Erythorbic acid
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
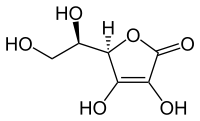
| IUPAC name
(5R)-5-[(1R)-1,2-Dihydroxyethyl]-3,4-dihydroxyfuran-2(5H)-one
| |
| Other names
D-Araboascorbic acid, Erythorbate, Isoascorbic acid, E315
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.753 |
| E number | E315 (antioxidants, ...) |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H8O6 | |
| Molar mass | 176.124 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.704 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 164–172 °C (decomposes) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Erythorbic acid (isoascorbic acid, D-araboascorbic acid)is a stereoisomer of ascorbic acid (vitamin C).[1] It is a natural product, a vegetable-derived food additive produced from sucrose. It is denoted by E number E315, and is widely used as an antioxidant in processed foods.[2]
Clinical trials have been conducted to investigate aspects of the nutritional value of erythorbic acid. One such trial investigated the effects of erythorbic acid on vitamin C metabolism in young women; no effect on vitamin C uptake or clearance from the body was found.[3] A later study found that erythorbic acid is a potent enhancer of nonheme-iron absorption.[4]
Since the U.S. Food and Drug Administration banned the use of sulfites as a preservative in foods intended to be eaten fresh (such as salad bar ingredients), the use of erythorbic acid as a food preservative has increased.
It is also used as a preservative in cured meats and frozen vegetables.[5]
See also
References
- ^ Erythorbic acid and its sodium salt Dr R. Walker, Professor of Food Science, Department of Biochemistry, University of Surrey, England.
- ^ Current EU approved additives and their E Numbers, Food Standards Agency
- ^ Sauberlich, HE; Tamura T; Craig CB; Freeberg LE; Liu T (September 1996). "Effects of erythorbic acid on vitamin C metabolism in young women". American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 64 (3): pp. 336–46. PMID 8780343.
{{cite journal}}:|pages=has extra text (help) - ^ Fidler, MC; Davidsson L; Zeder C; Hurrell RF (January 2004). "Erythorbic acid is a potent enhancer of nonheme-iron absorption". American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 79 (1): 99–102. PMID 14684404.
- ^ Hui YH (2006). Handbook of Food Science, Technology and Engineering. CRC Press. pp. 83–32. ISBN 0-8493-9848-7.
