小 分子 核 糖 核酸


這些RNA
1989
pri-miRNA长度
2024
命名 规则
[编辑]miR-
“miR-”
miRNA几乎
对于
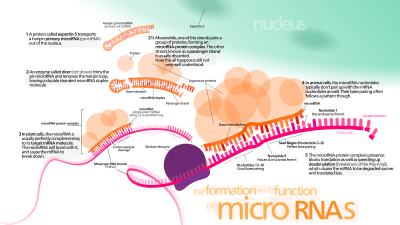
生物 合成 機 制
[编辑]
轉 錄
[编辑]miRNA
核 加工
[编辑]
而對於那些繞
核 輸出
[编辑]
細胞 質 加工
[编辑]此外,
植物 中 的 生物 合成
[编辑]参考 文献
[编辑]- ^
存 档副本 . [2021-07-06]. (原始 内容 存 档于2021-07-09). - ^ Ambros, V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. Sep 16, 2004, 431 (7006): 350–5. PMID 15372042. doi:10.1038/nature02871.
- ^ Bartel, DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. Jan 23, 2004, 116 (2): 281–97. PMID 14744438. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00045-5.
- ^ Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell. January 2009, 136 (2): 215–33. PMC 3794896
 . PMID 19167326. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002.
. PMID 19167326. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002.
- ^ Ruvkun G(1), Giusto J. The Caenorhabditis elegans heterochronic gene lin-14 encodes a nuclear protein that forms a temporal developmental switch. Nature. Mar 1989, 338 (6213): 313–9. PMID 2922060. doi:10.1038/338313a0.
- ^ The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2024. NobelPrize.org. [2024-10-07] (
美国 英 语). - ^ Lewis, Tanya. Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine Awarded for Discovery of MicroRNA Gene Regulation. Scientific American. [2024-10-07] (
英 语). - ^ Wright, MW; Bruford, EA. Naming 'junk': human non-protein coding RNA (ncRNA) gene nomenclature. Human genomics. Jan 2011, 5 (2): 90–8. PMC 3051107
 . PMID 21296742. doi:10.1186/1479-7364-5-2-90.
. PMID 21296742. doi:10.1186/1479-7364-5-2-90.
- ^ 9.0 9.1 Rodriguez A, Griffiths-Jones S, Ashurst JL, Bradley A; Griffiths-Jones; Ashurst; Bradley. Identification of mammalian microRNA host genes and transcription units. Genome Res. October 2004, 14 (10A): 1902–10. PMC 524413
 . PMID 15364901. doi:10.1101/gr.2722704.
. PMID 15364901. doi:10.1101/gr.2722704.
- ^ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Cai X, Hagedorn CH, Cullen BR; Hagedorn; Cullen. Human microRNAs are processed from capped, polyadenylated transcripts that can also function as mRNAs. RNA. December 2004, 10 (12): 1957–66. PMC 1370684
 . PMID 15525708. doi:10.1261/rna.7135204.
. PMID 15525708. doi:10.1261/rna.7135204.
- ^ Weber MJ. New human and mouse microRNA genes found by homology search. FEBS J. January 2005, 272 (1): 59–73. PMID 15634332. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.2004.04389.x.
- ^ Kim YK, Kim VN; Kim. Processing of intronic microRNAs. EMBO J. February 2007, 26 (3): 775–83. PMC 1794378
 . PMID 17255951. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601512.
. PMID 17255951. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601512.
- ^ Baskerville S, Bartel DP; Bartel. Microarray profiling of microRNAs reveals frequent coexpression with neighboring miRNAs and host genes. RNA. March 2005, 11 (3): 241–7. PMC 1370713
 . PMID 15701730. doi:10.1261/rna.7240905.
. PMID 15701730. doi:10.1261/rna.7240905.
- ^ 14.0 14.1 Lee Y, Kim M, Han J, Yeom KH, Lee S, Baek SH, Kim VN; Kim; Han; Yeom; Lee; Baek; Kim. MicroRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II. EMBO J. October 2004, 23 (20): 4051–60. PMC 524334
 . PMID 15372072. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600385.
. PMID 15372072. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600385.
- ^ Zhou X, Ruan J, Wang G, Zhang W; Ruan; Wang; Zhang. Characterization and identification of microRNA core promoters in four model species. PLoS Comput. Biol. March 2007, 3 (3): e37. Bibcode:2007PLSCB...3...37Z. PMC 1817659
 . PMID 17352530. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030037.
. PMID 17352530. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030037.
- ^ Faller M, Guo F; Guo. MicroRNA biogenesis: there's more than one way to skin a cat. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. November 2008, 1779 (11): 663–7. PMC 2633599
 . PMID 18778799. doi:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2008.08.005.
. PMID 18778799. doi:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2008.08.005.
- ^ Lee, Y; Ahn, C; Han, J; Choi, H; Kim, J; Yim, J; Lee, J; Provost, P; Rådmark, O; Kim, S; Kim, VN. The nuclear RNase III Drosha initiates microRNA processing.. Nature. 25 September 2003, 425 (6956): 415–9. PMID 14508493. doi:10.1038/nature01957.
- ^ Gregory RI, Chendrimada TP, Shiekhattar R; Chendrimada; Shiekhattar. MicroRNA biogenesis: isolation and characterization of the microprocessor complex. Methods Mol. Biol. 2006, 342: 33–47. ISBN 1-59745-123-1. PMID 16957365. doi:10.1385/1-59745-123-1:33.
