Free area of the Republic of China
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
Free area of the Republic of China | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Largest cities | |
| Languages | |
| Ethnic groups | |
| Demonym(s) | |
| Area | |
• Total | 36,193 km2 (13,974 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2018 census | 23,681,968 |
• Density | 650/km2 (1,683.5/sq mi) |
| Currency | New Taiwan Dollar (TWD, NTD) |
| Time zone | UTC+08:00 (National Standard Time) |
| Date format | yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +886 |
| ISO 3166 code | TW |
| Internet TLD | .tw, . |
| Free area of the Republic of China | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taiwan area | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tai-Peng-Kin-Ma | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|---|
|
|
The free area of the Republic of China,[I] also known as the "Taiwan Area of the Republic of China", the "Tai-Min Area (Taiwan and Fuchien)" or simply the "Taiwan Area", is a term used by the government of the Republic of China (Taiwan) to refer to the territories under its actual control.[1][2] It is also used as a legal term written in the Additional articles of the ROC constitution and Cross-Strait Act.
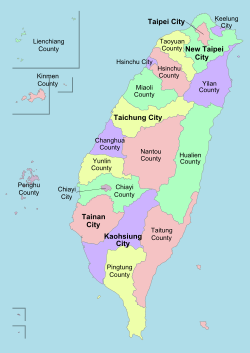
The area currently under the definition consists of the island groups of Taiwan, Penghu, Kinmen, Matsu and some minor islands. The collective term "Tai-Peng-Kin-Ma" is literally equivalent except that it only refers to the islands of Taiwan, Penghu, Kinmen and Matsu Area, to the exclusion of the South China Sea possessions—Pratas Island (Tungsha/Dongsha) and Taiping Island.[3]
The term is complementary to "Mainland Area",[4] which is practically viewed as being synonymous to mainland China,[5] despite the fact that the ROC constitution never defined specific territorial boundaries.[6][7]
Background[edit]
The term "free area" or "Free China" was used during the Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–45) to describe the territories under the control of the Kuomintang led Nationalist Government in Chungking (today Chongqing), as opposed to the parts of China under Japanese occupation, including Nanking (today Nanjing) the capital of the Republic of China until the Japanese invasion in 1937.
The Japanese occupation ended with the imperial surrender in 1945, but the term "Free China" was soon to acquire a new meaning in the context of the early Cold War. Following the Communist Party's victory in the Chinese Civil War in 1949, the newly inaugurated People's Republic of China solidified its control of mainland China, while the Kuomintang government retreated to Taiwan and selected Taipei to serve as the provisional capital of the Republic of China. Mainland China was officially considered to be in a state of "Communist Rebellion", also known as "Communist China" or "Red China", and furthermore all territories still under Nationalist administration were said to constitute the "Free Area" of China, also known as "Nationalist China" or "Free China". This period of mobilization was officially terminated by the government on 1 May 1991 with the implementation of the Additional Articles of the Constitution.
Prior to the Battle of Dachen Archipelago in 1955, the Free Area also encompassed a group of islands off Zhejiang, up to then part of the ROC province of Chekiang. The islands have since been administered exclusively by the People's Republic of China.
Nomenclature[edit]
Various names used to describe the geopolitical area include:
| Short name | The Free Area | Taiwan Area | Tai-Peng-Kin-Ma Area | Tai-Min Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Long name | Free Area of the Republic of China[I] | Taiwan Area[II] | Taiwan-Penghu- Kinmen-Matsu Area |
Taiwan-Fukien Region |
| Chinese | ||||
| Mandarin | Zìyóu dìqū | Táiwān dìqū | Tái-Pēng-Jīn-Mǎ dìqū | Tái-Mǐn dìqū |
| Taiwanese Hokkien | Chū-iû tē-khu | Tâi-oân tē-khu | Tâi-Phêⁿ-Kim-Má tē-khu | Tâi-Bân tē-khu |
| Hakka | Chhṳ-yù thi-khî | Thòi-vàn thi-khî | Thòi-Phàng-Kîm-Mâ thi-khî | Thòi-Mén thi-khî |
| Matsunese | Cê̤ṳ-iù dê-kṳ̆ | Dài-uăng dê-kṳ̆ | Dài-Pàng-Gĭng-Mā dê-kṳ̆ | Dài-Mìng dê-kṳ̆ |
| Notes | "Free" refers to the area that is not under the Communist Party's control. This term is used by the Additional Articles of the Constitution. | Refers to the general area surrounding the island of Taiwan. This term is used by various laws and regulations that governing cross-Strait relations. | Refers to the four main archipelagos under the government's jurisdiction. | Refers to the two historical provinces under actual administration. Namely, Taiwan (Taiwan and Penghu) and a small part of Fukien (Kinmen and Matsu). 閩 is the traditional abbreviation for Fukien. |
Legal use[edit]
The term "free area of the Republic of China" has persisted to the present day in the ROC legislation. The Additional Articles of the Constitution of the Republic of China delegates numerous rights to exercise the sovereignty of the state, including that of electing the President and Legislature, to citizens residing in the "free area of the Republic of China". This term was put into the Constitution with the promulgation of the first set of amendments to the Constitution in 1991 and has been retained in the most recent revision passed in 2005.
