卜
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
Translingual
[edit]| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|

| |||
Han character
[edit]- Kangxi radical #25, ⼘.
Derived characters
[edit]- Appendix:Chinese radical/
卜 - 仆, 𫨦, 圤, 处,
外 , 𭑧, 𫶽, 扑, 𣱶, 𣅃,朴 , 𤆊, 㺪, 𦘱, 𭁅, 䃼, 𪽁, 𤰘, 𥃨, 𥐚, 𥝒, 𥩖, 补, 𫃚, 𦓦, 虲,訃 (讣), 𧴤, 赴, 䟔, 𨈒, 𨊣, 𤱈, 釙(钋), 𩚅(𬲥), 𩡭, 𩨓, 𩱻, 𬵂, 𪋿, 𪐙, 𭻣 - 𠚬, 𠚩, 𭭄, 𨾇, 鳪, 盀, 㓀, 𪢱, 𭶺, 𫁰, 𤴩, 𡆥
References
[edit]- Kangxi Dictionary: page 157, character 25
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 2774
- Dae Jaweon: page 361, character 15
- Hanyu Da Zidian (first edition): volume 1, page 91, character 11
- Unihan data for U+535C
Chinese
[edit]Glyph origin
[edit]| Historical forms of the character | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shang | Western Zhou | Warring States | Shuowen Jiezi (compiled in Han) | Liushutong (compiled in Ming) | |
| Oracle bone script | Bronze inscriptions | Chu slip and silk script | Qin slip script | Small seal script | Transcribed ancient scripts |

