ಬ್ಯುಟಿರಿಕ್ ಆಮ್ಲ
| |||

| |||
| ಹೆಸರುಗಳು | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ಐಯುಪಿಎಸಿ ಹೆಸರು
ಬ್ಯುಟನೋಯಿಕ್ ಆಮ್ಲ
| |||
| Other names
ಬ್ಯುಟಿರಿಕ್ ಆಸಿಡ್;೧-ಪ್ರೊಪೇನ್ ಕಾರ್ಬೊಕ್ಸೀಲಿಕ್ ಆಮ್ಲ;ಪ್ರೊಪೇನ್ ಕಾರ್ಬೊಕ್ಸೀಲಿಕ್ ಆಮ್ಲ ; C4:0 (Lipid numbers)
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.212 | ||
| ಗುಣಗಳು | |||
| ಆಣ್ವಿಕ ಸೂತ್ರ | C4H8O2 | ||
| ಮೋಲಾರ್ ದ್ರವ್ಯರಾಶಿ | ೮೮.೧೧ g mol−1 | ||
| ಸಾಂದ್ರತೆ | 0.9595 g/mL | ||
| ಕರಗು ಬಿಂದು |
−7.9 °C, 265 K, 18 °F | ||
| ಕುದಿ ಬಿಂದು |
163.5 °C, 437 K, 326 °F | ||
| ಕರಗುವಿಕೆ ನೀರಿನಲ್ಲಿ | miscible | ||
| ಅಮ್ಲತೆ (pKa) | 4.82 | ||
| ವಕ್ರೀಕಾರಕ ಸೂಚಿ (nD) (ರಿಫ್ರಾಕ್ಟಿವ್ ಇಂಡೆಕ್ಸ್) | 1.3980 (19 °C) | ||
| ಸ್ನಿಗ್ಧತೆ (ವಿಸ್ಕಾಸಿಟಿ) | 0.1529 cP | ||
| ಸಂಬಂಧಿತ ಸಂಯುಕ್ತಗಳು | |||
Related
|
|||
Related compounds
|
|||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). > | |||
| Infobox references | |||
ಬ್ಯುಟಿರಿಕ್ ಆಮ್ಲ ಎನ್ನುವುದು ಒಂದುಪರ್ಯಾಪ್ತ ಕೊಬ್ಬಿನ ಆಮ್ಲ. ಕೊಬ್ಬಿನ ಅಮ್ಲಗಳನ್ನು ಮೂನೋಕಾರ್ಬೀಕ್ಸಿಲಿಕ್ ಆಮ್ಲಗಳು(monocarbolylic acid)ಎಂದು ಕರೆಯುತ್ತಾರೆ. ಬ್ಯುಟಿರಿಕ್ ಆಮ್ಲ ಎಣ್ಣೆಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಟ್ರೈ ಗ್ಲಿಜರಾಯಿಡ್ ರೂಪದಲ್ಲಿರುತ್ತದೆ. ಬ್ಯುಟಿರಿಕ್ ಆಮ್ಲವನ್ನು ಶಾಸ್ತ್ರೀಯವಾಗಿ ಬ್ಯುಟನೋಯಿಕ್ ಆಮ್ಲ(butanoic acid)ಎಂದು ಕರೆಯಲಾಗುತ್ತದೆ[೧] . ಗ್ರೀಕ್ ಬಾಷೆಯಲ್ಲೂ ಬ್ಯುಟರೋ ಅಂದರೆ ಬೆಣ್ಣೆಎಂದು ಅರ್ಥವಿದೆ. ಬ್ಯುಟಿರಿಕ್ ಆಮ್ಲವನ್ನು ಕ್ರಿ.ಶ.೧೮೧೪ ಸಂವತ್ಸರದಲ್ಲಿ ಫ್ರೆಂಚ್ ದೇಶದ ರಸಾಯನ ಶಾಸ್ತ್ರಜ್ಞ ಮೈಕೇಲ್ ಯುಜೆನ್ ಚೆವ್ರೆಲ್(Michel Eugen chereul)ಪತ್ತೆ ಹಚ್ಚಿದ್ದಾನೆ.[೨].
