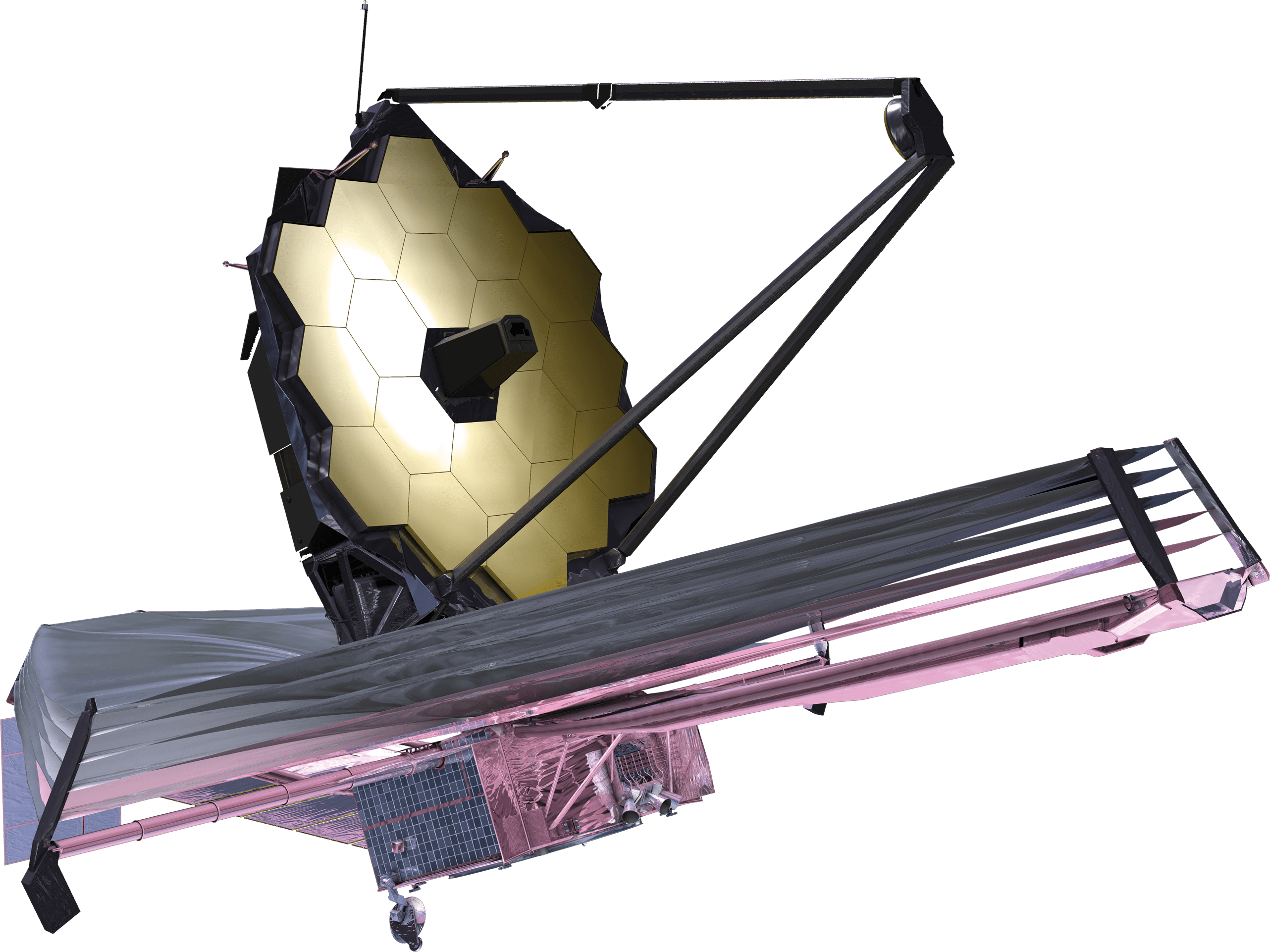
The International Webb Team
Webb is for the world, and from the world. Thousands of skilled scientists, engineers and technicians from 14 countries (and more than 29 U.S. states, and Washington, D.C.) contributed to the design, build, test, integration, launch, commissioning and operations of Webb. It is a joint NASA/ESA/CSA mission. Assembly and testing of the mirror and instruments occurred at NASA Goddard (GSFC).
Learn More