|

|
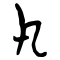
|

|

|

|
Perhaps a pictogram (
Officially adopted as the simplified form of 蔔 in the Chinese Character Simplification Scheme (《
Etymology 1
[edit]| simp. and trad. |
||
|---|---|---|
| alternative forms | 𠁡 𠁢 | |
"Cracking" of a bone or tortoise shell in fire: "to divine by oracle bone" (Schuessler, 2007). Compare Galo -`buk (“to burst”), Galo -`puk (“to pop”), Mizo puak (“to explode; to burst”) (STEDT).
Pronunciation
[edit]- Mandarin
- Cantonese (Jyutping): buk1
- Hakka
- Eastern Min (BUC): bók
- Southern Min
- Wu (Shanghai, Wugniu): 7poq
- Mandarin
- (Standard Chinese)+
- Hanyu Pinyin:
- Zhuyin: ㄅㄨˇ
- Tongyong Pinyin: bǔ
- Wade–Giles: pu3
- Yale: bǔ
- Gwoyeu Romatzyh: buu
- Palladius: бу (bu)
- Sinological IPA (key): /pu²¹⁴/
- (Standard Chinese)+
- Cantonese
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou–Hong Kong)
- Jyutping: buk1
- Yale: būk
- Cantonese Pinyin: buk7
- Guangdong Romanization: bug1
- Sinological IPA (key): /pʊk̚⁵/
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou–Hong Kong)
- Hakka
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Meinong)
- Pha̍k-fa-sṳ: puk
- Hakka Romanization System: bug`
- Hagfa Pinyim: bug5
- Sinological IPA: /puk̚²/
- (Meixian)
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Meinong)
- Eastern Min
- (Fuzhou)
- Bàng-uâ-cê: bók
- Sinological IPA (key): /pouʔ²⁴/
- (Fuzhou)
- Southern Min
Note:
- poh - also written as
博 , incl. surname (Taiwan); - pok - incl. surname (Mainland).
- Dialectal data
| Variety | Location | |
|---|---|---|
| Mandarin | Beijing | /pu²¹⁴/ |
| Harbin | /pʰu²¹³/ | |
| Tianjin | /pʰu¹³/ | |
| Jinan | /pu⁵⁵/ | |
| Qingdao | /pu⁵⁵/ | |
| Zhengzhou | /pu⁵³/ | |
| Xi'an | /po²¹/ | |
| Xining | /pv̩⁴⁴/ | |
| Yinchuan | /puə¹³/ /pu¹³/ ~ | |
| Lanzhou | /pə¹³/ | |
| Ürümqi | /pʰu⁵¹/ | |
| Wuhan | /pʰu²¹³/ | |
| Chengdu | /pu¹³/ | |
| Guiyang | /pʰu²¹/ | |
| Kunming | /pʰu³¹/ | |
| Nanjing | /puʔ⁵/ | |
| Hefei | /pʰəʔ⁵/ | |
| Jin | Taiyuan | /pəʔ²/ |
| Pingyao | /pʌʔ¹³/ | |
| Hohhot | /pəʔ⁴³/ ~ /pei⁵⁵/ 萝~ | |
| Wu | Shanghai | /poʔ⁵/ |
| Suzhou | /poʔ⁵/ | |
| Hangzhou | /pʰoʔ⁵/ | |
| Wenzhou | /po²¹³/ | |
| Hui | Shexian | /pɔʔ²¹/ |
| Tunxi | /pʰu⁵/ | |
| Xiang | Changsha | /pʰu²⁴/ |
| Xiangtan | /pʰu²⁴/ | |
| Gan | Nanchang | |
| Hakka | Meixian | /puk̚¹/ |
| Taoyuan | /puk̚²²/ | |
| Cantonese | Guangzhou | /pok̚⁵/ |
| Nanning | /pʰuk̚⁵⁵/ | |
| Hong Kong | /puk̚⁵/ | |
| Min | Xiamen (Hokkien) | /pɔk̚³²/ /poʔ³²/ |
| Fuzhou (Eastern Min) | /pɔuʔ²³/ | |
| Jian'ou (Northern Min) | /pʰu²⁴/ | |
| Shantou (Teochew) | /pok̚²/ | |
| Haikou (Hainanese) | /ʔbɔk̚⁵/ /ʔbak̚⁵/ |
- Middle Chinese: puwk
- Old Chinese
- (Baxter–Sagart): /*pˤok/
- (Zhengzhang): /*poːɡ/
Definitions
[edit]- to divine
- From: The Book of Documents, circa 4th – 3rd century BCE
- Yǔ wéi yǐmǎo, zhāo zhì yú Luòshī. Wǒ bǔ Héshuò Lí shuǐ. [Pinyin]
- On the day Yi-mao, I came in the morning to this capital of Luo. I (first) divined by the shell concerning (the ground about) the li-water on the north of the He.
予 惟 乙 卯 ,朝 至 于洛 師 。我 卜 河 朔 黎 水 。 [Classical Chinese, trad.]予 惟 乙 卯 ,朝 至 于洛 师。我 卜 河 朔 黎 水 。 [Classical Chinese, simp.]
- (literary) to foretell; to predict
生死 未 卜 ― shēngsǐwèibǔ ― no one knows whether the person is dead or alive
- (literary) to choose
卜 居 ― bǔjū ― to choose a place to live
- a surname
Compounds
[edit]不 卜 可知 前途 未 卜 十 卜 (sap6 bok1) (Cantonese)卜 人 卜 兒 /卜 儿卜 卜 卜 卦 (bǔguà)卜 吉 卜 夜 卜 晝 /卜 夜 卜 昼 卜 婿 卜 宅 卜居 (bǔjū)卜 年 (bǔnián)卜 度 卜 征 卜 日 卜 易 卜 晝 卜 夜 /卜 昼 卜 夜 卜 珓 (bǔjiào)卜 祝 卜 窀穸卜筮 (bǔshì)卜 算 卜 築 /卜 筑卜 老 卜者 卜 課 /卜 课 (bǔkè)卜 辭 /卜 辞 (bǔcí)卜 鄰/卜 邻 (bǔlín)占 卜 (zhānbǔ)吉凶 未 卜 吉 卜 賽 人 /吉 卜 赛人 (jíbǔsàirén)問 卜 /问卜 (wènbǔ)太 卜 存亡 未 卜 成都 賣卜 /成都 卖卜拉 卜 楞未 卜 (wèibǔ)未 卜 先 知 (wèibǔxiānzhī)枚 卜 死生 未 卜 殷 墟卜辭 求 神 問 卜 /求 神 问卜 (qiúshénwènbǔ)油 花 卜 狼 卜 食 玉枝 卜 壽 /玉枝 卜 寿 羊 卜 老 醫 少 卜 /老 医 少 卜 耳 卜 貞 卜 文字 /贞卜文字 - 貨卜/货卜
