Diethylthiambutene
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H21NS2 |
| Molar mass | 291.47 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 152 to 153 °C (306 to 307 °F) |
| |
| |
| | |
Diethylthiambutene (Thiambutene, Themalon, Diethibutin, N,N-Diethyl-1-methyl-3,3-di-2-thienylallylamine) is an opioid analgesic drug developed in the 1950s[2] which was mainly used as an anesthetic in veterinary medicine and continues, along with the other two thiambutenes dimethylthiambutene and ethylmethylthiambutene to be used for this purpose, particularly in Japan.[3][4] It is now under international control under Schedule I of the UN Single Convention On Narcotic Drugs 1961, presumably due to high abuse potential, although little more information is available. It is listed under Schedule I of the US Controlled Substances Act as a Narcotic and has an ACSCN of 9616 with zero annual manufacturing quota as of 2013.
Synthesis
[edit]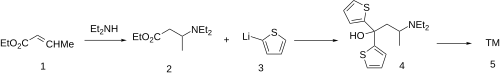
The conjugate addition of diethylamine [109-89-7] to ethyl crotonate [623-70-1] [10544-63-5] (1) gives ethyl 3-(diethylamino)butanoate, CID:10679145 (2). Addition of two equivalents of 2-thienyllithium to the ester gives the tertiary alcohol [94094-46-9] (4'). The dehydration of this then completes the synthesis of diethylthiambutene (5').
References
[edit]- ^ Anvisa (2023-03-31). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-04-04). Archived from the original on 2023-08-03. Retrieved 2023-08-16.
- ^ Beckett AH, Casy AF, Harper NJ, Phillips PM (November 1956). "Analgesics and their antagonists: some steric and chemical considerations. II. The influence of the basic group on physico-chemical properties and the activity of methadone and thiambutene-type compounds". The Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 8 (11): 860–73. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7158.1956.tb12216.x. PMID 13368083. S2CID 41750428.
- ^ Hayes MJ (November 1968). "The use of thiambutene hydrochloride". The Veterinary Record. 83 (20): 528. doi:10.1136/vr.83.20.528-a. PMID 5694027. S2CID 45820838.
- ^ Harbison WD, Slocombe RF, Watts SJ, Stewart GA (December 1974). "Thiambutene and acepromazine as analgesic and preanaesthetic agents in horses and sheep". Australian Veterinary Journal. 50 (12): 543–6. doi:10.1111/j.1751-0813.1974.tb14073.x. PMID 4156466.
- ^ Adamson, D. W. (1950). "180. Aminoalkyl tertiary carbinols and derived products. Part II. 3-Amino-1 : 1-di-2′-thienyl-alkan-1-ols and -alk-1-enes". J. Chem. Soc. 0 (0): 885–890. doi:10.1039/JR9500000885.
- ^ JP,43-006621,B (1968) JP,0528324,B