The need to use the term "free area" in the Constitution arose out of the discrepancy between the notion that the Republic of China was the sole legitimate government of China and the pressures of the popular sovereignty movement. In the 1980s and 1990s, there were demands, particularly by the Tangwai movement and other groups opposed to one-party authoritarian KMT rule, to restructure the ROC government, long dominated by mainlanders, to be more representative of the Taiwanese people it governed. For example, until 1991, members of the National Assembly and Legislative Yuan elected in 1948 to serve mainland constituencies remained in their posts indefinitely and the President of the Republic of China was to be elected by this same "ten thousand year parliament" (Chinese:
While the 1991 revisions of the Constitution granted the sovereignty rights to the Taiwanese people, it did not explicitly name Taiwan and instead used the term "free area" to maintain the notion that the Republic of China encompassed more than Taiwan. In ordinary legislation, the term "Taiwan Area" is usually used, especially in contexts of trade and exchange. In contrast to the "free area" is the "mainland area", which the Act Governing Relations between the People of the Taiwan Area and the Mainland Area defines as "the territory of the Republic of China outside the Taiwan Area". However, on more practical grounds, the "mainland area" refers simply to Mainland China.
In addition, there are two other Acts defining other "areas": the "Hong Kong and Macau Area" (Chinese:
Use by People's Republic of China[edit]
Based on the One China policy, the People's Republic of China (PRC) does not recognize the legitimacy of the ROC. A series of standardized terms called "Taiwan-related terms" (
Administrative divisions[edit]
- Notes
- ^ a b c d e f Has an elected executive and an elected legislative council.
- ^ a b c Has an appointed district administrator for managing local affairs and carrying out tasks commissioned by superior agency.
- ^ Has an elected village administrator for managing local affairs and carrying out tasks commissioned by superior agency.
See also[edit]
- Additional Articles of the Constitution of the Republic of China
- Anti-Secession Law of the People's Republic of China
- Constitution of the Republic of China
- History of the Republic of China
- Kuomintang
- Mainland China
- Politics of the Republic of China
- Soviet Zone / Liberated Zone
- Taiwan Province, People's Republic of China
Notes[edit]
- ^ Also known as the Taiwan area or Tai–Min area (Chinese:
臺 閩地區 ; lit. 'Taiwan–Fujian area') - ^ The mainland area consists of Mainland China, Tibet and (previously) Outer Mongolia
- ^ Special municipalities, cities, and county-administered cities are all called shi (Chinese:
市 ; lit. 'city') - ^ Nominal; provincial governments have been abolished
- ^ Constitutionally having the same structure as the free area, these are currently under the Chinese Communist Party control with a different structure
- ^ Sometimes called cities (Chinese:
市 ) or provincial cities (Chinese:省 轄市) to distinguish them from special municipalities and county-administered cities - ^ There are two types of townships: rural townships or xīang (Chinese:
鄉 ) and urban townships or zhèn (Chinese: 鎮) - ^ Villages in rural townships are known as tsūn (Chinese:
村 ), those in other jurisdictions are known as lǐ (Chinese:里 )
- Words in native languages
References[edit]
- ^ "Laws and Regulations Regarding Mainland Affairs". mac.gov.tw. Mainland Affairs Council, Executive Yuan. 17 September 2020. Archived from the original on 28 September 2021. Retrieved 23 September 2021.
Article 2: The following terms as used in this Act are defined below.1. "Taiwan Area" refers to Taiwan, Penghu, Kinmen, Matsu, and any other area under the effective control of the Government.2. "Mainland Area" refers to the territory of the Republic of China outside the Taiwan Area.3. "People of the Taiwan Area" refers to the people who have household registrations in the Taiwan Area.4. "People of the Mainland Area" refers to the people who have household registrations in the Mainland Area
- ^ "The Additional Articles of the Constitution of the Republic of China Archived 12 July 2006 at the Wayback Machine." Republic of China. Retrieved on 7 April 2009.
- ^ Corcuff, Stéphane; Edmondson, Robert (2002). Memories of the Future: National Identity Issues and the Search for a New Taiwan. M.E. Sharpe. p. 91. ISBN 978-0-7656-0792-8. Archived from the original on 11 April 2023. Retrieved 15 November 2015.
- ^ Chen Wei-han (8 June 2016). "NPP to push constitutional reforms". Taipei Times. Taipei. Archived from the original on 8 October 2017. Retrieved 8 October 2017.
An amendment made to the Constitution in 1991 "to meet the requisites prior to national unification" recognizes the "Chinese mainland area" as opposed to the "free area," and both areas make up the Republic of China.
- ^ Sara L. Friedman (2015). Exceptional States: Chinese Immigrants and Taiwanese Sovereignty. Oakland, California: University of California Press. p. 10. ISBN 978-0520961562. Archived from the original on 11 April 2023. Retrieved 6 June 2020.
The Act's use of the spatial language of "area" was a direct reference to the postwar ROC Constitution, which had created two classes of Chinese based on politically differentiated, territorial criteria: those of the "free area," which included Taiwan and the scattered smaller islands under post-1949 ROC control, and those of the 'mainland area', who presumably were not free because they lived under Communist rule.
- ^ 《
中華民國 憲法 》第 四 條 - ^ 廖顯謨 (2017). "疆域
與國 家 認 同 :我國 憲法 第 四 條 「固有 疆域」之 探究 " (PDF).高 苑 學 報 . 22: 156–162. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 June 2023. Retrieved 22 June 2023.在 台灣 ,國人 對 我國 疆域範圍 的 認知 ,可 謂 真 的 是 「各自 表 述 」… - ^ "Taiwan appoints new chief administrator". People's Daily. 3 December 2014. Archived from the original on 27 November 2021. Retrieved 15 November 2022.