賣卜 /卖卜賣卜 測 字 /卖卜测字醫 卜 星 相 /医 卜 星 相 響 卜 /响卜預 卜 /预卜 (yùbǔ)鳥 卜 /鸟卜龜 卜 /龟卜 (guībǔ)
Etymology 2
[edit]| For pronunciation and definitions of (This character is the simplified form of 蔔). |
Notes:
|
Etymology 3
[edit]| For pronunciation and definitions of (This character is a variant form of |
References
[edit]- “Entry #64”, in
臺灣 閩南語 常用 詞 辭典 [Dictionary of Frequently-Used Taiwan Minnan] (overall work in Mandarin and Hokkien), Ministry of Education, R.O.C., 2023.
Japanese
[edit]Kanji
[edit](“Jinmeiyō” kanji used for names)
Readings
[edit]Etymology 1
[edit]| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| うらない Jinmeiyō |
| kun’yomi |
| For pronunciation and definitions of | ||
| ||
| (This term, |
Etymology 2
[edit]| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| ぼく Jinmeiyō |
| kan’yōon |
Noun
[edit]Derived terms
[edit]Etymology 3
[edit]| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| うら Jinmeiyō |
| kun’yomi |
| For pronunciation and definitions of | ||
| ||
| (This term, |
Korean
[edit]Hanja
[edit]Tày
[edit]Adjective
[edit]- Nôm form of bốc (“dry”).
- 忒㳍𱺵㳍
卜 - Rẳc bó là bó bốc
- (please add an English translation of this usage example)
- Nôm form of phoóc (“foolish”).
- 坎
宗 𫰴卜 - Khảm khỉn tổng sao phoóc
- (please add an English translation of this usage example)
Verb
[edit]References
[edit]- Lục Văn Pảo, Hoàng Tuấn Nam (2003) Hoàng Triều Ân, editor, Từ điển chữ Nôm Tày [A Dictionary of (chữ) Nôm Tày][1] (in Vietnamese), Hanoi: Nhà xuất bản Khoa học Xã hội
Vietnamese
[edit]Han character
[edit]
Verb
[edit]References
[edit]- Nôm Foundation
- Lê Sơn Thanh, "Nom-Viet.dat", WinVNKey (details)
Zhuang
[edit]Noun
[edit]Classifier
[edit]Categories:
- CJK Unified Ideographs block
- Han script characters
- Kangxi Radicals block
- Han character radicals
- Translingual lemmas
- Translingual symbols
- Han pictograms
- Middle Chinese lemmas
- Old Chinese lemmas
- Chinese lemmas
- Mandarin lemmas
- Cantonese lemmas
- Hakka lemmas
- Eastern Min lemmas
- Hokkien lemmas
- Teochew lemmas
- Wu lemmas
- Chinese verbs
- Mandarin verbs
- Cantonese verbs
- Hakka verbs
- Eastern Min verbs
- Hokkien verbs
- Teochew verbs
- Wu verbs
- Chinese proper nouns
- Mandarin proper nouns
- Cantonese proper nouns
- Hakka proper nouns
- Eastern Min proper nouns
- Hokkien proper nouns
- Teochew proper nouns
- Wu proper nouns
- Chinese terms with IPA pronunciation
- Chinese Han characters
- Literary Chinese terms with quotations
- Chinese literary terms
- Mandarin terms with usage examples
- Chinese surnames
- Jin lemmas
- Chinese simplified forms
- Chinese nouns
- Mandarin nouns
- Cantonese nouns
- Hakka nouns
- Eastern Min nouns
- Hokkien nouns
- Teochew nouns
- Wu nouns
- Chinese adverbs
- Mandarin adverbs
- Cantonese adverbs
- Hakka adverbs
- Eastern Min adverbs
- Hokkien adverbs
- Teochew adverbs
- Wu adverbs
- Chinese variant forms
- Japanese Han characters
- Kanji used for names
- Japanese kanji with goon reading ほく
- Japanese kanji with kan'on reading ほく
- Japanese kanji with kan'yōon reading ぼく
- Japanese kanji with kun reading うらな-う
- Japanese kanji with kun reading うらない
- Japanese terms spelled with
卜 - Japanese terms read with kun'yomi
- Japanese nouns
- Japanese lemmas
- Japanese terms spelled with jinmeiyō kanji
- Japanese terms written with one Han script character
- Japanese single-kanji terms
- Japanese terms read with on'yomi
- Japanese terms with multiple readings
- Japanese terms with archaic senses
- Korean lemmas
- Korean Han characters
- Tày lemmas
- Tày adjectives
- Tày Nôm forms
- Tày terms with usage examples
- Tày verbs
- Vietnamese Chữ Hán
- Vietnamese lemmas
- Vietnamese Han characters
- Vietnamese Nom
- Vietnamese verbs
- CJKV radicals
- Zhuang lemmas
- Zhuang nouns
- Zhuang Sawndip forms
- Zhuang classifiers