ರಚನಾ-ಸ್ವರೂಪ
[ಬದಲಾಯಿಸಿ]
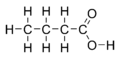
ಬ್ಯುಟ್ರಿಕ್ ಕೊಬ್ಬಿನ ಆಮ್ಲದಲ್ಲಿ ನಾಲ್ಕುಕಾರ್ಬನ್ಅಣುಗಳು, ೮ ಹೈಡ್ರೋಜನ್ಅಣುಗಳು, ಎರಡು ಆಕ್ಸಿಜನ್ಆಣುಗಳಿರುತ್ತವೆ. ಇದರ ರಚನಾ ಸಂಕೇತ CH3CH2CH2COOH ಅಥವಾC4H8O2.ಬ್ಯುಟಿರಿಕ್ ಆಮ್ಲ ಬಣ್ಣ ರಹಿತವಾಗಿ,ದ್ರವರೂಪದಲ್ಲಿರುತ್ತದೆ.ಬೆಣ್ಣೆಯಲ್ಲಿ ಟ್ರಿಗ್ಲಿಜರಾಯೀಡ್ ರೂಪದಲ್ಲಿರುತ್ತದೆ[೩] ಕಮಟಾಗಿದ ಬೆಣ್ಣೆಯಿಂದ ಹೈಡ್ರೋಲಿಸಿಸ್ ಚರ್ಯದಿಂದ ಬ್ಯುಟಿರಿಕ್ ಆಮ್ಲ ಉತ್ಪನ್ನವಾಗುತ್ತದೆ. ಬ್ಯುಟಿರಿಕ್ ಆಮ್ಲ ಕಮಟು ವಾಸನೆ ಹೊಂದಿರುತ್ತದೆ. ಬ್ಯುಟಿರಿಕ್ ಆಮ್ಲವು ನೀರಿನಲ್ಲಿ ಕರಗುತ್ತದೆ. ಇನ್ನೂ ಇಥೆನಾಲ್, ಇಥರ್ ಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಕರಗುತ್ತದೆ. ಬ್ಯುಟಿರಿಕ್ ಆಮ್ಲ ಜಿಡ್ಡಾಗಿರುತ್ತದೆ.
ಬ್ಯುಟಿರಿಕ್ ಆಮ್ಲದ ಗುಣಗಳ ಪಟ್ಟಿ[೪]
| ಲಕ್ಷಣ | ಮಿತಿ |
| ಅಣು ಸಂಕೇತ | C4H8O2 |
| ಅಣು ಭಾರ | 88.105 |
| ವಕ್ರೀ ಭವನ ಸೂಚಿಕೆ | 1.397-1.399 |
| ಸಾಂದ್ರತೆ | 0.964ಕೇ.ಜಿ /ಲೀ |
| ದ್ರವೀ ಭವನ ಬಿಂದು | 23-26 °C |
| ಕುದಿ ಬಿಂದು | 162-164 °C |
| ಫ್ಲಾಷ್ ಪಾಯಿಂಟ್ | 69 °C |
| LogP | 0.777 |
ಲಭ್ಯತೆ:ಬೆಣ್ಣೆಯಲ್ಲಿ ೩-೪% ವರೆಗೆ ಸಿಗುತ್ತದೆ. ಇದನ್ನುಮೇಕೆ, ಕುರಿ, ಎಮ್ಮೆಗಳ ಹಾಲಿನಲ್ಲಿ ಕಂಡು ಹಿಡಿಯಲಾಗಿದೆ. ಸಕ್ಕರೆ,ಗಂಜಿ ಪದಾರ್ಥಗಳನ್ನು ಕಿಣ್ವಪ್ರಕ್ರಿಯೆಗೆ ಒಳಗೊಂಡಿಸುವುರಿಂದ ಬ್ಯುಟಿರಿಕ್ ಆಮ್ಲವನ್ನು ಉತ್ಪನ್ನ ಮಾಡಬಹುದು.
ಬ್ಯುಟಿರಿಕ್ ಆಮ್ಲದ ಉತ್ಪನ್ನಗಳು
- ಪೊಟಾಷಿಯಂ ಡೈಕ್ರೋಮೇಟ್ ಅಥವಾ ಸಲ್ಫ್ಯೂರಿಕ್ ಆಮ್ಲವನ್ನು ಉಪಯೋಗಿಸಿ ಬ್ಯುಟಿರಿಕಿಕ್ ಆಮ್ಲದಿಂದ ಕಾರ್ಬನ್ ಡೈಆಕ್ಸೈಡ್, ಎಸಿಟಿಕ್ ಆಮ್ಲವನ್ನು ಉತ್ಪನ್ನಮಾಡಲಾಗುತ್ತದೆ. ಬ್ಯುಟಿರಿಕ್ ಆಮ್ಲವನ್ನು ಪೆರಾಕ್ಸೈಡ್ ಜೊತೆ ಆಕ್ಸಿಡೇಸನ್ ಚರ್ಯಗೆ ಒಳಗೊಂಡಿಸಿ ಎಸಿಟಿಕ್ ಆಮ್ಲ, ಏಸಿಟೊನ್ ಮುಂತಾದುವುಗಳನ್ನು ಉತ್ಪನ್ನ ಮಾಡಲಾಗುತ್ತದೆ[೫].