- ^ Han, J; Lee, Y; Yeom, KH; Kim, YK; Jin, H; Kim, VN. The Drosha-DGCR8 complex in primary microRNA processing.. Genes & Development. 15 December 2004, 18 (24): 3016–27. PMC 535913
 . PMID 15574589. doi:10.1101/gad.1262504.
. PMID 15574589. doi:10.1101/gad.1262504.
- ^ Han, J; Lee, Y; Yeom, KH; Nam, JW; Heo, I; Rhee, JK; Sohn, SY; Cho, Y; Zhang, BT; Kim, VN. Molecular basis for the recognition of primary microRNAs by the Drosha-DGCR8 complex.. Cell. 2 June 2006, 125 (5): 887–901. PMID 16751099. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.03.043.
- ^ Conrad, Thomas; Annalisa, Marsico; Gehre, Maja; Ørom, Ulf. Microprocessor activity controls differential miRNA biogenesis In Vivo.. Cell Reports. Oct 23, 2014, 9 (2): 542–554. PMID 25310978. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2014.09.007.
- ^ Auyeung, Vincent; Igor, Ulitsky; McGeary, SE; Bartel, DP. Beyond secondary structure: primary-sequence determinants license pri-miRNA hairpins for processing.. Cell. Feb 14, 2013, 152 (4): 844–858. PMC 3707628
 . PMID 23415231. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.01.031.
. PMID 23415231. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.01.031.
- ^ Ali PS, Ghoshdastider U, Hoffmann J, Brutschy B, Filipek S. Recognition of the let-7g miRNA precursor by human Lin28B. FEBS Letters. 2012, 586 (22): 3986–90. PMID 23063642. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2012.09.034.
- ^ Berezikov E, Chung WJ, Willis J, Cuppen E, Lai EC; Chung; Willis; Cuppen; Lai. Mammalian mirtron genes. Mol. Cell. October 2007, 28 (2): 328–36. PMC 2763384
 . PMID 17964270. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2007.09.028.
. PMID 17964270. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2007.09.028.
- ^ 25.0 25.1 Kawahara Y, Megraw M, Kreider E, Iizasa H, Valente L, Hatzigeorgiou AG, Nishikura K; Megraw; Kreider; Iizasa; Valente; Hatzigeorgiou; Nishikura. Frequency and fate of microRNA editing in human brain. Nucleic Acids Res. September 2008, 36 (16): 5270–80. PMC 2532740
 . PMID 18684997. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn479.
. PMID 18684997. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn479.
- ^ Winter J, Jung S, Keller S, Gregory RI, Diederichs S; Jung; Keller; Gregory; Diederichs. Many roads to maturity: microRNA biogenesis pathways and their regulation. Nat. Cell Biol. March 2009, 11 (3): 228–34. PMID 19255566. doi:10.1038/ncb0309-228.
- ^ Ohman M. A-to-I editing challenger or ally to the microRNA process. Biochimie. October 2007, 89 (10): 1171–6. PMID 17628290. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2007.06.002.
- ^ Murchison EP, Hannon GJ; Hannon. miRNAs on the move: miRNA biogenesis and the RNAi machinery. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. June 2004, 16 (3): 223–9. PMID 15145345. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2004.04.003.
- ^ 29.0 29.1 29.2 Lund E, Dahlberg JE; Dahlberg. Substrate selectivity of exportin 5 and Dicer in the biogenesis of microRNAs. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2006, 71: 59–66. PMID 17381281. doi:10.1101/sqb.2006.71.050.
- ^ Park, JE; Heo, I; Tian, Y; Simanshu, DK; Chang, H; Jee, D; Patel, DJ; Kim, VN. Dicer recognizes the 5' end of RNA for efficient and accurate processing.. Nature. 13 July 2011, 475 (7355): 201–5. PMID 21753850. doi:10.1038/nature10198.
- ^ Ji X. The mechanism of RNase III action: how dicer dices. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology. 2008, 320: 99–116. ISBN 978-3-540-75156-4. PMID 18268841. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-75157-1_5.
- ^ Mirihana Arachchilage G, Dassanayake AC, Basu S. A Potassium Ion-Dependent RNA Structural Switch Regulates Human Pre-miRNA 92b Maturation. Chem. Biol. 2015, 22: 262–272. PMID 25641166. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2014.12.013.
- ^ Lelandais-Brière C, Sorin C, Declerck M, Benslimane A, Crespi M, Hartmann C; Sorin; Declerck; Benslimane; Crespi; Hartmann. Small RNA diversity in plants and its impact in development. Current Genomics. March 2010, 11 (1): 14–23. PMC 2851111
 . PMID 20808519. doi:10.2174/138920210790217918.
. PMID 20808519. doi:10.2174/138920210790217918.
外部 連結
[编辑]- miRex: Registry of microRNA expression profiles Internet registry for microRNA expression profiles. The server is part of RNA@IGIB.
- A tutorial on miRNAs by Ambion (页面
存 档备份,存 于互联网档案 馆) - 3-D animations describing microRNA formation and function by Rosetta
- Eumir: Web server for prediction of eukaryotic microRNA precursors Web server implementing SVM based prediction of microRNA precursors. Also incorporates companion web server HairpinFetcher.The servers are part of RNA@IGIB.
微 RNA实验方法 (页面存 档备份,存 于互联网档案 馆)