- ಬ್ಯುಟಿರಿಕ್ ಆಮ್ಲದಿಂದ ಬ್ಯುಟರೆಟ್ಸ್ ಎನ್ನುವ ಆಮ್ಲದ ಲವಣಗಳನ್ನು, ಬ್ಯುಟನೋಟ್ಸು ಎನ್ನುವ ಎಸ್ಟರುಗಳನ್ನು ತಯಾರಿಸುತ್ತಾರೆ.
ಇವನ್ನೂ ನೋಡಿ
[ಬದಲಾಯಿಸಿ]ಬಾಹ್ಯಾಕೊಂಡಿಗಳು
[ಬದಲಾಯಿಸಿ]- http://avogadro.chem.iastate.edu/MSDS/n-butyric_acid.htm Archived 2014-11-04 ವೇಬ್ಯಾಕ್ ಮೆಷಿನ್ ನಲ್ಲಿ.
ಉಲ್ಲೇಖನ
[ಬದಲಾಯಿಸಿ]- ↑ "butyric acid (CH3CH2CH2CO2H)". britannica.com/. Retrieved 2013-11-29.
- ↑ Unfortunately, Chevreul did not publish his early research on butyric acid; instead, he deposited his findings in manuscript form with the secretary of the Academy of Sciences in Paris, France. This led to problems because Henri Braconnot, a French chemist, was also researching the composition of butter and was publishing his findings, and this led to disputes about priority. As early as 1815, Chevreul claimed that he had found the susbstance that's responsible for the smell of butter: Chevreul (1815) "Lettre de M. Chevreul à MM. les rédacteurs des Annales de chimie" (Letter from Mr. Chevreul to the editors of the Annals of Chemistry), Annales de chimie, vol. 94, pages 73-79; in a footnote spanning pages 75-76, he mentions that he had found a substance that is responsible for the smell of butter. By 1817, he published some of his findings regarding the properties of butyric acid: Chevreul (1817) "Extrait d'une lettre de M. Chevreul à MM. les Rédacteurs du Journal de Pharmacie" (Extract of a letter from Mr. Chevreul to the editors of the Journal of Pharmacy), Journal de Pharmacie et des sciences accessoires, vol. 3, pages 79-81. However, it was not until 1823 that he presented the properties of butyric acid in detail: E. Chevreul, Recherches chimiques sur les corps gras d'origine animale [Chemical researches on fatty substances of animal origin] (Paris, France: F.G. Levrault, 1823), pages 115-133.
- ↑ "butyric acid". thefreedictionary.com. Retrieved 2013-11-29.
- ↑ "butyric acid". chemspider.com. Retrieved 2013-11-29.
- ↑ "THE OXIDATION OF BUTYRIC ACID BY MEANS OF HYDROGEN PEROXIDE WITH FORMATION OF ACETONE,ALDEHYDES AND OTHER PRODUCTS" (PDF). jbc.org. Retrieved 2013-11-29.
References
[ಬದಲಾಯಿಸಿ]![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. {{cite encyclopedia}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters: |separator= and |HIDE_PARAMETER= (help); Invalid |ref=harv (help); Missing or empty |title= (help)
External links
[ಬದಲಾಯಿಸಿ]- Pages using duplicate arguments in template calls
- Chemical articles without CAS registry number
- Chemicals without a PubChem CID
- Articles without InChI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Articles without EBI source
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without UNII source
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- ವೆಬ್ ಆರ್ಕೈವ್ ಟೆಂಪ್ಲೇಟಿನ ವೇಬ್ಯಾಕ್ ಕೊಂಡಿಗಳು
- CS1 errors: empty unknown parameters
- CS1 errors: missing title
- CS1 errors: invalid parameter value
- Wikipedia articles incorporating a citation from the 1911 Encyclopaedia Britannica with no article parameter
- Wikipedia articles incorporating text from the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica
- Commons link is locally defined
- ಕೊಬ್ಬಿನ ಆಮ್ಲಗಳು
- ಪರ್ಯಾಪ್ತ ಕೊಬ್ಬಿನ ಆಮ್ಲಗಳು